
Panamalai lies 23 kilometers from Gingee, Viluppuram district in Tamil Nadu, India. The site is known as a location to various ancient structural temples built during the Pallava dynasty. One of them is the Talagirisvara Temple. [1]

Panamalai lies 23 kilometers from Gingee, Viluppuram district in Tamil Nadu, India. The site is known as a location to various ancient structural temples built during the Pallava dynasty. One of them is the Talagirisvara Temple. [1]
Narasimhavarman II, also known as Rajasimha or Rajamalla, is credited with constructing structural temples of Pallava dynasty namely the Shore Temple at Mamallapuram, Kailsanatha Temple and Talagirisvara temple at Panamalai. The temple is built on a small hillock overlooking the Panamalai lake. [2] This 7th Century structure has a Vimana which resembles that of Kailasanatha temple of Kanchipuram.
The garbhagriha houses a Dharalingam and as in Pallava temples of that time, there is a Somaskanda panel on rear wall of the sanctum. There is an Ardhamandapam (half Mandapam). On the walls of the Ardhamandapam one can see panels of deities such as Brahma with Saraswati and Vishnu with Lakshmi on either side. The shrine faces east and the garbhagriha is surrounded on all the three sides by sub-shrines (Anga Kovil or Limb Shrines – which are attached to the main shrine). [3] A few more sub-shrines and a Mahamandapam (a big Mandapam) have been added to the structure at much later period. The Vimana is three tiered and the top tier has been reconstructed. The pillars with squatting lions, a typical Pallava signature can also be found.
The sub-shrine to the north, has a small section of mural painting which has survived over the years, bearing testimony to the Pallavas' mastery of the art. [4]

The Kailasanathar temple (Kanchipuram), also referred to as the Kailasanatha temple, is a Pallava-era historic Hindu temple in Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu, India. Dedicated to Shiva, it is one of the oldest surviving monuments in Kanchipuram. It reflects a Dravidian architecture and was built about 700 CE by Narasimhavarman II with additions by Mahendravarman III. A square-plan temple, it has a mukha-mandapa (entrance hall), a maha-mandapa (gathering hall) and a primary garbha-griya (sanctum) topped with a four-storey vimana. The main sanctum is surrounded by nine shrines, seven outside and two inside flanking the entrance of the sanctum, all with forms of Shiva. The outer walls of the temple's prakara (courtyard) is also surrounded by cells.

Sittanavasal Cave is a 2nd-century Tamil Śramaṇa complex of caves in Sittanavasal village in Pudukottai district of Tamil Nadu, India. Its name is a distorted form of Sit-tan-na-va-yil, a Tamil word which means "the abode of great saints".

The period of the imperial Cholas in South India was an age of continuous improvement and refinement of Chola art and architecture. They utilised the wealth earned through their extensive conquests in building long-lasting stone temples and exquisite bronze sculptures, in an almost exclusively Hindu cultural setting.

Karpaka Vinayaka Temple or Pillaiyarpatti Pillaiyar Temple is a 7th-century CE rock-cut cave shrine, significantly expanded over the later centuries. It is located in Pillayarpatti village in Tiruppathur Taluk, Sivaganga district in Tamil Nadu, India.

Dravidian architecture, or the South Indian temple style, is an architectural idiom in Hindu temple architecture that emerged from South India, reaching its final form by the sixteenth century. It is seen in Hindu temples, and the most distinctive difference from north Indian styles is the use of a shorter and more pyramidal tower over the garbhagriha or sanctuary called a vimana, where the north has taller towers, usually bending inwards as they rise, called shikharas. However, for modern visitors to larger temples the dominating feature is the high gopura or gatehouse at the edge of the compound; large temples have several, dwarfing the vimana; these are a much more recent development. There are numerous other distinct features such as the dwarapalakas – twin guardians at the main entrance and the inner sanctum of the temple and goshtams – deities carved in niches on the outer side walls of the garbhagriha.
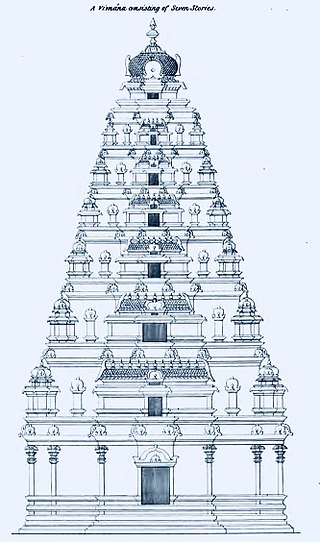
Vimana is the structure over the garbhagriha or inner sanctum in the Hindu temples of South India and Odisha in East India. In typical temples of Odisha using the Kalinga style of architecture, the vimana is the tallest structure of the temple, as it is in the shikhara towers of temples in West and North India. By contrast, in large South Indian temples, it is typically smaller than the great gatehouses or gopuram, which are the most immediately striking architectural elements in a temple complex. A vimana is usually shaped as a pyramid, consisting of several stories or tala. Vimana are divided in two groups: jati vimanas that have up to four tala and mukhya vimana that have five tala and more.

Marundeeswarar Temple is a temple dedicated to Hindu deity Shiva, located in Thiruvanmiyur, Chennai adjacent to the beach of Bay of Bengal. It is one of the 275 Paadal Petra Sthalams where two of the most revered Nayanars, Appar and Tirugnana Sambandar, have glorified the temple with their verses during the 7th century CE. The temple has been widely expanded by Chola kings during the 11th century CE. The temple has two seven-tiered gateway towers, a huge tank, with the overall temple area covering 1 acre. The Marundeeswarar temple has been a place of curative worship for people with diseases.

