
In the United States, the ACH Network is the national automated clearing house (ACH) for electronic funds transfers established in the 1960s and 1970s. It is a financial utility owned by US banks, and is one of the largest payments networks in the United States, both by volume and by customer reach; virtually every bank account in the US, whether personal or commercial, is connected to the network.
Cheque clearing or bank clearance is the process of moving cash from the bank on which a cheque is drawn to the bank in which it was deposited, usually accompanied by the movement of the cheque to the paying bank, either in the traditional physical paper form or digitally under a cheque truncation system. This process is called the clearing cycle and normally results in a credit to the account at the bank of deposit, and an equivalent debit to the account at the bank on which it was drawn, with a corresponding adjustment of accounts of the banks themselves. If there are not enough funds in the account when the cheque arrived at the issuing bank, the cheque would be returned as a dishonoured cheque marked as non-sufficient funds.

Wire transfer, bank transfer, or credit transfer, is a method of electronic funds transfer from one person or entity to another. A wire transfer can be made from one bank account to another bank account, or through a transfer of cash at a cash office.

A giro transfer, often shortened to giro, is a payment transfer between current bank accounts and initiated by the payer, not the payee. The debit card has a similar model. Giros are primarily used in Europe; although electronic payment systems exist in the United States, it is not possible to perform third-party transfers with them. In the European Union, the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) allows electronic giro or debit card payments in euros to be executed to any euro bank account in the area.
In banking and finance, clearing refers to all activities from the time a commitment is made for a transaction until it is settled. This process turns the promise of payment into the actual movement of money from one account to another. Clearing houses were formed to facilitate such transactions among banks.
A payment system is any system used to settle financial transactions through the transfer of monetary value. This includes the institutions, payment instruments such as payment cards, people, rules, procedures, standards, and technologies that make its exchange possible. A payment system is an operational network which links bank accounts and provides for monetary exchange using bank deposits. Some payment systems also include credit mechanisms, which are essentially a different aspect of payment.
A direct debit or direct withdrawal is a financial transaction in which one organisation withdraws funds from a payer's bank account. Formally, the organisation that calls for the funds instructs their bank to collect an amount directly from another's bank account designated by the payer and pay those funds into a bank account designated by the payee. Before the payer's banker will allow the transaction to take place, the payer must have advised the bank that they have authorized the payee to directly draw the funds. It is also called pre-authorized debit (PAD) or pre-authorized payment (PAP). After the authorities are set up, the direct debit transactions are usually processed electronically.
Sort codes are the domestic bank codes used to route money transfers between financial institutions in the United Kingdom, and formerly in the Republic of Ireland. They are six-digit hierarchical numerical addresses that specify clearing banks, clearing systems, regions, large financial institutions, groups of financial institutions and ultimately resolve to individual branches. In the UK they continue to be used to route transactions domestically within clearance organizations and to identify accounts, while in the Republic of Ireland they have been deprecated and replaced by the Single European Payment Area (SEPA) systems and infrastructure.

Electronic funds transfer (EFT) is the transfer of money from one bank account to another, either within a single financial institution or across multiple institutions, via computer-based systems.
Clearing house or Clearinghouse may refer to:
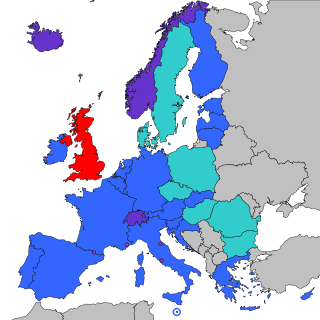
The Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) is a payment integration initiative of the European Union for simplification of bank transfers denominated in euros. As of 2020, there were 36 members in SEPA, consisting of the 27 member states of the European Union, the four member states of the European Free Trade Association, and the United Kingdom. Some microstates participate in the technical schemes: Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City.
A Systemically Important Payment System (SIPS) is a payment systems whose failure could potentially endanger the operation of the whole economy. In general, these are the major payment clearing systems or real-time gross settlement systems of individual countries, but in the case of Europe, there are certain pan-European payment systems. T2 is a pan-European SIPS dealing with major inter-bank payments. STEP2, operated by the Euro Banking Association, is a major pan-European clearing system for retail payments which has the potential to become a SIPS.
The Clearing House is a banking association and payments company owned by the largest commercial banks in the United States. The Clearing House is the parent organization of The Clearing House Payments Company L.L.C., which owns and operates core payments system infrastructure in the United States, including ACH, wire payments, check image clearing, and real-time payments through the RTP network, a modern real-time payment system for the U.S.
The Clearing House Payments Company L.L.C. (PayCo) is a U.S.-based limited liability company formed by Clearing House Association. PayCo is a private sector, payment system infrastructure that operates an electronic check clearing and settlement system (SVPCO), a clearing house, and a wholesale funds transfer system (CHIPS).
Payments as a service (PaaS) is a marketing phrase used to describe software as a service to connect a group of international payment systems. The architecture is represented by a layer – or overlay – that resides on top of these disparate systems and provides for two-way communications between the payment system and the PaaS. Communication is governed by standard APIs created by the PaaS provider.
The International Payments Framework (IPF) was an initiative launched in 2010 to create a global framework for payment processing by the International Payments Framework Association, a trade association headquartered in Atlanta, in the United States. The initiative and the association concluded in 2023 after achieving its objectives.
EBA Clearing is a provider of pan-European payment infrastructure wholly owned by shareholders that consist of major European banks. It derives its name from the Euro Banking Association which was instrumental in its establishment in June 1998, but has always been a separate organization.
A clearing house is a financial institution formed to facilitate the exchange of payments, securities, or derivatives transactions. The clearing house stands between two clearing firms.

An automated clearing house (ACH) is a computer-based electronic network for processing transactions, usually domestic low value payments, between participating financial institutions. It may support both credit transfers and direct debits. The ACH system is designed to process batches of payments containing numerous transactions, and it charges fees low enough to encourage its use for low-value payments.

TBB pank is an Estonian commercial bank which headquarters are located in Tallinn, Estonia. One office is located in Narva.


