
Lotus 1-2-3 is a discontinued spreadsheet program from Lotus Software. It was the first killer application of the IBM PC, was hugely popular in the 1980s, and significantly contributed to the success of IBM PC-compatibles in the business market.

An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central processing unit, sourced either from Intel or a second source like AMD, Cyrix or other vendors such as Texas Instruments, Fujitsu, OKI, Mitsubishi or NEC and is capable of using interchangeable commodity hardware such as expansion cards. Initially such computers were referred to as PC clones, IBM clones or IBM PC clones, but the term "IBM PC compatible" is now a historical description only, as the vast majority of microcomputers produced since the 1990s are IBM compatible. IBM itself no longer sells personal computers, having sold its division to Lenovo in 2005. "Wintel" is a similar description that is more commonly used for modern computers.

GEM is a discontinued operating environment released by Digital Research in 1985. GEM is known primarily as the native graphical user interface of the Atari ST series of computers, providing a WIMP desktop. It was also available for IBM PC compatibles and shipped with some models from Amstrad. GEM is used as the core for some commercial MS-DOS programs, the most notable being Ventura Publisher. It was ported to other computers that previously lacked graphical interfaces, but never gained traction. The final retail version of GEM was released in 1988.

Digital Research, Inc. was a privately held American software company created by Gary Kildall to market and develop his CP/M operating system and related 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit systems like MP/M, Concurrent DOS, FlexOS, Multiuser DOS, DOS Plus, DR DOS and GEM. It was the first large software company in the microcomputer world. Digital Research was originally based in Pacific Grove, California, later in Monterey, California.
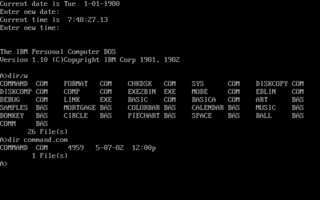
IBM PC DOS, also known as PC DOS or IBM DOS, is a discontinued disk operating system for the IBM Personal Computer, its successors, and IBM PC compatibles. It was sold by IBM from the early 1980s into the 2000s. Developed by Microsoft, it was also sold by that company to the open market as MS-DOS. Both operating systems were identical or almost identical until 1993, when IBM began selling PC DOS 6.1 with its own new features. The collective shorthand for PC DOS and MS-DOS was DOS, which is also the generic term for disk operating system, and is shared with dozens of disk operating systems called DOS.
The Print Shop is a desktop publishing software package originally published in 1984 by Broderbund. It was unique in that it provided libraries of clip art and templates through a simple interface to build signs, posters and banners with household dot-matrix printers. Over the years, the software has been updated to accommodate changing file formats and printer technologies.

Cinemaware was a video game developer and publisher. It had released several titles in the 1980s based on various film themes. The company was resurrected in 2000, before being acquired by eGames in 2005.

Norton Utilities is a utility software suite designed to help analyze, configure, optimize and maintain a computer. The latest version of the original series of Norton Utilities is Norton Utilities 16 for Windows XP/Vista/7/8, released 26 October 2012.
Timeworks Publisher was a desktop publishing (DTP) program produced by GST Software in the United Kingdom and published by Timeworks, Inc., in the United States.
Merge is a software system which allows a user to run DOS/Windows 3.1 on SCO UNIX, in an 8086 virtual machine.

The Playroom is an educational video game published in 1989 for MS-DOS, Apple II, and Mac. The game was compatible with the TouchWindow utility. It was ported to the Amiga and FM Towns computers in 1992 and 1994 respectively and then remade for Microsoft Windows and Macintosh in 1995. It was designed for ages 3 to 6 manufactured by Broderbund. A follow-up game titled The Treehouse was released in 1991 and a sequel to this game, called The Backyard in 1993.
A self-booting disk is a floppy disk for home computers or personal computers that loads—or boots—directly into a standalone application when the system is turned on, bypassing the operating system. This was common, even standard, on some computers in the late 1970s to early 1990s. Video games were the type of application most commonly distributed using this technique.
Central Point Software, Inc. was a leading software utilities maker for the PC market, supplying utilities software for the MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows markets. It also produced Apple II copy programs. Through a series of mergers, the company was acquired by Symantec in 1994.

Following the introduction of the IBM Personal Computer in 1981, many other personal computer architectures became extinct within just a few years. It led to a wave of IBM PC compatible systems being released.
This article presents a timeline of events in the history of 16-bit x86 DOS-family disk operating systems from 1980 to present. Non-x86 operating systems named "DOS" are not part of the scope of this timeline.

Falcon is a combat flight simulator video game and the first official entry in the Falcon series of the F-16 jet fighter's simulators by Spectrum HoloByte. Originally developed by Sphere for Macintosh and MS-DOS in 1987 and ported to several platforms between 1988 and 1992, the game earned commercial success and critical acclaim.

Banner Mania was a banner making program for IBM PC compatible computers, enabling the user to create banners, posters, signs and logos. It was released by Broderbund in 1989 and was developed for Pixellite Group by Presage Software Development and written by Christopher Schardt and Dane Bigham.

Tetris is a 1988 video game published by Spectrum HoloByte in the United States and Mirrorsoft in the United Kingdom. It was the first commercial release of Tetris, a puzzle game developed in the Soviet Union in the mid-1980s, and was released on multiple home personal computer systems. Tetris received positive reviews overall, winning multiple Excellence in Software Awards, and would eventually sell over one million copies.












