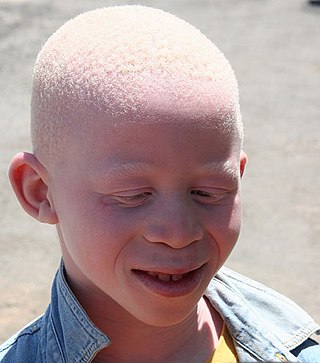
Albinism is a congenital condition characterized in humans by the partial or complete absence of pigment in the skin, hair and eyes. Albinism is associated with a number of vision defects, such as photophobia, nystagmus, and amblyopia. Lack of skin pigmentation makes for more susceptibility to sunburn and skin cancers. In rare cases such as Chédiak–Higashi syndrome, albinism may be associated with deficiencies in the transportation of melanin granules. This also affects essential granules present in immune cells, leading to increased susceptibility to infection.

Tietz syndrome, also called Tietz albinism-deafness syndrome or albinism and deafness of Tietz, is an autosomal dominant congenital disorder characterized by deafness and leucism. It is caused by a mutation in the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) gene. Tietz syndrome was first described in 1963 by Walter Tietz (1927–2003) a German Physician working in California.

X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be always expressed in males and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation, see zygosity. Females with one copy of the mutated gene are carriers.

A coloboma is a hole in one of the structures of the eye, such as the iris, retina, choroid, or optic disc. The hole is present from birth and can be caused when a gap called the choroid fissure, which is present during early stages of prenatal development, fails to close up completely before a child is born. Ocular coloboma is relatively uncommon, affecting less than one in every 10,000 births.
Microphthalmia, also referred as microphthalmos, is a developmental disorder of the eye in which one or both eyes are abnormally small and have anatomic malformations. Microphthalmia is a distinct condition from anophthalmia and nanophthalmia. Although sometimes referred to as 'simple microphthalmia', nanophthalmia is a condition in which the size of the eye is small but no anatomical alterations are present.

Mulibrey nanism is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder. It causes severe growth failure along with abnormalities of the heart, muscle, liver, brain and eye. TRIM37 is responsible for various cellular functions including developmental patterning.
WAGR syndrome is a rare genetic syndrome in which affected children are predisposed to develop Wilms' tumour, aniridia, genitourinary anomalies, and mental retardation. The "G" is sometimes instead given as "gonadoblastoma", since the genitourinary anomalies can include tumours of the gonads.

Paired box protein Pax-6, also known as aniridia type II protein (AN2) or oculorhombin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PAX6 gene.
Denys–Drash syndrome (DDS) or Drash syndrome is a rare disorder or syndrome characterized by gonadal dysgenesis, nephropathy, and Wilms' tumor.

Kaufman oculocerebrofacial syndrome, also known as blepharophimosis-ptosis-intellectual disability syndrome, is an extremely rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder characterized by severe mental retardation, brachycephaly, upslanting palpebral fissures, eye abnormalities, and highly arched palate. It was characterized in 1971; eight cases had been identified as of 1995. To date, the amount of cases is disputed, with sources claiming the number ranges from 14 to 31.

Papillorenal syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder marked by underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the kidney and colobomas of the optic nerve.

Macular hypoplasia is a rare medical condition involving the underdevelopment of the macula, a small area on the retina responsible for seeing in detail and sensing light. Macular hypoplasia is often associated with albinism.
Zonular cataract and nystagmus, also referred as nystagmus with congenital zonular cataract, is a rare congenital disease associated with Nystagmus and zonular cataract of the eye.

Wilms tumor protein (WT33) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WT1 gene on chromosome 11p.
Frasier syndrome is a urogenital anomaly associated with the WT1 gene.

Gillespie syndrome, also called aniridia, cerebellar ataxia and mental deficiency, is a rare genetic disorder. The disorder is characterized by partial aniridia, ataxia, and, in most cases, intellectual disability. It is heterogeneous, inherited in either an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive manner. Gillespie syndrome was first described by American ophthalmologist Fredrick Gillespie in 1965.

Forkhead box protein E3 (FOXE3) also known as forkhead-related transcription factor 8 (FREAC-8) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXE3 gene located on the short arm of chromosome 1.

Cataract-microcornea syndrome is a rare genetic syndrome characterized by congenital cataracts and microcornea in the absence of any other systemic anomaly or dysmorphism. Clinical findings include a reduction in corneal diameter in both meridians in an otherwise normal eye, as well as an inherited cataract, that is primarily bilateral posterior polar with opacification within the lens periphery which advances to form a total cataract after visual maturity is achieved. Other ocular manifestations, such as myopia, iris coloboma, sclerocornea, and Peters anomaly, may be observed.
Fryns-Aftimos syndrome is a rare chromosomal condition and is associated with pachygyria, severe mental retardation, epilepsy and characteristic facial features. This syndrome is a malformation syndrome, characterized by numerous facial dysmorphias not limited to hypertelorism, iris or retinal coloboma, cleft lip, and congenital heart defects. This syndrome has been seen in 30 unrelated people. Characterized by a de novo mutation located on chromosome 7p22, there is typically no family history prior to onset. The severity of the disorder can be determined by the size of the deletion on 7p22, enveloping the ACTB gene and surrounding genes, which is consistent with a contiguous gene deletion syndrome. Confirming a diagnosis of Fryns-Aftimos syndrome typically consists of serial single-gene testing or multigene panel of genes of interest or exome sequencing.
Meacham syndrome is a rare genetic disorder which is characterized by lung, diaphragmatic and genitourinary anomalies.











