Related Research Articles

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves, and blood. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months.

Inflammation is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function.

The synovial membrane is a specialized connective tissue that lines the inner surface of capsules of synovial joints, tendon sheaths, and synovial bursas. It makes direct contact with the fibrous membrane on the outside surface and with the synovial fluid lubricant on the inside surface. In contact with the synovial fluid at the tissue surface are many rounded macrophage-like synovial cells and also type B cells, which are also known as fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). Type A cells maintain the synovial fluid by removing wear-and-tear debris. As for the FLS, they produce hyaluronan, as well as other extracellular components in the synovial fluid.

A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments.
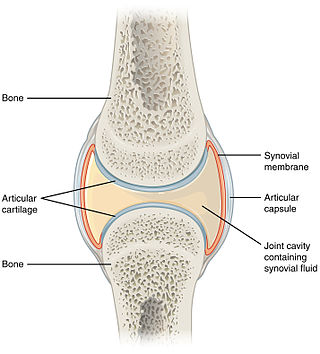
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid. The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer of fibrous membrane, which keeps the bones together structurally, and an inner layer, the synovial membrane, which seals in the synovial fluid.
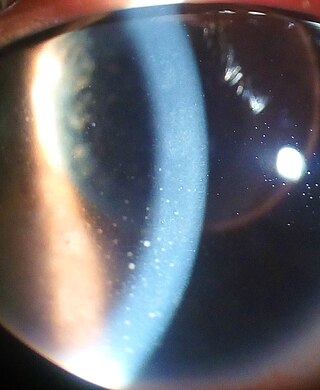
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis (iridocyclitis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20–60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mechanisms may be overcome resulting in inflammation and tissue destruction associated with T-cell activation.
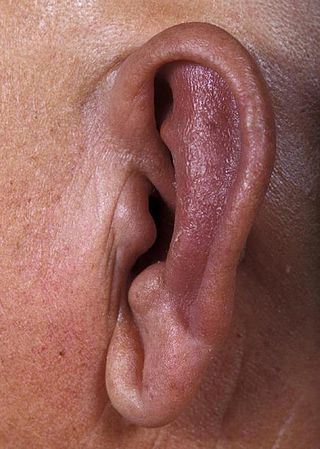
Relapsing polychondritis is a systemic disease characterized by repeated episodes of inflammation and in some cases deterioration of cartilage. The disease can be life-threatening if the respiratory tract, heart valves, or blood vessels are affected. The exact mechanism is poorly understood.

Scleritis is a serious inflammatory disease that affects the white outer coating of the eye, known as the sclera. The disease is often contracted through association with other diseases of the body, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis or rheumatoid arthritis. There are three types of scleritis: diffuse scleritis, nodular scleritis, and necrotizing scleritis. Scleritis may be the first symptom of onset of connective tissue disease.
Felty's syndrome (FS), also called Felty syndrome, is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by the triad of rheumatoid arthritis, enlargement of the spleen and low neutrophil count. The condition is more common in those aged 50–70 years, specifically more prevalent in females than males, and more so in Caucasians than those of African descent. It is a deforming disease that causes many complications for the individual.
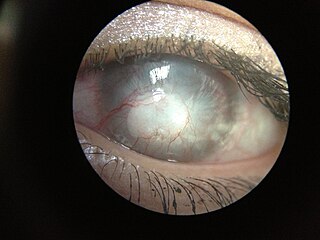
Corneal neovascularization (CNV) is the in-growth of new blood vessels from the pericorneal plexus into avascular corneal tissue as a result of oxygen deprivation. Maintaining avascularity of the corneal stroma is an important aspect of healthy corneal physiology as it is required for corneal transparency and optimal vision. A decrease in corneal transparency causes visual acuity deterioration. Corneal tissue is avascular in nature and the presence of vascularization, which can be deep or superficial, is always pathologically related.
Synovectomy is a procedure where the synovial tissue surrounding a joint is removed. This procedure is typically recommended to provide relief from a condition in which the synovial membrane or the joint lining becomes inflamed and irritated and is not controlled by medication alone. If arthritis is not controlled, it can lead to irreversible joint damage. The synovial membrane or "synovium" encloses each joint and also secretes a lubricating fluid that allows different joint motions such as rolling, folding and stretching. When the synovium becomes inflamed or irritated, it increases fluid production, resulting in warmth, tenderness, and swelling in and around the joint.

