
An explosive is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may be composed of a single ingredient or a combination of two or more.

Nitrogen is a chemical element with symbol N and atomic number 7. It was first discovered and isolated by Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772. Although Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Henry Cavendish had independently done so at about the same time, Rutherford is generally accorded the credit because his work was published first. The name nitrogène was suggested by French chemist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal in 1790, when it was found that nitrogen was present in nitric acid and nitrates. Antoine Lavoisier suggested instead the name azote, from the Greek ἀζωτικός "no life", as it is an asphyxiant gas; this name is instead used in many languages, such as French, Russian, Romanian and Turkish, and appears in the English names of some nitrogen compounds such as hydrazine, azides and azo compounds.
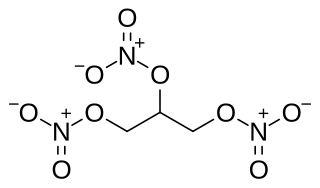
Nitroglycerin (NG), also known as nitroglycerine, trinitroglycerin (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by nitrating glycerol with white fuming nitric acid under conditions appropriate to the formation of the nitric acid ester. Chemically, the substance is an organic nitrate compound rather than a nitro compound, yet the traditional name is often retained. Invented in 1847, nitroglycerin has been used as an active ingredient in the manufacture of explosives, mostly dynamite, and as such it is employed in the construction, demolition, and mining industries. Since the 1880s, it has been used by the military as an active ingredient, and a gelatinizer for nitrocellulose, in some solid propellants, such as cordite and ballistite.

Trinitrotoluene (; TNT), or more specifically 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. This yellow solid is sometimes used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard measure of bombs and the power of explosives. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts.

Pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN), also known as PENT, PENTA, TEN, corpent, or penthrite, is an explosive material. It is the nitrate ester of pentaerythritol, and is structurally very similar to nitroglycerin. Penta refers to the five carbon atoms of the neopentane skeleton. PETN is a powerful explosive material with a relative effectiveness factor of 1.66. When mixed with a plasticizer, PETN forms a plastic explosive. Along with RDX it is the main ingredient of Semtex.

Picric acid is an organic compound with the formula (O2N)3C6H2OH. Its IUPAC name is 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP). The name "picric" comes from the Greek πικρός (pikros), meaning "bitter", reflecting its bitter taste. It is one of the most acidic phenols. Like other highly nitrated organic compounds, picric acid is an explosive, hence its primary use. It has also been used in medicine (antiseptic, burn treatments) and dyes.

A hypergolic propellant combination used in a rocket engine is one whose components spontaneously ignite when they come into contact with each other.

ANFO is a widely used bulk industrial explosive. Its name is commonly pronounced as "an-fo".

In chemistry, an oxidizing agent is a substance that has the ability to oxidize other substances — in other words to cause them to lose electrons. Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and the halogens.

Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide.
Monomethylhydrazine (MMH) is a volatile hydrazine chemical with the chemical formula CH3(NH)NH2. It is used as a rocket propellant in bipropellant rocket engines because it is hypergolic with various oxidizers such as nitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) and nitric acid (HNO3). As a propellant, it is described in specification MIL-PRF-27404.

Flash powder is a pyrotechnic composition, a mixture of oxidizer and metallic fuel, which burns quickly and if confined produces a loud report. It is widely used in theatrical pyrotechnics and fireworks and was once used for flashes in photography.
Accelerants are substances that can bond, mix or disturb another substance and cause an increase in the speed of a natural, or artificial chemical process. Accelerants play a major role in chemistry—most chemical reactions can be hastened with an accelerant. Accelerants alter a chemical bond, speed up a chemical process, or bring organisms back to homeostasis. Accelerants are not necessarily catalysts as they may be consumed by the process.
Tannerite is a brand of binary explosive targets used for firearms practice and sold in kit form. The targets comprise a combination of oxidizers and a fuel – primarily aluminum powder – that is supplied as two separate components that are mixed by the user. The combination is relatively stable when subjected to forces less severe than a high-velocity bullet impact. A hammer blow, being dropped, or impact from a low-velocity bullet or shotgun blast will not initiate a reaction. It is also designed to be non-flammable, although its explosion can cause other flammable material to ignite.
White fuming nitric acid (WFNA) is a storable liquid oxidizer used with kerosene and hydrazine rocket fuel. It consists of nearly pure nitric acid (HNO3). WFNA is commonly specified as containing no more than 2% water and less than 0.5% dissolved nitrogen dioxide or dinitrogen tetroxide.
A pyrotechnic composition is a substance or mixture of substances designed to produce an effect by heat, light, sound, gas/smoke or a combination of these, as a result of non-detonative self-sustaining exothermic chemical reactions. Pyrotechnic substances do not rely on oxygen from external sources to sustain the reaction.

Calcium permanganate is an oxidizing agent and chemical compound with the chemical formula Ca(MnO4)2. It consists of the metal calcium and two permanganate ions. It is noncombustible, but, being a strong oxidizing agent, it will accelerate the burning of combustible material. If the combustible material is finely divided, the resulting mixture may be explosive. Contact with liquid combustible materials may result in spontaneous ignition. Contact with sulfuric acid may cause fires or explosions. Mixtures with acetic acid or acetic anhydride can explode if not kept cold. Explosions can occur when mixtures of calcium permanganate and sulfuric acid come into contact with benzene, carbon disulfide, diethyl ether, ethyl alcohol, petroleum, or other organic matter.














