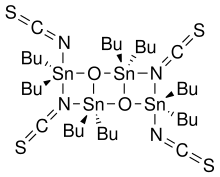
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Octabutyltetrathiocyanatostannoxane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C36H72N4O2S4Sn4 | |
| Molar mass | 1196.08 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Otera's catalyst, named after Japanese chemist Junzo Otera, is an organostannane compound which has been used as a transesterification catalyst. This isothioscyanate compound is a member of a family of organostannanes reported by Wada and coworkers, [1] and elaborated upon by Otera and coworkers. [2]