Related Research Articles

Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the digestive system of many vertebrates, where it hydrolyzes proteins. Trypsin is formed in the small intestine when its proenzyme form, the trypsinogen produced by the pancreas, is activated. Trypsin cuts peptide chains mainly at the carboxyl side of the amino acids lysine or arginine. It is used for numerous biotechnological processes. The process is commonly referred to as trypsinogen proteolysis or trypsinization, and proteins that have been digested/treated with trypsin are said to have been trypsinized.

A protease is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in numerous biological pathways, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism, and cell signaling.

A transmembrane protein is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents.
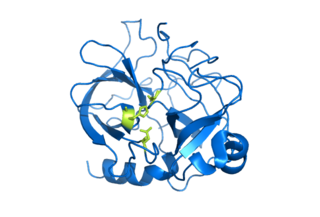
Serine proteases are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins. Serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the (enzyme's) active site. They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Serine proteases fall into two broad categories based on their structure: chymotrypsin-like (trypsin-like) or subtilisin-like.

A metalloproteinase, or metalloprotease, is any protease enzyme whose catalytic mechanism involves a metal. An example is ADAM12 which plays a significant role in the fusion of muscle cells during embryo development, in a process known as myogenesis.

Porins are beta barrel proteins that cross a cellular membrane and act as a pore, through which molecules can diffuse. Unlike other membrane transport proteins, porins are large enough to allow passive diffusion, i.e., they act as channels that are specific to different types of molecules. They are present in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria and some gram-positive mycobacteria, the outer membrane of mitochondria, and the outer chloroplast membrane.

Papain, also known as papaya proteinase I, is a cysteine protease enzyme present in papaya and mountain papaya. It is the namesake member of the papain-like protease family.
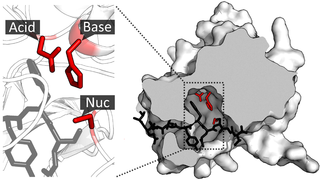
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes. An acid-base-nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to release the product and regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine or even selenocysteine. The 3D structure of the enzyme brings together the triad residues in a precise orientation, even though they may be far apart in the sequence.
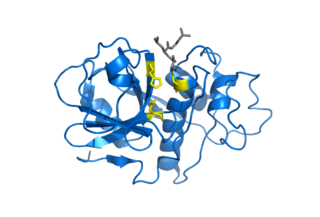
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad.
In molecular biology, the Signal Peptide Peptidase (SPP) is a type of protein that specifically cleaves parts of other proteins. It is an intramembrane aspartyl protease with the conserved active site motifs 'YD' and 'GxGD' in adjacent transmembrane domains (TMDs). Its sequences is highly conserved in different vertebrate species. SPP cleaves remnant signal peptides left behind in membrane by the action of signal peptidase and also plays key roles in immune surveillance and the maturation of certain viral proteins.

Insulin-degrading enzyme, also known as IDE, is an enzyme.
MEROPS is an online database for peptidases and their inhibitors. The classification scheme for peptidases was published by Rawlings & Barrett in 1993, and that for protein inhibitors by Rawlings et al. in 2004. The most recent version, MEROPS 12.4, was released in late October 2021.

General bacterial porins are a family of porin proteins from the outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. The porins act as molecular filters for hydrophilic compounds. They are responsible for the 'molecular sieve' properties of the outer membrane. Porins form large water-filled channels which allow the diffusion of hydrophilic molecules into the periplasmic space. Some porins form general diffusion channels that allow any solute up to a certain size to cross the membrane, while other porins are specific for one particular solute and contain a binding site for that solute inside the pores. As porins are the major outer membrane proteins, they also serve as receptor sites for the binding of phages and bacteriocins.

Mitochondrial-processing peptidase subunit beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PMPCB gene. This gene is a member of the peptidase M16 family and encodes a protein with a zinc-binding motif. This protein is located in the mitochondrial matrix and catalyzes the cleavage of the leader peptides of precursor proteins newly imported into the mitochondria, though it only functions as part of a heterodimeric complex.

Subtilases are a family of subtilisin-like serine proteases. They appear to have independently and convergently evolved an Asp/Ser/His catalytic triad, like in the trypsin serine proteases. The structure of proteins in this family shows that they have an alpha/beta fold containing a 7-stranded parallel beta sheet.
CUB domain is an evolutionarily conserved protein domain. The CUB domain is a structural motif of approximately 110 residues found almost exclusively in extracellular and plasma membrane-associated proteins, many of which are developmentally regulated. These proteins are involved in a diverse range of functions, including complement activation, developmental patterning, tissue repair, axon guidance and angiogenesis, cell signalling, fertilisation, haemostasis, inflammation, neurotransmission, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and tumour suppression. Many CUB-containing proteins are peptidases belonging to MEROPS peptidase families M12A (astacin) and S1A (chymotrypsin).
Omptins are a family of bacterial proteases. They are aspartate proteases, which cleave peptides with the use of a water molecule. Found in the outer membrane of gram-negative enterobacteria such as Shigella flexneri, Yersinia pestis, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella enterica. Omptins consist of a widely conserved beta barrel spanning the membrane with 5 extracellular loops. These loops are responsible for the various substrate specificities. These proteases rely upon binding of lipopolysaccharide for activity.

In molecular biology, the CLP protease family is a family of serine peptidases belong to the MEROPS peptidase family S14. ClpP is an ATP-dependent protease that cleaves a number of proteins, such as casein and albumin. It exists as a heterodimer of ATP-binding regulatory A and catalytic P subunits, both of which are required for effective levels of protease activity in the presence of ATP, although the P subunit alone does possess some catalytic activity.

Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, also known as Scytalidoglutamic peptidase and Scytalidopepsin B is a proteolytic enzyme. It was previously thought to be an aspartic protease, but determination of its molecular structure showed it to belong a novel group of proteases, glutamic protease.
Asparagine peptide lyase are one of the seven groups in which proteases, also termed proteolytic enzymes, peptidases, or proteinases, are classified according to their catalytic residue. The catalytic mechanism of the asparagine peptide lyases involves an asparagine residue acting as nucleophile to perform a nucleophilic elimination reaction, rather than hydrolysis, to catalyse the breaking of a peptide bond.
References
- ↑ Yoshihara E, Yoneyama H, Ono T, Nakae T (June 1998). "Identification of the catalytic triad of the protein D2 protease in Pseudomonas aeruginosa". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 247 (1): 142–5. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.8745. PMID 9636669.