Orthodontics is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, management, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, as well as misaligned bite patterns. It may also address the modification of facial growth, known as dentofacial orthopedics.

Orthodontic retainers are custom-made devices, usually made of wires or clear plastic, that hold teeth in position after surgery or any method of realigning teeth. Once a phase of orthodontic treatment has been completed to straighten teeth, there remains a lifelong risk of relapse due to a number of factors: recoil of periodontal fibres, pressure from surrounding soft tissues, the occlusion and patient’s continued growth and development. By using retainers to hold the teeth in their new position for a length of time, the surrounding periodontal fibres adapt to changes in the bone which can help minimize any changes to the final tooth position after the completion of orthodontic treatment. Retainers may also be used to treat overjets.

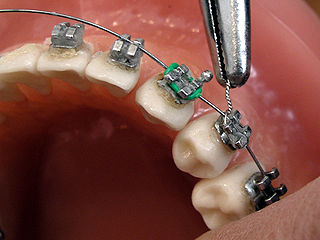
Dental braces are devices used in orthodontics that align and straighten teeth and help position them with regard to a person's bite, while also aiming to improve dental health. They are often used to correct underbites, as well as malocclusions, overbites, open bites, gaps, deep bites, cross bites, crooked teeth, and various other flaws of the teeth and jaw. Braces can be either cosmetic or structural. Dental braces are often used in conjunction with other orthodontic appliances to help widen the palate or jaws and to otherwise assist in shaping the teeth and jaws.
A quad helix is an orthodontic appliance for the upper teeth that is cemented in the mouth. It is attached to the molars by 2 bands and has two or four active helix springs that widen the arch of the mouth to make room for crowded teeth, or correct a posterior cross-bite, where lower teeth are buccal (outer) than upper teeth. It is usually made from 38 mil stainless steel wire and is primarily indicated in mixed dentition, cleft patients and those that have performed the act of thumbsucking. A variety of this appliance is inserted into attachments that are welded to the bands. In this way the orthodontist can adjust the appliance without removing the bands.

Orthodontic headgear is a type of orthodontic appliance typically attached to the patient's head with a strap or number of straps around the patient's head or neck. From this, a force is transferred to the mouth/jaw(s) of the subject.

In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855–1930), the "father of modern orthodontics", popularised it. The word "malocclusion" derives from occlusion, and refers to the manner in which opposing teeth meet.

A palatal expander is a device in the field of orthodontics which is used to widen the upper jaw (maxilla) so that the bottom and upper teeth will fit together better. This is a common orthodontic procedure. The use of an expander is most common in children and adolescents 8–18 years of age. It can also be used in adults, although expansion is more uncomfortable and takes longer in adults. A patient who would rather not wait several months for the end result achieved by a palatal expander may be able to opt for a surgical separation of the maxilla. Use of a palatal expander is most often followed by braces to then straighten the teeth.
A dental emergency is an issue involving the teeth and supporting tissues that are of high importance to be treated by the relevant professional. Dental emergencies do not always involve pain, although this is a common signal that something needs to be looked at. Pain can originate from the tooth, surrounding tissues or can have the sensation of originating in the teeth but be caused by an independent source. Depending on the type of pain experienced an experienced clinician can determine the likely cause and can treat the issue as each tissue type gives different messages in a dental emergency.
Orthodontic technology is a specialty of dental technology that is concerned with the design and fabrication of dental appliances for the treatment of malocclusions, which may be a result of tooth irregularity, disproportionate jaw relationships, or both.

Overjet is the extent of horizontal (anterior-posterior) overlap of the maxillary central incisors over the mandibular central incisors. In class II malocclusion the overjet is increased as the maxillary central incisors are protruded.
Pre-eruption guidance is an orthodontic treatment method that allows for expansion of existing erupting teeth long before they appear in the mouth. The use off pre-eruption guidance appliances and the timing of extractions of certain deciduous teeth aligns the teeth naturally as opposed to orthodontic mechanical movement of permanent teeth into alignment after they have erupted. Research shows that pre-eruption guidance produces far more stable tooth alignment than alternative treatments.
Lingual braces are one of the many types of the fixed orthodontic treatment appliances available to patients needing orthodontics. They involve attaching the orthodontic brackets on the inner sides of the teeth. The main advantage of lingual braces is their near invisibility compared to the standard braces, which are attached on the buccal (cheek) sides of the tooth. Lingual braces were invented by Craven Kurz in 1976.

