| Palace of São João Novo(Palácio de São João Novo) | |
| Palace (Palácio) | |
An oblique view of the principal facade of the Palace | |
| Official name:Palácio de São João Novo/Museu de Etnografia e História/Museu de Etnologia do Porto | |
| Country | |
|---|---|
| Region | Norte |
| Subregion | Greater Porto |
| District | Porto |
| Municipality | Porto |
| Location | Cedofeita, Santo Ildefonso, Sé, Miragaia, São Nicolau e Vitória |
| - coordinates | 41°8′33″N8°37′4″W / 41.14250°N 8.61778°W Coordinates: 41°8′33″N8°37′4″W / 41.14250°N 8.61778°W |
| Architects | Nicolau Nasoni, António Pereira,Jaime Ferreira Alves |
| Style | Baroque |
| Materials | Granite, Azulejo, Wood, Tile, Iron |
| Origin | 1747 |
| Owner | Portuguese Republic |
| For public | Private |
| Easiest access | Largo São João Novo |
| Management | Instituto Gestão do Patrimonio Arquitectónico e Arqueológico |
| Operator | DRCNorte (Decree 114/2012, Diário da República, Série 1, 102, 25 May 2012) |
| Status | Property of Public Interest Imóvel de Interesse Público |
| Listing | Decree 129/77, Diário da República, Série 1, 226, 29 September 1977 |
| Wikimedia Commons: Palácio de São João Novo | |
The Palace of São João Novo (Portuguese : Palácio de São João Novo) is a palace/residence in the civil parish of Cedofeita, Santo Ildefonso, Sé, Miragaia, São Nicolau e Vitória, in the municipality of Porto, in the Portuguese district of the same name.
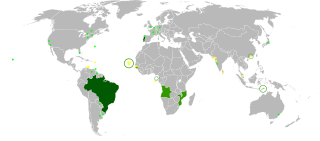
Portuguese is a Western Romance language originating in the Iberian Peninsula. It is the sole official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Angola, and São Tomé and Príncipe. It also has co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea and Macau in China. As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese and Portuguese creole speakers are also found in Goa, Daman and Diu in India; in Batticaloa on the east coast of Sri Lanka; in the Indonesian island of Flores; in the Malacca state of Malaysia; and the ABC islands in the Caribbean where Papiamento is spoken, while Cape Verdean Creole is the most widely spoken Portuguese-based Creole. Reintegrationists maintain that Galician is not a separate language, but a dialect of Portuguese. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation is referred to as "Lusophone" (Lusófono).

Freguesia, usually translated as "parish" or "civil parish", is the third-level administrative subdivision of Portugal, as defined by the 1976 Constitution. It is also a local administrative unit in the former Portuguese overseas territories of Cape Verde and Macau. In the past, was also an administrative division of the other Portuguese overseas territories. The parroquia in the Spanish autonomous communities of Galicia and Asturias is similar to a freguesia.

Cedofeita, Santo Ildefonso, Sé, Miragaia, São Nicolau e Vitória is a civil parish in the municipality of Porto, Portugal. It was formed in 2013 by the merger of the former parishes Cedofeita, Santo Ildefonso, Sé, Miragaia, São Nicolau and Vitória. The population in 2011 was 40,440, in an area of 5.43 km². It covers the historic part of the city of Porto.


















