In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration. A concentration can be any kind of chemical mixture, but most frequently solutes and solvents in solutions. The molar (amount) concentration has variants such as normal concentration and osmotic concentration.
A descriptive statistic is a summary statistic that quantitatively describes or summarizes features of a collection of information, while descriptive statistics in the mass noun sense is the process of using and analyzing those statistics. Descriptive statistics is distinguished from inferential statistics, in that descriptive statistics aims to summarize a sample, rather than use the data to learn about the population that the sample of data is thought to represent. This generally means that descriptive statistics, unlike inferential statistics, is not developed on the basis of probability theory, and are frequently nonparametric statistics. Even when a data analysis draws its main conclusions using inferential statistics, descriptive statistics are generally also presented. For example, in papers reporting on human subjects, typically a table is included giving the overall sample size, sample sizes in important subgroups, and demographic or clinical characteristics such as the average age, the proportion of subjects of each sex, the proportion of subjects with related comorbidities, etc.
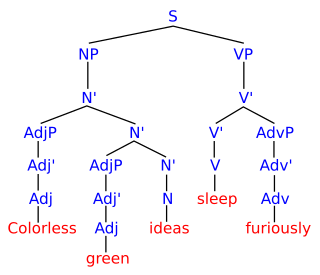
In mathematics, computer science, and linguistics, a formal language consists of words whose letters are taken from an alphabet and are well-formed according to a specific set of rules.
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the principal communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.

In Norse mythology, Ragnarök (; is a series of events, including a great battle, foretold to lead to the death of a number of great figures, natural disasters and the submersion of the world in water. After these events, the world will resurface anew and fertile, the surviving and returning gods will meet and the world will be repopulated by two human survivors. Ragnarök is an important event in Norse mythology and has been the subject of scholarly discourse and theory in the history of Germanic studies.

A troll is a class of being in Norse mythology and Scandinavian folklore. In Old Norse sources, beings described as trolls dwell in isolated rocks, mountains, or caves, live together in small family units, and are rarely helpful to human beings.
Black supremacy or black supremacism is a racial supremacist belief which maintains that black people are superior to people of other races. The term has been used by the Southern Poverty Law Center (SPLC), an American legal advocacy organization, to describe several fringe religious groups in the United States.

Standard anatomical terms of location deal unambiguously with the anatomy of animals, including humans.
Dream pop is a subgenre of alternative rock and neo-psychedelia that developed in the 1980s. The style is typified by a preoccupation with sonic texture and atmosphere as much as melody. It often overlaps with the related genre of shoegazing, and the two genre terms have at times been used interchangeably.
A military operation is the coordinated military actions of a state, or a non-state actor, in response to a developing situation. These actions are designed as a military plan to resolve the situation in the state or actor's favor. Operations may be of a combat or non-combat nature and may be referred to by a code name for the purpose of national security. Military operations are often known for their more generally accepted common usage names than their actual operational objectives.

A formation or geological formation is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy. A formation consists of a certain amount of rock strata that have a comparable lithology, facies or other similar properties. Formations are not defined by the thickness of their rock strata; therefore the thickness of different formations can vary widely.
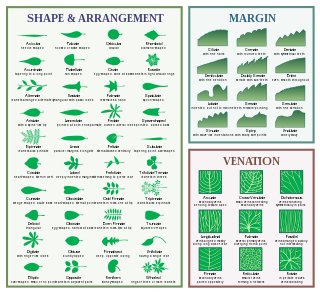
The following is a defined list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple or compound. The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, may be smooth or bearing hair, bristles or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article.

Dark fantasy is a subgenre of fantasy literary, artistic, and cinematic works that incorporate darker and frightening themes of fantasy. It also often combines fantasy with elements of horror or has a gloomy, dark atmosphere, or a sense of horror and dread.

Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the joints. Anatomists use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing the uniqueness of the movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes.

Metadata is "data [information] that provides information about other data". Many distinct types of metadata exist, among these descriptive metadata, structural metadata, administrative metadata, reference metadata and statistical metadata.

Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors.

The word bespoke has evolved from a verb meaning "to speak for something" to its contemporary usage as an adjective that has changed from describing first tailor-made suits and shoes, and later, to anything commissioned to a particular specification, and finally to a general marketing and branding concept implying exclusivity and appealing to snobbery.
Al-Masdar News is an online newspaper founded by Leith Abou Fadel. Al-Masdar is Arabic for "the source". Al-Masdar's coverage focuses largely on conflict zones in the Middle East: Syria, Yemen, and Iraq. Al-Masdar has been described as being pro-president Bashar al-Assad.