Brihadishvara Temple, called Rajarajesvaram by its builder, and known locally as Thanjai Periya Kovil and Peruvudaiyar Kovil, is a Shaivite Hindu temple built in a Chola architectural style located on the south bank of the Cauvery river in Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India. It is one of the largest Hindu temples and an exemplar of Tamil architecture. It is also called Dakshina Meru. Built by Chola emperor Rajaraja I between 1003 and 1010 CE, the temple is a part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site known as the "Great Living Chola Temples", along with the Chola-era Gangaikonda Cholapuram temple and Airavatesvara temple, which are about 70 kilometres (43 mi) and 40 kilometres (25 mi) to its northeast respectively.

Thiru Parameswara Vinnagaram or Vaikunta Perumal Temple is a temple dedicated to Vishnu, located in Kanchipuram in the South Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Constructed in the Dravidian style of architecture, the temple is glorified in the Nalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th through the 9th centuries CE. It is one among the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to Vishnu, who is worshipped as Vaikuntanathan and his consort Lakshmi as Sri Vaikundavalli. The temple is considered the second oldest extant temple in Kanchipuram after the Kailasanathar temple.

Tirupullamangai or Thirupullamangai is a Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Siva located in Pasupathikoil, Papanasam taluk of Thanjavur district, Tamil Nadu, India. It is one of the shrines of the 275 Paadal Petra Sthalams - Shiva Sthalams glorified in the early medieval Tevaram poems by Tamil Saivite Nayanar Tirugnanasambandar.

Iconography of Shiva temples in Tamil Nadu is governed by the Shaiva Agamas (IAST:Āgama) that revere the ultimate reality as the Hindu deity, Shiva. Āgama in the Hindu religious context means a traditional doctrine or system which commands faith. Temple worship according to Āgamic rules can be said to have started during the Pallava dynasty in South India, but they were fully under establishment during the Chola dynasty The temples during the Chola period expanded to Sri Lanka and islands in South East Asia. The temple complex was expanding with niches for various deities on the stipulated sides of the sanctum. Lingam was universalised and prakarams (precincts) with subsequent deities came up. The temple parivara expanded considerably during the Chola period. The niches of following Āgamic rules for building Shiva temples in Tamil Nadu, a South Indian state continues even in the modern era. Some of the prime images like that of lingam, Vinayagar and Parvati are present in all the Shiva temples. Almost all the temples follow the same custom during festivals and worship methods with minor exceptions. Most of the Shiva temples in Tamil Nadu and Sri Lanka are built in Dravidian architecture.

Tamil Nadu is known for its ancient temple architecture. Nearly 33,000 ancient temples, many at least 800 to 2000 years old, are found scattered all over Tamil Nadu. As per Tamil Nadu Hindu Endowments Board, there are 38,615 temples. Most of the largest Hindu Temples reside here. Studded with complex architecture, a variety of sculptures, and rich inscriptions, the temples remain the very essence of the culture and heritage of Tamil land, with historical records dating back to at least 3,000 years.

Talagirisvara Temple is a Hindu temple located in the village of Panamalai in the Viluppuram district of Tamil Nadu, India.

The Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram is a collection of 7th- and 8th-century CE religious monuments in the coastal resort town of Mahabalipuram, Tamil Nadu, India and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It is on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal, about 60 kilometres (37 mi) south of Chennai.

The Shore Temple is a complex of temples and shrines that overlooks the shore of the Bay of Bengal. It is located in Mahabalipuram, about 60 kilometres (37 mi) south of Chennai in Tamil Nadu, India.

Arjuna Ratha is a monument from the Pallava Period at Mahabalipuram, on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal, in Kancheepuram district of Tamil Nadu, India. Dated to the seventh century, it is an example of early Dravidian architecture and of monolith Indian rock-cut architecture dating from the late 7th century during reign of King Mahendravarman I and his son Narasimhavarman I of the Pallava Kingdom. One of the Pancha Rathas, it is believed to have been completed before the Dharmaraja Ratha, and like that and the Bhima Ratha, the stone temple is a replica of an earlier wooden version which preceded it. It is one of the Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1984.

The Olakkannesvara Temple is in Mahabalipuram town, overlooking the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal in Kancheepuram District in Tamil Nadu, India. Like the Shore Temple, the Olakkannesvara Temple is a structural temple. Built in the 8th century, it is situated directly above the Mahishasuramardini mandapa on a hillock which provides scenic views of the town. As the area is within a high security zone because of a nuclear power station a few kilometres to its south, photography is prohibited. The Olakkannesvara Temple is sometimes mistakenly referred to as a Mahishasura temple. It is dedicated to an incarnation of Shiva. It is one of the Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram that were designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1984.

Vijayalaya Choleeswaram in Narthamalai, a panchayat town in Pudukottai district in the South Indian state of Tamil Nadu, India, is a temple dedicated to the Hindu god Shiva. Constructed in the Dravida style and rock cut architecture, the temple is believed to have been built during the 9th century by Mutharaiyar dynasty kings, the cardinals of Pallavas, with later expansion from the Cholas. The rock-cut architecture is an early example of Cholan Art, continuing the tradition of the Pallavas. The other portions of Narthamalai houses the 8th century Jaina Abode, the Aluruttimalai Jain Caves. There are also two rock-cut caves, one of which houses twelve life size sculptures of Vishnu. The temple is considered one of the oldest stone temples in South India.

The Pandyan empire is believed to have first emerged circa 600 BC and was one of the leading Tamil dynasties of Southern India. There were various forms of art and many architectural communities within the empire, and their work was sold to overseas markets. Rock cutting and structural temples are examples of these, playing a significant role in Pandyan culture. The rock carvings typically depicted religious figures, floral motifs and animals and were made to surround temples and shrines.
Latitude 12.1010300 N Longitude 79.3823500 E