| Vision disorder | |
|---|---|
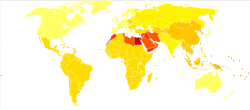 | |
| Disability-adjusted life year for vision disorders (age-related) per 100,000 inhabitants in 2002. [1] no data less than 100 100–200 200–300 300–400 400–450 450–500 500–600 600–700 700–750 750–800 800–850 more than 850 | |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology |
A vision disorder is an impairment of the sense of vision.
Contents
Vision disorder is not the same as an eye disease. Although many vision disorders do have their immediate cause in the eye, there are many other causes that may occur at other locations in the optic pathway.