Related Research Articles

Gamma Volantis, Latinized from γ Volantis, is a wide binary star system in the southern constellation of Volans. Based upon parallax measurements, it is approximately 133 light years from Earth. It is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye and can be found around 9° to the east-southeast of the Large Magellanic Cloud.

HD 80606 and HD 80607 are two stars comprising a binary star system. They are approximately 217 light-years away in the constellation of Ursa Major. Both stars orbit each other at an average distance of 1,200 astronomical units. The binary system is listed as Struve 1341 in the Struve Catalogue of Double Stars; however, this designation is not in wide use and the system is usually referred to by the HD designations of its constituent stars. An extrasolar planet has been confirmed to orbit HD 80606 in a highly elliptical orbit.

Alpha Microscopii (α Microscopii) is a star in the southern constellation of Microscopium. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.89. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 8.2508 mas as seen from the Earth, it is located 395 light years from the Sun, give or take 7 light years. The star is moving nearer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of −15 km/s
PKS 0521-365 is an active galactic nucleus in the southern constellation of Columba. Because of its proximity, the source is a strong emitter from radio to gamma frequencies. The object is at a redshift of z = 0.056.
HD 86226 is a star with a pair of orbiting exoplanet companions, found in the constellation of Hydra. With an apparent visual magnitude of 7.93, it is too dim to be visible with the naked eye. The distance to this system has been determined by the parallax method, yielding a range of 149 light years. It is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of +19.6 km/s. A survey in 2015 has ruled out the existence of any stellar companions at projected distances above 12 astronomical units.
HD 101570 is a single star in the southern constellation of Centaurus. It has a yellow hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.93. The star is located at a distance of approximately 1,080 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +18 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −2.24.

Q Scorpii, also designated as HD 159433, is an astrometric binary located in the southern zodiac constellation Scorpius. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.27, making it readily visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. It lies in the tail of Scorpius, between the stars λ Scorpii and μ Scorpii and is located 7′ away from the faint globular cluster Tonantzintla 2. Based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, the system is estimated to be 158 light years distant, but is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −49 km/s.

HD 121228 is a blue supergiant star located in the constellation Centaurus. The star is noted for its close visual proximity to the planetary nebula SuWt 2.

PKS 1353−341, also known as LEDA 88936 is a quasar located in the southern constellation Centaurus. It has an apparent magnitude of 18.5, making it only visible in powerful telescopes. Based on the object's luminosity, it is estimated to be 3.7 billion light years distant from the Solar System. It is receding from the Milky Way with a heliocentric radial velocity of 59,531 km/s

AP Librae is a BL Lacertae object located at a distance of 700 million light years in the southern constellation of Libra. In the visual band it is one of the most active blazars known. AP Lib is surrounded by an extended source with a spectrum characteristic of a red-shifted giant elliptical galaxy. The derived visual magnitude of this region is 15.0, and it follows a radially decreasing brightness that is characteristic of an elliptical. Seven fainter galaxies are visible within an angular radius of 9′, suggesting it is the brightest member of a galactic cluster.
HD 46568 is a solitary star in the southern constellation Columba. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of 5.25. Parallax measurements place the object at a distance of 284 light years and is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 39 km/s.
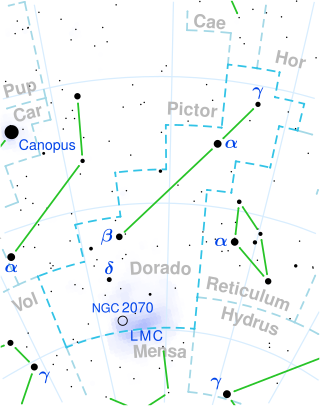
Lambda Doradus, Latinized from λ Doradus, is a solitary yellow hued star located in the southern constellation Dorado. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.13, making it faintly visible to the naked eye if viewed under ideal conditions. Parallax measurements place the star at a distance of 551 light years, and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 10 km/s.

PKS 1144-379 also known as PKS B1144-379, is a quasar located in the constellation of Centaurus. At the redshift of 1.048, the object is located nearly 8 billion light-years from Earth.

PKS 1402+044 is a quasar located in the constellation of Virgo. It has a redshift of 3.207, estimating the object to be located 11.3 billion light-years away from Earth.

