
Sadr City, formerly known as Al-Thawra and Saddam City, is a suburb district of the city of Baghdad, Iraq. It was built in 1959 by Prime Minister Abdul Karim Qassim and named Al-Rafidain District. After the US-led invasion of Iraq and the toppling of Saddam, it was unofficially renamed Sadr City after Ayatollah Muhammad al-Sadr.

The occupation of Iraq (2003–2011) began on 20 March 2003, when the United States invaded with a military coalition to overthrow Iraqi president Saddam Hussein and his Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party, and continued until 18 December 2011, when the final batch of American troops left the country. While the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia were the largest contributors to the coalition, 29 other countries, such as Japan, were involved in the Iraq War in a lesser capacity. Additionally, several private military contractors took part in enforcing the occupation.

The following is a timeline of major events during the Iraq War, following the 2003 invasion of Iraq.

Muqtada al-Sadr is an Iraqi Shia Muslim cleric, politician and militia leader. He inherited the leadership of the Sadrist Movement from his father. He founded the now dissolved Mahdi Army militia in 2003 that resisted the American occupation of Iraq. He also founded the Promised Day Brigade militia after the dissolution of the Mahdi Army; both were backed by Iran. In 2014, he founded the Peace Companies militia and is its current head. In 2018, he joined his Sadrist political party to the Saairun alliance, which won the highest number of seats in the 2018 and 2021 Iraqi parliamentary elections.

The Mahdi Army was an Iraqi Shia militia created by Muqtada al-Sadr in June 2003 and disbanded in 2008.

The Black Banner Organisation was an Iraqi guerrilla organization that battled multinational troops in Iraq. The organization's ideology was believed to be radical Sunni Islamism.

The Amal Movement is a Lebanese political party and militia affiliated mainly with the Shia community of Lebanon. It was founded by Musa al-Sadr and Hussein el-Husseini in 1974 as the "Movement of the Deprived." The party has been led by Nabih Berri since 1980.
Members of the Iraqi insurgency began taking foreign hostages in Iraq beginning in April 2004. Since then, in a dramatic instance of Islamist kidnapping they have taken captive more than 200 foreigners and thousands of Iraqis; among them, dozens of hostages were killed and others rescued or freed. In 2004, executions of captives were often filmed, and many were beheaded. However, the number of the recorded killings decreased significantly. Many hostages remain missing with no clue as to their whereabouts. The United States Department of State Hostage Working Group was organized by the U.S. Embassy, Baghdad, in the summer of 2004 to monitor foreign hostages in Iraq.
Hezbollah originated within the Shiite block of Lebanese society. According to the CIA World Factbook estimate in 2022, Shiites comprise 31.2 percent of Lebanon's population, predominating in three areas of Lebanon: Southern Lebanon, Beirut and its environs (Dahieh), and the northern Beqaa valley region.

Micah Garen is an American documentary filmmaker and journalist whose work has focused on conflict zones in the Middle East and Afghanistan. He survived a kidnapping ordeal in Iraq in 2004. He wrote a book about the kidnapping, which included his confinement as well as the efforts of friends and relatives to secure his release; according to a report in Kirkus Reviews, the book was "extraordinarily compelling" and "gripping." In addition, Garen is a prize-winning photographer. He has written for Vanity Fair, Newsweek, The New York Times and other publications. Micah Garen and Marie-Helene Carleton have directed four documentaries for Al Jazeera's Correspondent series, including Identity and Exile: an American's struggle with Zionism featuring photojournalist Matthew Cassel. The film was awarded the top Golden Nymph prize at the Monte Carlo Television Festival in 2014. Garen has made a number of short documentaries, including one describing the lives of Egyptian women during the political upheavals in 2011 one on an American airman killed in Afghanistan and one on refugees fleeing Turkey to Greece by boat. With Marie-Hélène Carleton, Garen is working on a feature documentary from Iraq entitled The Road to Nasiriyah which was selected for Film Independent's inaugural documentary lab in 2011. Garen founded ScreeningRoom in 2015, an online community for filmmakers with tools including collaborative feedback on cuts, festival submissions and film grants.

