Related Research Articles
An identity document is any document that may be used to prove a person's identity. If issued in a small, standard credit card size form, it is usually called an identity card, or passport card. Some countries issue formal identity documents, as national identification cards which may be compulsory or non-compulsory, while others may require identity verification using regional identification or informal documents. When the identity document incorporates a person's photograph, it may be called photo ID.

The Matrícula Consular de Alta Seguridad (MCAS) is an identification card issued by the Government of Mexico through its consulate offices to Mexican nationals residing outside of Mexico. Also known as the Mexican CID card, it has been issued since 1871. The issue of the card has no bearing on immigration status in the foreign country they are residing in. The purpose of the card is to demonstrate that the bearer is a Mexican national living outside of Mexico. It includes a Government of Mexico issued ID number and bears a photograph and address outside of Mexico of the Mexican National to whom it is issued.

Transgender rights in Canada, including procedures for changing legal gender and protections from discrimination, vary among provinces and territories, due to Canada's nature as a federal state.

An electronic identification ("eID") is a digital solution for proof of identity of citizens or organizations. They can be used to view to access benefits or services provided by government authorities, banks or other companies, for mobile payments, etc. Apart from online authentication and login, many electronic identity services also give users the option to sign electronic documents with a digital signature.
A national identification number, national identity number, or national insurance number is used by the governments of many countries as a means of tracking their citizens, permanent residents, and temporary residents for the purposes of work, taxation, government benefits, health care, and other governmentally-related functions.

The Real ID Act of 2005, Pub.L. 109–13 (text)(PDF), 119 Stat. 302, enacted May 11, 2005, is an Act of Congress that modifies U.S. federal law pertaining to security, authentication, and issuance procedure standards for drivers' licenses and identity documents, as well as various immigration issues pertaining to terrorism.
Identity documents in the United States are typically the regional state-issued driver's license or identity card, while also the Social Security card and the United States Passport Card may serve as national identification. The United States passport itself also may serve as identification. There is, however, no official "national identity card" in the United States, in the sense that there is no federal agency with nationwide jurisdiction that directly issues an identity document to all US citizens for mandatory regular use.
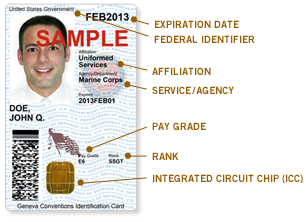
The Common Access Card, also commonly referred to as the CAC is a smart card about the size of a credit card. It is the standard identification for Active Duty United States Defense personnel, to include the Selected Reserve and National Guard, United States Department of Defense (DoD) civilian employees, United States Coast Guard (USCG) civilian employees and eligible DoD and USCG contractor personnel. It is also the principal card used to enable physical access to buildings and controlled spaces, and it provides access to defense computer networks and systems. It also serves as an identification card under the Geneva Conventions. In combination with a personal identification number, a CAC satisfies the requirement for two-factor authentication: something the user knows combined with something the user has. The CAC also satisfies the requirements for digital signature and data encryption technologies: authentication, integrity and non-repudiation.

The cédula de identidade is the official national identity document in Brazil. It is often informally called carteira de identidade, "RG" or simply identidade in Portuguese. The card contains the name of the bearer, filiation, place of birth, date of birth, signature and thumbprint of the bearer. Other national documents can legally be used as an identity card, such as a federative unit-issued driver's license, passport or, for minors, a birth certificate. Each card has a unique RG number.

A travel document is an identity document issued by a government or international entity pursuant to international agreements to enable individuals to clear border control measures. Travel documents usually assure other governments that the bearer may return to the issuing country, and are often issued in booklet form to allow other governments to place visas as well as entry and exit stamps into them. The most common travel document is a passport, which usually gives the bearer more privileges like visa-free access to certain countries. While passports issued by governments are the most common variety of travel document, many states and international organisations issue other varieties of travel documents that the holder to travel internationally to countries that recognise the documents. For example, stateless persons are not normally issued a national passport, but may be able to obtain a refugee travel document or the earlier "Nansen passport" which enables them to travel to countries which recognise the document, and sometimes to return to the issuing country.

The United States passport card is an optional national identity card and a travel document issued by the United States federal government in the size of a credit card. Like a U.S. passport book, the passport card is only issued to U.S. nationals exclusively by the U.S. Department of State, compliant to the standards for identity documents set by the REAL ID Act, and can be used as proof of U.S. citizenship and identity. The passport card allows its holders to travel by domestic air flights within the United States, and to travel by land and sea within North America. However, the passport card cannot be used for international air travel.

The Brazilian passport is the official document for foreign travel issued by the federal government, through the Federal Police.

In the United States, driver's licenses are issued by each individual state, territory, and the District of Columbia rather than by the federal government due to federalism. Drivers are normally required to obtain a license from their state of residence and all states recognize each other's licenses for non-resident age requirements. There are also licenses for motorcycle use. Generally, a minimum age of 16 is required to obtain a drivers/M1 license. A state may also suspend an individual's driving privilege within its borders for traffic violations. Many states share a common system of license classes, with some exceptions, e.g. commercial license classes are standardized by federal regulation at 49 CFR 383. Many driving permits and ID cards display small digits next to each data field. This is required by the American Association of Motor Vehicle Administrators’ design standard and has been adopted by many US states. According to the United States Department of Transportation, as of 2018, there are approximately 227 million licensed drivers in the United States.
Consular identification (CID) cards are issued by some governments to their citizens who are living in foreign countries. They may be used, for example, by an embassy to allow its citizens to vote in a foreign country. Some jurisdictions accept them for some identification purposes. They are not certifications of legal residence within foreign countries, so CID card holders could be legal or illegal aliens.
Transgender rights in the United States vary considerably by jurisdiction. By the end of 2021, at least 130 bills had been introduced in 33 states to restrict the rights of transgender people.
Transgender disenfranchisement is the prevention by bureaucratic, institutional and social barriers, of transgender individuals from voting or participating in other aspects of civic life. Transgender people may be disenfranchised if the sex indicated on their identification documents does not match their gender presentation, and they may be unable to update necessary identity documents because some governments require individuals to undergo sex reassignment surgery first, which many cannot afford, are not medical candidates for, or do not want.
Biometrics refers to the automated recognition of individuals based on their biological and behavioral characteristics, not to be confused with statistical biometrics; which is used to analyse data in the biological sciences. Biometrics for the purposes of identification may involve DNA matching, facial recognition, fingerprints, retina and iris scanning, voice analysis, handwriting, gait, and even body odor.

Multiple countries legally recognize non-binary or third gender classifications. These classifications are typically based on a person's gender identity. In some countries, such classifications may only be available to intersex people, born with sex characteristics that "do not fit the typical definitions for male or female bodies."
Australia does not have a national identity card. Instead, various documents may be used or required to prove a person's identity, whether for government or commercial purposes such as:
Texas Senate Bill 5 is a bill that implements a form of voter identification law in the state of Texas. It is a revamped version of a previous Texas voter ID law that was introduced in 2011.
References
- ↑ Chad Vander Veen (Aug 14, 2009). "Is PASS ID Better Than REAL ID? (Analysis)". Government Technology Magazine/e.Republic, Inc.