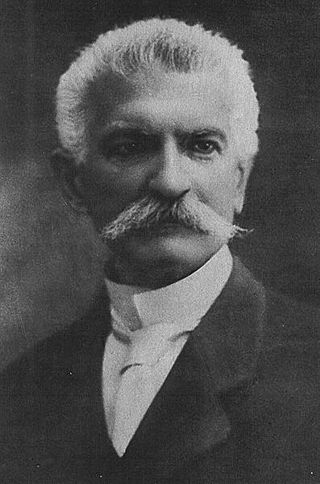Sir Robert Laird Borden was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the eighth prime minister of Canada from 1911 to 1920. He is best known for his leadership of Canada during World War I.

David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. A Liberal Party politician from Wales, he was known for leading the United Kingdom during the First World War, for social-reform policies, for his role in the Paris Peace Conference, and for negotiating the establishment of the Irish Free State. He was the last Liberal prime minister; the party fell into third-party status towards the end of his premiership.

Georges Benjamin Clemenceau was a French statesman who served as Prime Minister of France from 1906 to 1909 and again from 1917 until 1920. A physician turned journalist, he played a central role in the politics of the Third Republic, particularly amid the end of the First World War. He was a key figure of the Independent Radicals, advocating for the separation of church and state, as well as the amnesty of the Communards exiled to New Caledonia.

The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms to the United States Congress by President Woodrow Wilson. However, his main Allied colleagues were skeptical of the applicability of Wilsonian idealism.

The Paris Peace Conference was a set of formal and informal diplomatic meetings in 1919 and 1920 after the end of World War I, in which the victorious Allies set the peace terms for the defeated Central Powers. Dominated by the leaders of Britain, France, the United States and Italy, the conference resulted in five treaties that rearranged the maps of Europe and parts of Asia, Africa and the Pacific Islands, and also imposed financial penalties. Germany, Austria-Hungary, Turkey and the other losing nations were not given a voice in the deliberations; this later gave rise to political resentments that lasted for decades. The arrangements made by this conference are considered one of the great watersheds of 20th-century geopolitical history.

George Nicoll Barnes was a British Labour Party politician and a Leader of the Labour Party (1910–1911).
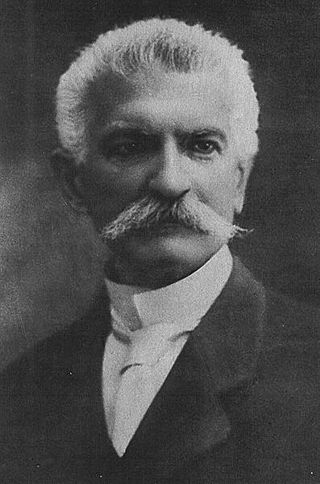
Sidney Costantino, Baron Sonnino was an Italian statesman, 19th prime minister of Italy and twice served briefly as one, in 1906 and again from 1909 to 1910. He also was the Italian minister of Foreign Affairs during the First World War, representing Italy at the 1919 Paris Peace Conference.
In diplomacy and international relations, shuttle diplomacy is the action of an outside party in serving as an intermediary between principals in a dispute, without direct principal-to-principal contact. Originally and usually, the process entails successive travel ("shuttling") by the intermediary, from the working location of one principal, to that of another.
The Supreme War Council was a central command based in Versailles that coordinated the military strategy of the principal Allies of World War I: Britain, France, Italy, the United States, and Japan. It was founded in 1917 after the Russian Revolution and with Russia's withdrawal as an ally imminent. The council served as a second source of advice for civilian leadership, a forum for preliminary discussions of potential armistice terms, later for peace treaty settlement conditions, and it was succeeded by the Conference of Ambassadors in 1920.

Margaret Olwen MacMillan, is a Canadian historian and professor at the University of Oxford. She is former provost of Trinity College, Toronto, and professor of history at the University of Toronto and previously at Ryerson University. MacMillan is an expert on the history of international relations.

Vittorio Emanuele Orlando was an Italian statesman, who served as the prime minister of Italy from October 1917 to June 1919. Orlando is best known for representing Italy in the 1919 Paris Peace Conference with his foreign minister Sidney Sonnino. He was also known as "Premier of Victory" for defeating the Central Powers along with the Entente in World War I. Italy entered into World War I in 1915 with the aim of completing national unity: for this reason, it is also considered the Fourth Italian War of Independence, in a historiographical perspective that identifies in the latter the conclusion of the unification of Italy, whose military actions began during the revolutions of 1848 with the First Italian War of Independence.

Hunin was a Palestinian Arab village in the Galilee Panhandle part of Mandatory Palestine, close to the Lebanese border. It was the second largest village in the district of Safed, but was depopulated in 1948. The inhabitants of this village were, similar to the inhabitants of Southern Lebanon, Shia Muslims.
Events from the year 1919 in France.

The Big Four or the Four Nations refer to the four top Allied powers of World War I and their leaders who met at the Paris Peace Conference in January 1919. The Big Four is also known as the Council of Four. It was composed of Georges Clemenceau of France, David Lloyd George of the United Kingdom, Vittorio Emanuele Orlando of Italy, and Woodrow Wilson of the United States.

The Heavenly Twins was the name assigned to two British delegates, the Judge Lord Sumner and the Banker Lord Cunliffe, during the 1919 Treaty of Versailles negotiations who were to set the terms of the peace to be imposed on Germany following the end of World War I. The two lords, together with the Prime Minister of Australia Billy Hughes, were responsible for presenting the British and British Dominions' case concerning the amount of compensatory payments, or war reparations, that were to be extracted from Germany.
The Racial Equality Proposal(Japanese: 人種的差別撤廃提案, lit. "Proposal to abolish racial discrimination") was an amendment to the Treaty of Versailles that was considered at the 1919 Paris Peace Conference. Proposed by Japan, it was never intended to have any universal implications, but one was attached to it anyway, which caused its controversy. Japanese Foreign Minister Uchida Kōsai stated in June 1919 that the proposal was intended not to demand the racial equality of all coloured peoples but only that of members of the League of Nations.
Events from the year 1919 in Italy.
The foreign policy under the presidency of Woodrow Wilson deals with American diplomacy, and political, economic, military, and cultural relationships with the rest of the world from 1913 to 1921. Although Wilson had no experience in foreign policy, he made all the major decisions, usually with the top advisor Edward M. House. His foreign policy was based on his messianic philosophical belief that America had the utmost obligation to spread its principles while reflecting the 'truisms' of American thought.
The Rue Nitot meeting was an important First World War event, when the British Empire delegates at the Peace Conference in Versailles got together to register the harsh terms of the Treaty of Versailles, and tried to soften the conditions for peace with Germany. The meeting was held at Prime Minister David Lloyd George's flat, 23 Rue Nitot, in Paris, on June 1, 1919.