Cape Arkona is a 45-metre-high cape on the island of Rügen in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It forms the tip of the Wittow peninsula, just a few kilometres north of the Jasmund National Park. The protected landscape of Cape Arkona, together with the fishing village of Vitt, belongs to the municipality of Putgarten and is one of the most popular tourist destinations on Rügen, receiving about 800,000 visitors annually.
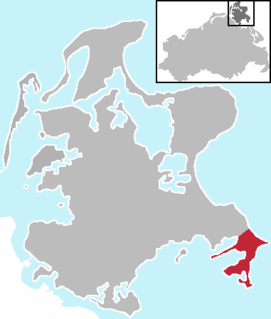
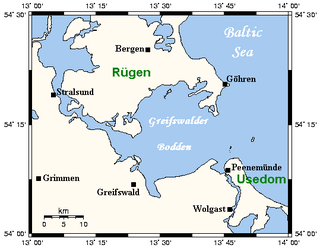
Mönchgut is a peninsula of 29.44 square kilometers with 6600 inhabitants in the southeast of Rügen island in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It lies just between the Greifswalder Bodden and the rest of the Baltic Sea. Mönchgut contains the districts of Göhren and Thiessow; the peninsula is part of the Mönchgut-Granitz administration area. It is also a part of the Biosphere Reserve of Südost-Rügen.

Garz is a town in the county of Vorpommern-Rügen in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The town is administered by the Amt of Bergen auf Rügen, in the town of the same name.
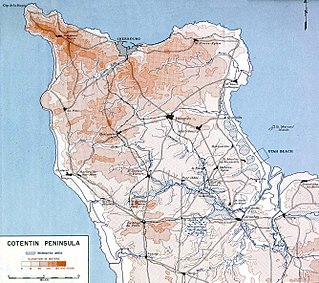
The Battle of Cherbourg was part of the Battle of Normandy during World War II. It was fought immediately after the successful Allied landings on June 6, 1944. Allied troops, mainly American, isolated and captured the fortified port, which was considered vital to the campaign in Western Europe, in a hard-fought, month-long campaign.

Binz is the largest seaside resort on the German island of Rügen.
Operation Accumulator was an Allied naval operation near the Channel Islands on the night of 12/13 June 1944, in support of Operation Overlord, the invasion of France.
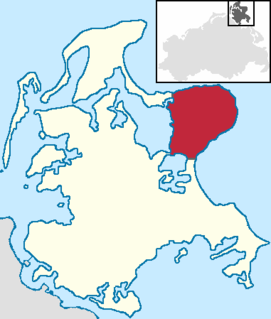
Jasmund is a peninsula of the island of Rügen in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is connected to the Wittow peninsula and to the Muttland main section of Rügen by the narrow land bridges Schaabe and Schmale Heide, respectively. Sassnitz, Sagard and the Mukran international ferry terminal are on Jasmund. Jasmund is also famous for the Stubbenkammer chalk cliffs within the Jasmund National Park, a nature reserve in the northeast of Rügen island.
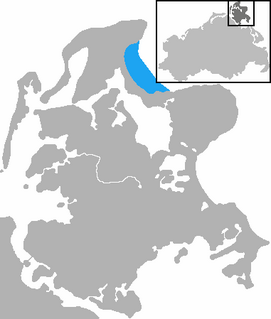
The Tromper Wiek is a bay on the Baltic Sea between the peninsulas of Wittow and Jasmund on the island of Rügen in northeast Germany.

The Wittow Ferry is a ferry service for foot passengers and vehicles from the heart of the German Baltic Sea island of Rügen, the Muttland, to the peninsula of Wittow to the north. It has also given its name to the parish of Wittower Fähre in the municipality of Wiek. This lies on the Rassower Strom at the tip of the tongue of land between the lagoons of Wieker Bodden and Breetzer Bodden on its northern shore. On the southern shore the ferry landing stage is located between the villages of Vaschvitz and Fischersiedlung in the municipality of Trent.

Bug is the name both of the westernmost tongue of land (Landzunge) on the peninsula of Wittow on the German island of Rügen, as well as the name of the former village there. Bug begins south of the village of Dranske and belongs territorially to that municipality.
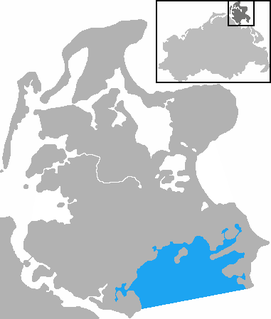
The Rügische Bodden is a bay which is part of a larger stretch of water, the Greifswalder Bodden, bounded on two sides by the German mainland and on a third by the Baltic Sea island of Rügen. It is located southeast of Rügen island between Mönchgut and the Zudar peninsula. At Mönchgut, several headlands project into the bodden: the Reddevitz Höft, the Klein Zicker and the Großer Zicker. The inlet between Rügen and the Reddevitzer Höft is known as Having; between the Reddevitzer Höft and the Großer Zicker lies the inlet of Hagensche Wiek. Other bays are the Schoritzer Wiek, the Selliner See and the Neuensiener See. Its southern boundary would be the line between the headlands of the Zudar and Mönchgut peninsulas. There are harbours in Lauterbach, Baabe and Seedorf.

The invasion of Rügen of 22 to 24 September 1678 was a military operation in the Swedish-Brandenburg War, or Scanian War, that ended with the annexation of the Swedish-ruled island of Rügen by the Allies: Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark.

The Prussia Columns are two monuments, over 15 metres (49 ft) high, that were erected in the years 1854 and 1855 by order of the Prussian king, Frederick William IV on the southeast coast of the German island of Rügen near Neukamp and Groß Stresow. Both villages are today part of the municipality of Putbus.

The Nordperd(Perd = Slavic for protrusion or prominence) is a cape on the German Baltic Sea island of Rügen. It is part of the Southeast Rügen Biosphere Reserve and the Mönchgut Nature Reserve.

The Southeast Rügen Biosphere Reserve is a biosphere reserve in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, which covers the southeastern part of the island of Rügen, the lagoon of Rügischer Bodden between Putbus and Thiessow, the outer coast between Thiessow and Binz and the island of Vilm.

The successful Landing on Groß Stresow by Prussian, Danish and Saxon troops took place on 15 November 1715 on the island of Rügen, Germany during the Great Northern War. The landing was followed with cavalry assaults from the Swedish defences on the island, commanded by Charles XII king of Sweden who despite the huge numerical disadvantage of - one up against five - chose to attack the fortified camp. The Swedes managed to get past the "Cheval de frise" and break through, but was then rapidly repulsed and routed after taking heavy casualties.

The fishing village of Vitt lies on the German Baltic Sea island of Rügen, more precisely on the Wittow peninsula near Cape Arkona. The village is part of the municipality of Putgarten. Because of its location in a coastal gully on the cliffed coast, called Liete, Vitt is not visible from afar. However, from the edge of the gully there is a view over the thatched roofs of the village. It is a popular tourist destination; often described as "the most romantic place on Rügen". The Marco Polo guide rates it as one of the top 15 highlights on the island of Rügen.

The Landing at Humlebæk took place on August 4, 1700, in the Swedish invasion of Denmark during the Great Northern War 1700-1721. It was the first offensive during the war by the Swedish army, and it was directly led by Charles XII of Sweden commanding the right flank and Arvid Horn together with Carl Gustav Rehnskiöld at the left. The Swedes were victorious and utterly routed the Danish forces led by Jens Rostgaard.