
Oryza sativa, commonly known as Asian rice, is the plant species most commonly referred to in English as rice. Oryza sativa is a grass with a genome consisting of 430Mb across 12 chromosomes. It is renowned for being easy to genetically modify, and is a model organism for cereal biology.
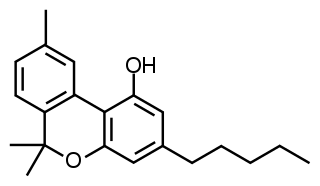
Cannabinol (CBN) is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid found only in trace amounts in Cannabis, and is mostly found in aged Cannabis. Pharmacologically relevant quantities are formed as a metabolite of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). CBN acts as a partial agonist at the CB1 receptors, but has a higher affinity to CB2 receptors; however, it has lower affinities relative to THC. Degraded or oxidized cannabis products, such as low-quality baled cannabis and traditionally produced hashish, are high in CBN.

Tetrahydrocannabivarin is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) having a propyl (3-carbon) side chain instead of a pentyl (5-carbon) group on the molecule, which makes it produce very different effects from THC.

Cannabis indica, formally known as Cannabis sativa forma indica, is an annual plant in the Cannabaceae family originating from the Indian subcontinent. It is a putative species of the genus Cannabis. Whether it and Cannabis sativa are truly separate species is a matter of debate. Many uses come from Cannabis indica, such as extraction, cultivation, cloth from the fibers, psychoactivity, medical uses, and a plant. Cannabis indica produces large amounts of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The large amounts of THC makes it most commonly used as a drug, whether it be for recreational or medical purposes.

Cannabis ruderalis is a low-THC species of Cannabis which is native to Central and Eastern Europe and Russia. Many scholars accept Cannabis ruderalis as its own species due to its unique traits and phenotypes which distinguish it from Cannabis indica and Cannabis sativa; however, it is widely debated as to whether or not ruderalis is a sub-species of Cannabis sativa.

Cannabis tea is a cannabis-infused drink prepared by steeping various parts of the cannabis plant in hot or cold water. Cannabis tea is commonly recognized as an alternative form of preparation and consumption of the cannabis plant, more popularly known as marijuana, pot, or weed. This plant has long been recognized as an herbal medicine employed by health professionals worldwide to ease symptoms of disease, as well as a psychoactive drug used recreationally and in spiritual traditions. Though less commonly practiced than popular methods like smoking or consuming edibles, drinking cannabis tea can produce comparable physical and mental therapeutic effects. Such effects are largely attributed to the THC content of the tea, levels of which are drastically dependent on individual preparation techniques involving volume, amount of cannabis, and boiling time. Also in common with these administration forms of cannabis is the heating component performed before usage. Due to the rather uncommon nature of this particular practice of cannabis consumption in modern times, the research available on the composition of cannabis tea is limited and based broadly around what is known of cannabis as it exists botanically.

Caryophyllene, or (−)-β-caryophyllene, is a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene that is a constituent of many essential oils, especially clove oil, the oil from the stems and flowers of Syzygium aromaticum (cloves), the essential oil of Cannabis sativa, rosemary, and hops. It is usually found as a mixture with isocaryophyllene and α-humulene, a ring-opened isomer. Caryophyllene is notable for having a cyclobutane ring, as well as a trans-double bond in a 9-membered ring, both rarities in nature.
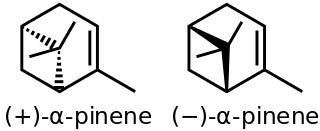
α-Pinene is an organic compound of the terpene class, one of two isomers of pinene. It is an alkene and it contains a reactive four-membered ring. It is found in the oils of many species of many coniferous trees, notably the pine. It is also found in the essential oil of rosemary and Saturejamyrtifolia Both enantiomers are known in nature; (1S,5S)- or (−)-α-pinene is more common in European pines, whereas the (1R,5R)- or (+)-α-isomer is more common in North America. The racemic mixture is present in some oils such as eucalyptus oil and orange peel oil.

Partitiviridae is a family of viruses. Fungi and plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 60 species in this family, divided among 5 genera or unassigned to a genus. The family name comes from the Latin partitius which means divided and they are called this as they have segmented genomes.

Pseudomonas cannabina is a gray, Gram-negative, fluorescent, motile, flagellated, aerobic bacterium that causes leaf and stem rot of hemp, from which it derives its name. It was formerly classified as a pathovar of Pseudomonas syringae, but following ribotypical analysis, it was reinstated as a species. The type strain is CFBP 2341.

Cannabigerol (CBG) is one of more than 120 identified cannabinoid compounds found in the plant genus Cannabis. Cannabigerol is the non-acidic form of cannabigerolic acid, the parent molecule from which other cannabinoids are synthesized. Cannabigerol is a minor constituent of cannabis. During growth, most of the cannabigerol is converted into other cannabinoids, primarily tetrahydrocannabinol or cannabidiol, usually leaving somewhere below 1% cannabigerol in the plant.

Cannabis strains are either pure or hybrid varieties of the plant genus Cannabis, which encompasses the species C. sativa, C. indica, and C. ruderalis.

Olivetol, also known as 5-pentylresorcinol or 5-pentyl-1,3-benzenediol, is an organic compound found in certain species of lichen; it is also a precursor in various syntheses of tetrahydrocannabinol.

Cannabaceae is a small family of flowering plants. As now circumscribed, the family includes about 170 species grouped in about 11 genera, including Cannabis, Humulus (hops) and Celtis (hackberries). Celtis is by far the largest genus, containing about 100 species.

Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the formation of THCA from cannabigerolic acid (CBGA). THCA is the direct precursor of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the principal psychoactive component of cannabis, which is produced from various strains of Cannabis sativa. Therefore, THCA synthase is considered to be a key enzyme controlling cannabis psychoactivity. Polymorphisms of THCA synthase result in varying levels of THC in Cannabis plants, resulting in "drug-type" and "fiber-type" C. sativa varieties.
Cannabidiolic acid synthase is an enzyme with systematic name cannabigerolate:oxygen oxidoreductase . It is an oxidoreductase found in Cannabis sativa that catalyses the formation of cannabidiolate, a carboxylated precursor of cannabidiol.
Penicillium flavescens is a species of the genus of Penicillium.
Hemp protein is the protein content of hemp seeds. The protein in hemp seeds is made up of the two globulin types of proteins, edestin (60–80%) and albumin, with edestin also being rich in the essential amino acids. Hemp protein has a PDCAAS score of 0.61 and a biological value of 87. The total proportion of essential amino acids in hemp protein isolate, is also significantly higher than that of soy protein isolate.














