| Phthisis bulbi | |
|---|---|
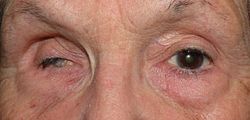 | |
| Phthisis bulbi of the right eye | |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Ophthalmology |
| Symptoms | Shrunken eye with little or no function |
| Causes | Eye surgery |
| Risk factors | Eye injury, Eye surgery, eye disease |
| Prevention | By treating the condition before the eye goes to pthisis |
| Treatment | Surgery |
| Prognosis | Usually permanent blindness in affected eye |
| Deaths | 0 |
Phthisis bulbi is a shrunken, [1] non-functional eye. It may result from severe eye disease, inflammation [2] or injury, or it may represent a complication of eye surgery. [3] Treatment options include insertion of a prosthesis, which may be preceded by enucleation of the eye. [4] [5]