Related Research Articles

Hywel Dda, sometimes anglicised as Howel the Good, or Hywel ap Cadell, was a king of Deheubarth who eventually came to rule most of Wales. He became the sole king of Seisyllwg in 920 and shortly thereafter established Deheubarth, and proceeded to gain control over the entire country from Prestatyn to Pembroke. As a descendant of Rhodri Mawr through his father Cadell, Hywel was a member of the Dinefwr branch of the dynasty. He was recorded as King of the Britons in the Annales Cambriæ and the Annals of Ulster.

The National Library of Wales, Aberystwyth, is the national legal deposit library of Wales and is one of the Welsh Government sponsored bodies. It is the biggest library in Wales, holding over 6.5 million books and periodicals, and the largest collections of archives, portraits, maps and photographic images in Wales. The Library is also home to the national collection of Welsh manuscripts, the National Screen and Sound Archive of Wales, and the most comprehensive collection of paintings and topographical prints in Wales. As the primary research library and archive in Wales and one of the largest research libraries in the United Kingdom, the National Library is a member of Research Libraries UK (RLUK) and the Consortium of European Research Libraries (CERL).

The White Book of Rhydderch is one of the most notable and celebrated surviving manuscripts in Welsh. Mostly written in southwest Wales in the middle of the 14th century it is the earliest collection of Welsh prose texts, though it also contains some examples of early Welsh poetry. It is now part of the collection of the National Library of Wales, having been preserved in the library at Hengwrt, near Dolgellau, Gwynedd, of the 17th century antiquary Robert Vaughan, who inherited it from the calligrapher John Jones and passed it to his descendants. The collection later passed to the newly established National Library of Wales as the Peniarth or Hengwrt-Peniarth Manuscripts.

Cyfraith Hywel, also known as Welsh law, was the system of law practised in medieval Wales before its final conquest by England. Subsequently, the Welsh law's criminal codes were superseded by the Statute of Rhuddlan in AD 1284 and its civil codes by Henry VIII's series of Laws in Wales Acts between 1535 and 1542.

Sir John Williams, 1st Baronet, was a Welsh physician, who attended Queen Victoria and was raised to the baronetcy by her in 1894. He is remembered chiefly for his contribution to the collection of the National Library of Wales. He resided for part of his life at Plas Llanstephan, Carmarthenshire, a house he acquired by lease.
Brenhinoedd y Saeson is the medieval title of three Middle Welsh annalistic chronicles known from three 14th-century manuscripts recording events from 682 to the English conquest of Wales in 1282. The title Brenhinoedd y Saeson is found only in the rubric to the earlier of the two surviving manuscripts of version S: the other two texts are commonly known as Brut y Tywysogion, but this title is found only in manuscripts of the late 16th century and cannot be considered authentic.

Brut y Brenhinedd is a collection of variant Middle Welsh versions of Geoffrey of Monmouth's Latin Historia Regum Britanniae. About 60 versions survive, with the earliest dating to the mid-13th century. Adaptations of Geoffrey's Historia were extremely popular throughout Western Europe during the Middle Ages, but the Brut proved especially influential in medieval Wales, where it was largely regarded as an accurate account of the early history of the Celtic Britons.

The White Book of Hergest was an important Welsh manuscript compiled in c. 1450. It contained many Welsh poems and prose texts and was a significant source for several antiquaries of the 17th and 18th centuries, but disappeared in the early 19th century, probably being destroyed in a fire in a London bookbinder's shop in around 1810.
Welsh units of measurement are those in use in Wales between the Sub-Roman period and the 13th-century Edwardian conquest. Modern Wales no longer employs these units even for customary purposes but instead follows the custom as elsewhere in Britain of using a mixture of metric and Imperial units.
The Black Book of Chirk is a 13th-century Welsh-language manuscript, known also as the Chirk Codex. It is Peniarth 29 of the National Library of Wales, and deals with legal and historical matters. It contains also an elegy addressed at Llywelyn ap Iorwerth; king of Wales. This poem was probably written by his grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd who lived in the 13th century.

The Peniarth Manuscripts, also known as the Hengwrt–Peniarth Manuscripts, are a collection of medieval Welsh manuscripts now held by the National Library of Wales in Aberystwyth. The collection was originally assembled by Robert Vaughan of Hengwrt, Merionethshire. During the 19th century it was held in Peniarth Mansion, Llanegryn.
Wales has produced a number of manuscripts over the centuries. Although most were written in Middle Welsh or Old Welsh, some were also written in Latin. In some of the more recent manuscripts it is not uncommon to have texts in Welsh, Latin, French and English in the same volume. However, some of the most important medieval manuscripts were written in Latin only, e.g. the Cyfraith Hywel.

NLW MS 20143A is a Welsh-language manuscript of the laws of Hywel Dda dating from the middle of the 14th century. It is one of the few surviving Welsh manuscripts of the period to have a medieval binding, and has been digitised by the National Library of Wales, which acquired the manuscript in 1969.
Peniarth Manuscript 259B, known as Pomffred since it had previously been owned by the constable of Pontefract Castle, is a version of the Laws of Hywel Dda. Aneurin Owen assigned this manuscript the siglum Z in his Ancient laws and institutes of Wales. It is one of the Peniarth Manuscripts in the National Library of Wales. It was transcribed in the mid-sixteenth century by two hands: Richard Longford and his amanuensis, from an earlier exemplar owned by Einion ab Addain, who was serving a prison sentence in Pontefract at the time that it was copied.
Peniarth Manuscript 32 is a fifteenth-century volume of the laws of Hywel Dda that contains a brief chronicle from Gwrtheyrn Gwrtheneu to King John, Paul's Vision, the Tree of the Cross, Brutus Saxonum, and various englynion. It is beautifully written on vellum in the hand of the scribe responsible for the Mabinogion in the Red Book of Hergest, and is bound in white vellum.
Daniel Huws is the world's leading authority of the last hundred years on Welsh manuscripts, with contributions that are held to represent a significant advance on those of John Gwenogvryn Evans.
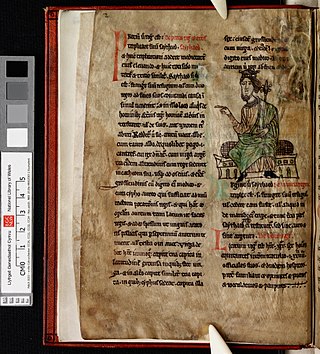
Peniarth 28 is the earliest of the surviving copy of the Laws of Hywel Dda. The manuscript, which is written in Latin, dates from the second half of the thirteenth century. It is part of the Peniarth Manuscript Collection that was the foundation collection of the National Library of Wales.
Thomas Wiliems was a Welsh-language antiquarian.
References
- ↑ "Peniarth 164". Cyfraith Hywel. Retrieved 27 November 2015.