The Battle of Najaf was fought between United States and Iraqi forces on one side and the Mahdi Army led by Muqtada al-Sadr on the other in the Iraqi city of Najaf in August 2004.
Ismail Hafidh al-Lami — known as Abu Deraa is an Iraqi Shia militant whose men have been accused of retaliatory terrorizing and killing of Sunnis.

The 2004 Iraq spring fighting was a series of operational offensives and various major engagements during the Iraq War. It was a turning point in the war; the spring fighting marked the entrance into the conflict of militias and religiously based militant Iraqi groups, such as the Shi'a Mahdi Army.
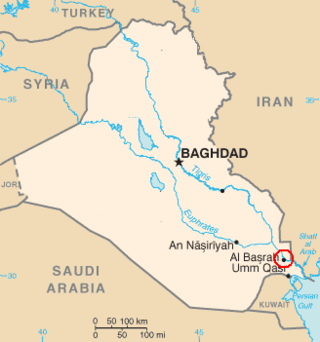
The Battle of Basra began on 25 March 2008, when the Iraqi Army launched an operation to drive the Mahdi Army militia out of the southern Iraqi city of Basra. The operation was the first major operation to be planned and carried out by the Iraqi Army since the invasion of 2003.

The siege of Sadr City was a blockade of the Shi'a district of northeastern Baghdad carried out by US and Iraqi government forces in an attempt to destroy the main power base of the insurgent Mahdi Army in Baghdad. The siege began on 4 April 2004 – later dubbed "Black Sunday" – with an uprising against the Coalition Provisional Authority following the government banning of a newspaper published by Muqtada Al-Sadr's Sadrist Movement. The most intense periods of fighting in Sadr City occurred during the first uprising in April 2004, the second in August the same year, during the sectarian conflict that gripped Baghdad in late 2006, during the Iraq War troop surge of 2007, and during the spring fighting of 2008.
Special Groups (SGs) is a designation given by the United States military to the cell-based Shi'a paramilitary organizations operating within Iraq. According to the United States these groups are funded, trained, and armed by the Iranian Quds Force, part of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC). According to the United States Department of Defense, 603 American troops in total were confirmed to have been killed by IRGC-backed Shia militias during the Iraq War.
Tyler Portis Hicks is a photojournalist who works as a staff photographer for The New York Times. Based in Kenya, he covers foreign news for the newspaper with an emphasis on conflict and war.

Muntadhar al-Zaidi is an Iraqi broadcast journalist who served as a correspondent for Iraqi-owned, Egyptian-based Al-Baghdadia TV. As of February 2011, al-Zaidi works with a Lebanese TV channel.

Qais Hadi Sayed Hasan al-Khazali is an Iraqi politician and militant leader who is the founder and Secretary-General of the Asa'ib Ahl al-Haq, an Iraqi Shi'ite paramilitary organization and political party. He is best known as the founder and leader of the Iran-backed Special Groups in Iraq from June 2006 until his capture by British forces in March 2007. As head of the Special Groups, Khazali directed arms shipment, formation of squads to participate in fighting, and insurgent operations, most notably the 20 January 2007 attack on American forces in Karbala. A former follower of Muqtada al-Sadr, he was expelled from the Mahdi Army in 2004 for giving "unauthorized orders" and founded his own group: Asa'ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH) also known as the "Khazali Network" that was later designated as a terrorist group by the U.S. Department of State. During his incarceration, Akram al-Kaabi became acting commander of the organization until his release in January 2010.

Asa'ib Ahl al-Haq, also known as the Khazali Network, is a radical Iraqi Shia Islamist political party and paramilitary organization previously active in the Iraqi insurgency and Syrian Civil War. During the Iraq War it was known as Iraq's largest "Special Group", and it is part of the Popular Mobilization Forces (PMF) in the 41st, 42nd, and 43rd Brigades, cooperating with the Iraqi government in its fight against ISIS.














