
The RWD 8 was a Polish parasol wing monoplane trainer aircraft produced by RWD. It was used from 1934 to 1939 by the Polish Air Force and civilian aviation.

The PWS-33 Wyżeł was a Polish twin-engined military trainer aircraft from a period before World War II constructed by Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów or PWS. Although destined for production it got no further than the prototypes before Poland was invaded.

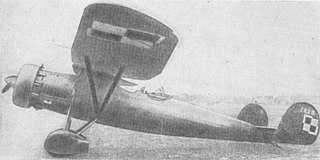
The PWS-10 was a Polish fighter aircraft, constructed in the PWS. It was the first Polish-designed fighter to enter serial production.
The PWS-19 was a Polish reconnaissance and bomber plane prototype of the 1930s, constructed in the PWS.
The PWS-18 was a Polish trainer aircraft, used from 1937 to 1939 by the Polish Air Force, a modified licence variant of the British Avro Tutor.

The Bartel BM.4 was a Polish biplane primary trainer aircraft used from 1929 to 1939 by the Polish Air Force and Polish civilian aviation, manufactured in the Samolot factory in Poznań. It was the first plane of Polish design put into production.

The PWS-21 was a Polish passenger aircraft for 4 passengers, built in PWS factory in 1930, that remained a prototype.

The PWS-1 was a Polish two-seat fighter and reconnaissance aircraft constructed by Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów (PWS) in 1927. It remained a prototype for its entire lifespan.

The JD-2 was a Polish sports plane of 1926. It was the first sports plane designed in Poland, that was built in a small series.

The PWS-12 was a biplane trainer designed and developed by Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów (PWS). It entered production as the PWS-14.

The PWS-50,(PWS - Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów - Podlasie Aircraft Factory), was a prototype Polish single-engine mid-wing monoplane sports aircraft of 1930, constructed by Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów.

The PWS-51 was a Polish sports plane of 1930, a single-engine low-wing monoplane, constructed by the Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów (PWS), that remained a prototype.

The PWS-52 was a Polish sports aircraft of 1930, a single-engine high-wing monoplane, constructed by the Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów (PWS), that remained a prototype.

The PWS-5 or PWS-5t2, was a multi-seated Polish liaison aircraft, developed in 1928 by PWS.

The PWS-6, was a Polish liaison aircraft, developed in 1930 by the PWS, that remained a prototype.

The PWS-11 was a Polish aerobatic and trainer aircraft, developed in 1928-1929 by PWS, which remained a prototype.

The PWS 3 was a Polish sport aircraft, developed in 1927 by PWS, which remained a prototype.

The PWS-4 was a prototype Polish sports aircraft, developed in 1928 by Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów.

The PWS-35 Ogar was a two-seat, aerobatic training biplane that was designed by Kazimierz Nowicki, Marian Piątka and Michał Rosnowski at the Lviv Polytechnic in 1935/1936.

PWS-40 Junak was a Polish trainer aircraft of the 1930s. First flown in the spring of 1939, it was to become the standard training aircraft of the Polish Air Force's fighter pilot schools before more advanced trainers could be delivered. However, due to the outbreak of World War II only the prototype was completed and test-flown.



















