Related Research Articles

A chromosome is a package of DNA with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation.

A spermatozoon is a motile sperm cell produced by male animals relying on internal fertilization. A spermatozoon is a moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete that joins with an ovum to form a zygote.

Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any number of complete chromosome sets is called a euploid cell.

Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division (mitosis/meiosis). There are three forms of nondisjunction: failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I, failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis II, and failure of sister chromatids to separate during mitosis. Nondisjunction results in daughter cells with abnormal chromosome numbers (aneuploidy).
Endocrine disruptors, sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds are chemicals that can interfere with endocrine systems. These disruptions can cause numerous adverse human health outcomes, including alterations in sperm quality and fertility; abnormalities in sex organs‚ endometriosis‚ early puberty‚ altered nervous system or immune function; certain cancers; respiratory problems; metabolic issues; diabetes, obesity, or cardiovascular problems; growth, neurological and learning disabilities, and more. Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors "interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis ."
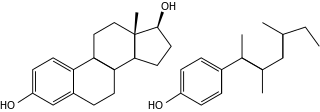
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound primarily used in the manufacturing of various plastics. It is a colourless solid which is soluble in most common organic solvents, but has very poor solubility in water. BPA is produced on an industrial scale by the condensation reaction of phenol and acetone. Global production in 2022 was estimated to be in the region of 10 million tonnes.
Xenoestrogens are a type of xenohormone that imitates estrogen. They can be either synthetic or natural chemical compounds. Synthetic xenoestrogens include some widely used industrial compounds, such as PCBs, BPA, and phthalates, which have estrogenic effects on a living organism even though they differ chemically from the estrogenic substances produced internally by the endocrine system of any organism. Natural xenoestrogens include phytoestrogens which are plant-derived xenoestrogens. Because the primary route of exposure to these compounds is by consumption of phytoestrogenic plants, they are sometimes called "dietary estrogens". Mycoestrogens, estrogenic substances from fungi, are another type of xenoestrogen that are also considered mycotoxins.

Bisphenol S (BPS) is an organic compound with the formula (HOC6H4)2SO2. It has two phenol functional groups on either side of a sulfonyl group. It is commonly used in curing fast-drying epoxy resin adhesives. It is classified as a bisphenol, and a close molecular analog of bisphenol A (BPA). BPS differentiates from BPA by possessing a sulfone group (SO2) as the central linker of the molecule instead of a dimethylmethylene group (C 2), which is the case of bisphenol A.

Reproductive toxicity refers to the potential risk from a given chemical, physical or biologic agent to adversely affect both male and female fertility as well as offspring development. Reproductive toxicants may adversely affect sexual function, ovarian failure, fertility as well as causing developmental toxicity in the offspring. Lowered effective fertility related to reproductive toxicity relates to both male and female effects alike and is reflected in decreased sperm counts, semen quality and ovarian failure.

Angelika Amon was an Austrian American molecular and cell biologist, and the Kathleen and Curtis Marble Professor in Cancer Research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Amon's research centered on how chromosomes are regulated, duplicated, and partitioned in the cell cycle. Amon was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 2017.

Diethard Tautz is a German biologist and geneticist, who is primarily concerned with the molecular basis of the evolution of mammals. Since 2006 he is director at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology in Plön.
Sex reversal is a biological process whereby the pathway directed towards the already determined-sex fate is flipped towards the opposite sex, creating a discordance between the primary sex fate and the sex phenotype expressed. The process of sex reversal occurs during embryonic development or before gonad differentiation. In GSD species, sex reversal means that the sexual phenotype is discordant with the genetic/chromosomal sex. In TSD species, sex reversal means that the temperature/conditions that usually trigger the differentiation towards one sexual phenotype are producing the opposite sexual phenotype.

