The early history of Suriname dates from 3000 BCE when Native Americans first inhabited the area. The Dutch acquired Suriname from the English, and European settlement in any numbers dates from the 17th century, when it was a plantation colony utilizing slavery for sugar cultivation. With abolition in the late 19th century, planters sought labor from China, Madeira, India, and Indonesia, which was also colonized by the Dutch. Dutch is Suriname's official language. Owing to its diverse population, it has also developed a creole language, Sranan Tongo.

Paramaribo is the capital and largest city of Suriname, located on the banks of the Suriname River in the Paramaribo District. Paramaribo has a population of roughly 241,000 people, almost half of Suriname's population. The historic inner city of Paramaribo has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2002.

Commewijne is a district of Suriname, located on the right bank of the Suriname River. Commewijne's capital city is Nieuw Amsterdam. Tamanredjo is another major town, while Meerzorg is the most populated.

Nickerie is a district of Suriname, on the north-west coast. Nickerie's capital city is Nieuw-Nickerie. Another town is Wageningen. The district borders the Atlantic Ocean to the north, the Surinamese district of Coronie to the east, the Surinamese district of Sipaliwini to the south and the region of East Berbice-Corentyne in Guyana to the west.

Para is a district of northern Suriname. Para's capital city is Onverwacht, with other towns including Paranam, and Zanderij. Para has a population of 24,700 and an area of 5,393 km2. The district is the mining and forestry centre of Suriname, with many large bauxite mining operations operating. The district is a mixture of forest and savannas.

The Berbice River, located in eastern Guyana, is one of the country's major rivers. It rises in the highlands of the Rupununi region and flows northward for 595 kilometres (370 mi) through dense forests to the coastal plain. The river's tidal limit is between 160 and 320 km (99–199 mi) from the sea.

The Aluku are a Bushinengue ethnic group living mainly on the riverbank in Maripasoula in southwest French Guiana. The group are sometimes called Boni, referring to the 18th-century leader, Bokilifu Boni.

Berbice is a region along the Berbice River in Guyana, which was between 1627 and 1792 a colony of the Dutch West India Company and between 1792 and 1815 a colony of the Dutch state. After having been ceded to the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in the latter year, it was merged with Demerara-Essequibo to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. It became a county of British Guiana in 1838 till 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana.

Jodensavanne was a Jewish plantation community in Suriname, South America, and was for a time the centre of Jewish life in the colony. It was established in the 1600s by Sephardi Jews and became more developed and wealthy after a group of Jews fleeing persecution in Brazil settled there in the 1660s. It was located in what is now Para District, about 50 km (31 mi) south of the capital Paramaribo, on the Suriname River. Sugarcane plantations were established by forcing Black African people to work as slaves. At its height in around 1700, Jodensavanne was home to roughly 500 plantation owners and 9000 enslaved people. The colony faced regular attacks from Indigenous people, slave revolts, and even raids from the French navy. The community eventually relocated to the capital of Paramaribo. Clearing of grave sites and maintenance of the synagogue ruins has been attempted at various times from the 1940s to the 21st century.

Meerzorg is a town and resort (municipality) in Suriname, located on the eastern bank of the Suriname River, directly opposite the capital Paramaribo. Its population at the 2012 census was 12,405. Since 2000 it has been connected to Paramaribo by the Jules Wijdenbosch Bridge, named after the former President Jules Wijdenbosch.

Carolina is a resort in Suriname, located in the Para District. Its population at the 2012 census was 343. Most of the inhabitants are indigenous.
The (northern) East-West Link is a road in Suriname between Albina in the eastern part of the country to Nieuw Nickerie in the western part, via the capital city of Paramaribo. The southern East-West Link connects Paramaribo with Apoera via Bitagron. Construction of the road link started in the 1960s.

The Ndyuka people or Aukan people (Okanisi), are one of six Maroon peoples in the Republic of Suriname and one of the Maroon peoples in French Guiana. The Aukan or Ndyuka speak the Ndyuka language. They are subdivided into the Opu, who live upstream of the Tapanahony River in the Tapanahony resort of southeastern Suriname, and the Bilo, who live downstream of that river in Marowijne District.

Pikin Santi, sometimes spelt as Pikien Santi, is a Ndyuka village on the Cottica River in Suriname inhabited by the Pinasi and Piika lo. Pikin Santi is situated upstream from Pinatjaimi and Lantiwei, and downstream from Tamarin. It lies in the vicinity of the Buku creek and should therefore be close to the ruins Fort Buku, which as of yet have not been identified.

The Lawa Railway was a 173-kilometre-long single-track metre gauge railway in Suriname. It was built during the gold rush in the early 20th century, from the harbour town Paramaribo to Dam at the Sara Creek, but it was not extended to the gold fields at the Lawa River, as originally intended.
Bokilifu Boni was a freedom fighter and guerrilla leader in Suriname, when it was under Dutch colonial rule. Born in Cottica to an enslaved African mother who escaped from her Dutch master, he grew up with her among the Maroons in the forest. He was such a powerful leader that his followers were known as Boni's people after him. They built a fort in the lowlands and conducted raids against Dutch plantations along the coast. Under pressure from Dutch regular army and hundreds of freedmen, they went east across the river into French Guiana. Boni continued to conduct raids from there, but was ultimately killed in warfare.

The Waterkant is the oldest and one of the most important streets of Paramaribo, Suriname. The street is located in the historic centre on the Suriname River, and was the location where ships used to arrive. The street starts at the Onafhankelijkheidsplein and extends to the Central Market. As of 2002, it has been designated a Unesco World Heritage Site.
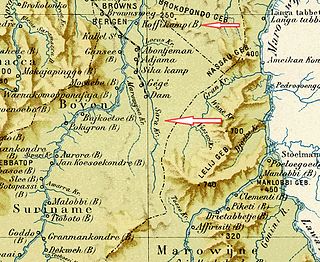
Sara Creek is a former tributary of the Suriname River located in the Para District of Suriname. After the completion of the Afobaka Dam in 1964, the Sara Creek flows into the Brokopondo Reservoir. In 1876, gold was discovered along the Sara Creek, and a railway line from Paramaribo to the river was completed in 1911.

Berlijn is a village and former wood plantation in the resort of Zuid in the Para District in Suriname. It is located on the Para Creek, and about 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) from the Johan Adolf Pengel International Airport.

Coropina Creek is a blackwater river in the Para district of Suriname. The river originates in swamp forests in southern Para, meanders through the district, and eventually merges with the Para River.