PKS 1830-211 is a gravitationally-lensed blazar in the southern constellation of Sagittarius, one of the most powerful such objects known. It has a high redshift (z) of 2.507, an indicator of its significant distance. This flat-spectrum radio quasar (FSRQ) is one of the brightest extraterrestrial radio sources. In visible light, identification of this object is hampered by the galactic plane and an M-type star that lies near the line of sight.

PKS 0537-441 is a blazar located in the constellation of Pictor. It has a redshift of 0.896 and was discovered in 1973 by an American astronomer named Olin J. Eggen, who noted it as a luminous quasar. This is a BL Lacertae object in literature because of its featureless optical spectra as well as both a possible gravitational microlensing and a gravitationally lensed candidate. Its radio source is found compact and is characterized by a spectral peak in the gigahertz range, making it a gigahertz-peaked spectrum source (GPS).

PKS 2004-447 is a narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxy located in the constellation of Sagittarius. It has a redshift of (z) 0.24 and is the radio-loudest gamma ray emitting AGN known in the southern hemisphere. It was first identified as an astronomical radio source during a very-long-baseline interferometry survey in 1989. The radio spectrum appears to be powerful and compact, making it a compact steep spectrum source. The X-ray emission for this source is described by a simple power-law in the energy range.

PKS 0420-014 is a blazar located in the constellation of Eridanus. This is a high polarized quasar with a redshift of (z) 0.915, first discovered as an astronomical radio source by astronomers in 1975. The radio spectrum of this source appears to be flat, making it a flat-spectrum radio quasar (FRSQ).

PKS 0735+178 is a classical BL Lac object in the northern constellation of Gemini. This is one of the brightest objects of its type in the night sky. It has a redshift of z = 0.424, with a luminosity distance of 7,380 million light-years (2,263 Mpc). PKS 0735+178 is a nearly point-like source with an angular size of a milliarcsecond.

PKS 1622-297 is a blazar located in the constellation of Scorpius. It is one of the brightest objects of its type in the gamma ray region. It has a redshift of (z) 0.815. This blazar was first discovered as a compact astronomical radio source in 1970 by astronomers who were conducting interferometer observations and identified with an optical counterpart in 1984. In addition, the radio spectrum of the source appears flat, making it a flat-spectrum radio quasar (FRSQ).
References
- ↑ "PKSCAT90 - Parkes Southern Radio Source Catalog, Version 1.01". heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov.
- ↑ "PKSCAT90 - The Southern RadioSource Database". www.parkes.atnf.csiro.au.
- ↑ "PKS 0637-752: NASA Unveils First Images From Chandra X-Ray Observatory". harvard.edu.
- ↑ "SNR PKS1209". nasa.gov.
- ↑ Jackson, C. A.; Wall, J. V.; Shaver, P. A.; Kellermann, K. I.; Hook, I. M.; Hawkins, M. R. S. (2002). "The Parkes quarter-Jansky flat-spectrum sample: I. Sample selection and source identifications". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 386 (1): 97–113. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020119. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ↑ Liuzzo, E.; Falomo, R.; Treves, A.; Donato, D.; Sambruna, M.; Arcidiacono, C.; Giovannini, G.; Farinato, J.; Moretti, A.; Ragazzoni, R.; Diolaiti, E.; Lombini, M.; Brast, R.; Donaldson, R.; Kolb, J.; Marchetti, E.; Tordo, S. (April 1, 2011). "The jet of the BL Lacertae object PKS 2201+044: MAD near-IR adaptive optics observations and comparison with optical, radio and X-ray data". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 528: A34. arXiv: 1012.3620 . Bibcode:2011A&A...528A..34L. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201015570 – via www.aanda.org.
- ↑ Bahcall, John N.; Kirhakos, Sofia; Schneider, Donald P.; Schneider, D. P. (1995). "PKS 2349–014: A Luminous Quasar with Thin Wisps, a Large Off-Center Nebulosity, and a Close Companion Galaxy". The Astrophysical Journal. 447: L1–L4. arXiv: astro-ph/9504076 . Bibcode:1995ApJ...447L...1B. doi:10.1086/309548. S2CID 119342203.