Corneal ulcer, also called keratitis, is an inflammatory or, more seriously, infective condition of the cornea involving disruption of its epithelial layer with involvement of the corneal stroma. It is a common condition in humans particularly in the tropics and in farming. In developing countries, children afflicted by vitamin A deficiency are at high risk for corneal ulcer and may become blind in both eyes persisting throughout life. In ophthalmology, a corneal ulcer usually refers to having an infection, while the term corneal abrasion refers more to a scratch injury.

A rheumatoid nodule is a lump of tissue, or an area of swelling, that appears on the exterior of the skin usually around the olecranon or the interphalangeal joints, but can appear in other areas. There are four different types of rheumatoid nodules: subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules, cardiac nodules, pulmonary nodules, and central nervous systems nodules. These nodules occur almost exclusively in association with rheumatoid arthritis. Very rarely do rheumatoid nodules occur as rheumatoid nodulosis in the absence of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid nodules can also appear in areas of the body other than the skin. Less commonly they occur in the lining of the lungs or other internal organs. The occurrence of nodules in the lungs of miners exposed to silica dust was known as Caplan’s syndrome. Rarely, the nodules occur at diverse sites on body.
Interstitial keratitis (IK) is corneal scarring due to chronic inflammation of the corneal stroma. Interstitial means space between cells i.e. corneal stroma which lies between the epithelium and the endothelium. Keratitis means corneal inflammation.

White blood cells, also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. White blood cells include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes.
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) represent a specialised cell type located inside joints in the synovium. These cells play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
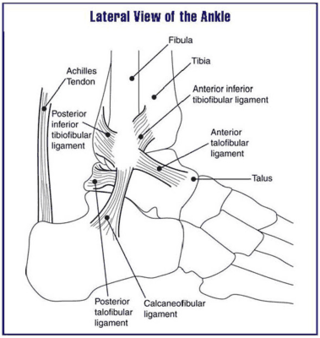
Ankle problems occur frequently, having symptoms of pain or discomfort in the ankles.

An antiarthritic is any drug used to relieve or prevent arthritic symptoms, such as joint pain or joint stiffness. Depending on the antiarthritic drug class, it is used for managing pain, reducing inflammation or acting as an immunosuppressant. These drugs are typically given orally, topically or through administration by injection. The choice of antiarthritic medication is often determined by the nature of arthritis, the severity of symptoms as well as other factors, such as the tolerability of side effects.
Peripheral Ulcerative Keratitis (PUK) is a group of destructive inflammatory diseases involving the peripheral cornea in human eyes. The symptoms of PUK include pain, redness of the eyeball, photophobia, and decreased vision accompanied by distinctive signs of crescent-shaped damage of the cornea. The causes of this disease are broad, ranging from injuries, contamination of contact lenses, to association with other systemic conditions. PUK is associated with different ocular and systemic diseases. Mooren's ulcer is a common form of PUK. The majority of PUK is mediated by local or systemic immunological processes, which can lead to inflammation and eventually tissue damage. Standard PUK diagnostic test involves reviewing the medical history and a completing physical examinations. Two major treatments are the use of medications such as corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive agents and surgical resection of the conjunctiva. The prognosis of PUK is unclear with one study providing potential complications. PUK is a rare condition with an estimated incidence of 3 per million annually.
Acquired hand deformity refers to the structural or functional abnormalities that develop in the hand. There are multiple varying causes of acquired hand deformity, triggering significant consequences and complications. Trauma, including blunt force, penetrating injuries, burns, and sports-related incidents, is a primary cause of acquired hand deformities. Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus can also contribute to hand deformities by affecting the joints. Degenerative arthritis, specifically osteoarthritis, functions to evoke impaired hand function due to the gradual deterioration of cartilage. Neurological disorders like cerebral palsy can result in hand contractures due to increased muscle tone and stiffness. There are different types of acquired hand deformities, each with distinct characteristics and underlying causes, such as boutonnière deformity, Dupuytren's contracture, gamekeeper's thumb, hand osteoarthritis deformity, mallet finger, swan-neck deformity, ulnar claw hand, among many others.
References
- ↑ Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
- ↑ Ranatunga, Sriya K M (2023-09-05). "Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology". Medscape Reference. Retrieved 2024-08-08.
- ↑ Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Macip-Rodríguez, P.M.; Cabral, A.R. (2008). "Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis pannus have similar qualitative metabolic characteristics and pro-inflammatory cytokine response" . Retrieved December 5, 2015.