Rong Li is the Director of Mechanobiology Institute, a Singapore Research Center of Excellence, at the National University of Singapore. She is a Distinguished Professor at the National University of Singapore's Department of Biological Sciences and Bloomberg Distinguished Professor of Cell Biology and Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and Whiting School of Engineering. She previously served as Director of Center for Cell Dynamics in the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine’s Institute for Basic Biomedical Sciences. She is a leader in understanding cellular asymmetry, division and evolution, and specifically, in how eukaryotic cells establish their distinct morphology and organization in order to carry out their specialized functions.
Magdalena Żernicka-Goetz is a Polish-British developmental biologist. She is Professor of Mammalian Development and Stem Cell Biology in the Department of Physiology, Development and Neuroscience and Fellow of Sidney Sussex College, Cambridge. She also serves as Bren Professor of Biology and Biological Engineering at California Institute of Technology (Caltech).

Bisphenol A controversy centers on concerns and debates about the biomedical significance of bisphenol A (BPA), which is a precursor to polymers that are used in some consumer products, including some food containers. The concerns began with the hypothesis that BPA is an endocrine disruptor, i.e. it mimics endocrine hormones and thus has the unintended and possibly far-reaching effects on people in physical contact with the chemical.

Melina Schuh is a German biochemist and Director at the Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences. She is known for her work on meiosis in mammalian oocytes, for her studies on the mechanisms leading to the age-related decline in female fertility, and for the development of the Trim-Away protein depletion method.
Ovum quality is the measure of the ability of an oocyte to achieve successful fertilisation. The quality is determined by the maturity of the oocyte and the cells that it comprises, which are susceptible to various factors which impact quality and thus reproductive success. This is of significance as an embryo's development is more heavily reliant on the oocyte in comparison to the sperm.
Elizabeth Mary Claire Fisher is a British geneticist and Professor at University College London. Her research investigates the degeneration of motor neurons during amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease triggered by Down syndrome.
Sarah K. England is a physiologist and biophysicist and the Alan A. and Edith L. Wolff Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology at Washington University School of Medicine. England conducts research on cation channels in uterine smooth muscle to understand the biological correlates of preterm birth and is the Associate Program Director of the Prematurity Research Center at Washington University as well as the Vice Chair of Research for the Center for Reproductive Health Sciences. In 2005, England was selected as a Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Health Policy Fellow in the Office of Senator Hillary Clinton where she used her scientific expertise in obstetrics and gynaecology to guide policy changes.
Nina Wedell is a professor of evolutionary biology at the University of Exeter in the United Kingdom. She was appointed as the Australian Research Council Laureate Fellow in 2019. She will investigate the evolutionary dynamics of sexual conflict and insecticide resistance genes at the University of Melbourne. Professor Wedell has pioneered the field of sexual selection, and is best known for her research on female multiple mating, polyandry. Her work has encompassed many insect systems including butterflies, moths, and flies.
References
- 1 2 Hunt, Patricia (October 2012). "Patricia Hunt". Current Biology. 22 (20): R856–R858. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.08.010 . PMID 23256202. S2CID 22388678.
- 1 2 Faculty page of the Washington State University
- ↑ Hunt, Patricia A.; Koehler, Kara E.; Susiarjo, Martha; Hodges, Craig A.; Ilagan, Arlene; Voigt, Robert C.; Thomas, Sally; Thomas, Brian F.; Hassold, Terry J. (1 April 2003). "Bisphenol A Exposure Causes Meiotic Aneuploidy in the Female Mouse". Current Biology. 13 (7): 546–553. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00189-1 . PMID 12676084. S2CID 10168552.
- ↑ Horan, Tegan S.; Pulcastro, Hannah; Lawson, Crystal; Gerona, Roy; Martin, Spencer; Gieske, Mary C.; Sartain, Caroline V.; Hunt, Patricia A. (24 September 2018). "Replacement Bisphenols Adversely Affect Mouse Gametogenesis with Consequences for Subsequent Generations". Current Biology. 28 (18): 2948–2954.e3. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2018.06.070. PMC 6156992 . PMID 30220498.