
In snakes, the paraventral scales are the longitudinal rows of dorsal scales that contact the ventral scales. These are the first rows of dorsal scales on either side of the body and are usually slightly larger than the scales located more dorsally. In species that have mostly keeled scales, the paraventrals are usually smooth or only weakly keeled. [1]

In snakes, the dorsal scales are the longitudinal series of plates that encircle the body, but do not include the ventral scales.
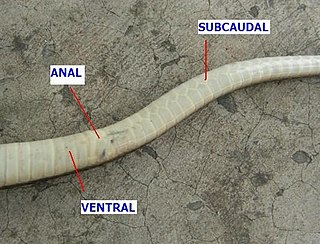
In snakes, the ventral scales or gastrosteges are the enlarged and transversely elongated scales that extend down the underside of the body from the neck to the anal scale. When counting them, the first is the anteriormost ventral scale that contacts the paraventral (lowermost) row of dorsal scales on either side. The anal scale is not counted.

Keeled scales refer to reptile scales that, rather than being smooth, have a ridge down the center that may or may not extend to the tip of the scale, making them rough to the touch. According to Street's (1979) description of European lizards and snakes, in those that have keeled scales the keels are usually stronger in male specimens and are consistently arranged according to the species of reptiles, even though many others do not have them. With European lizards, the dorsal scales are usually well keeled, while those on the flanks are more weakly keeled and those on the belly smooth.
Contents
The term paraventral may also refer to the area on either side of the ventral scales. [1]