Anchorage in orthodontics is defined as a way of resisting movement of a tooth or number of teeth by using different techniques. Anchorage is an important consideration in the field of orthodontics as this is a concept that is used frequently when correcting malocclusions. Unplanned or unwanted tooth movement can have dire consequences in a treatment plan, and therefore using anchorage stop a certain tooth movement becomes important. Anchorage can be used from many different sources such as teeth, bone, implants or extra-orally.
Elastics are rubber bands frequently used in the field of orthodontics to correct different types of malocclusions. The elastic wear is prescribed by an orthodontist or a dentist in an orthodontic treatment. The longevity of the elastic wear may vary from two weeks to several months. The elastic wear can be worn from 12 to 23 hours a day, either during the night or throughout the day depending on the requirements for each malocclusion. The many different types of elastics may produce different forces on teeth. Therefore, using elastics with specific forces is critical in achieving a good orthodontic occlusion.
Pendulum is an orthodontic appliance, developed by James J. Hilgers in 1992, that use forces to distalize the upper 1st molars to create space for eruption of impacted teeth or allowing correction of Class 2 malocclusion. This appliance is a fixed type of distalizing appliance that does not depend on the compliance of each patient to work. Hilgers published an article in Journal of Clinical Orthodontics in 1992 describing the appliance.
ACCO or Acrylic Cervical Occipital Anchorage is an appliance in field of orthodontics which is used for distalization of maxillary molars. This appliance is a removable type of appliance which was developed by Herbert I. Margolis. This appliance is intended to be worn 24 hours a day except during meals. It is one of the few removable appliances made for distalization of molars and thus require patient compliance for the treatment to be successful.
Intrusion is a movement in the field of orthodontics where a tooth is moved partially into the bone. Intrusion is done in orthodontics to correct an anterior deep bite or in some cases intrusion of the over-erupted posterior teeth with no opposing tooth. Intrusion can be done in many ways and consists of many different types. Intrusion, in orthodontic history, was initially defined as problematic in early 1900s and was known to cause periodontal effects such as root resorption and recession. However, in mid 1950s successful intrusion with light continuous forces was demonstrated. Charles J. Burstone defined intrusion to be "the apical movement of the geometric center of the root (centroid) in respect to the occlusal plane or plane based on the long axis of tooth".
Open bite is a type of orthodontic malocclusion which has been estimated to occur in 0.6% of the people in the United States. This type of malocclusion has no vertical overlap or contact between the anterior incisors. The term "open bite" was coined by Carevelli in 1842 as a distinct classification of malocclusion. Different authors have described the open bite in a variety of ways. Some authors have suggested that open bite often arises when overbite is less than the usual amount. Additionally, others have contended that open bite is identified by end-on incisal relationships. Lastly, some researchers have stated that a lack of incisal contact must be present to diagnose an open bite.
The Herbst appliance is an orthodontic appliance used by orthodontists to correct class 2 retrognathic mandible in a growing patient, meaning that the lower jaw is too far back. This is also called bitejumping. Herbst appliance parts include stainless steel surgical frameworks that are secured onto the teeth by bands or acrylic bites. These are connected by sets of telescoping mechanisms that apply gentle upward and backward force on the upper jaw, and forward force on the lower jaw. The original bite-jumping appliance was designed by Dr. Emil Herbst and reintroduced by Dr. Hans Pancherz using maxillary and mandibular first molars and first bicuspids. The bands were connected with heavy wire soldered to each band and carried a tube and piston assembly that allowed mandibular movement but permanently postured the mandible forward. The appliance not only corrected a dental Class II to a dental Class I but also offered a marked improvement of the classic Class II facial profile.








