
Blue cheese is a general classification of cheeses that have had cultures of the mold Penicillium added so that the final product is spotted or veined throughout with blue mold that carries a distinct smell, either from that or various specially cultivated bacteria. Some blue cheeses are injected with spores before the curds form, and others have spores mixed in with the curds after they form. Blue cheeses are typically aged in a temperature-controlled environment such as a cave. Blue cheese can be eaten by itself or can be spread, crumbled or melted into or over foods.

Penicillium roqueforti is a common saprotrophic fungus in the genus Penicillium. Widespread in nature, it can be isolated from soil, decaying organic matter, and plants.
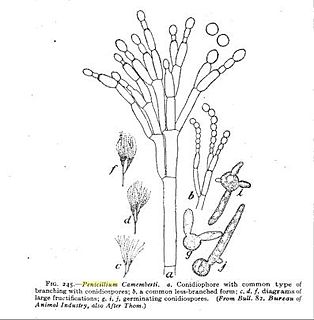
Penicillium camemberti is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is used in the production of Camembert, Brie, Langres, Coulommiers, and Cambozola cheeses, on which colonies of P. camemberti form a hard, white crust. It is responsible for giving these cheeses their distinctive flavors. An allergy to the antibiotic penicillin does not necessarily imply an allergy to cheeses made using P. camemberti.
Chrysovirus is a genus of viruses. It is the only genus in the family Chrysoviridae. They are class III double stranded RNA viruses which infect fungi, in particular Penicillium. Their name is derived from the Greek word chrysos which means yellow-green. There are currently nine species in this genus including the type species Penicillium chrysogenum virus.
Penicillium griseofulvum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces patulin, penifulvin A, cyclopiazonic acid, roquefortine C, shikimic acid and griseofulvin. Penicillium griseofulvum occurs on cereals and nuts.

Penicillium chrysogenum or P. notatum (formerly) is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It was previously known as Penicillium notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.
Penicillium echinulatum is a mold species in the genus Penicillium. It is a source of cellulase.

Charles Thom was an American microbiologist and mycologist. Born and raised in Illinois, he received his PhD from the University of Missouri, the first such degree awarded by that institution. He was best known for his work on the microbiology of dairy products and soil fungi, and in particular his research into the genera Aspergillus and Penicillium. His work influenced the establishment of standards for food handling and processing in the USA. He pioneered the use of culture media to grow microorganisms, and, with food chemist James N. Currie, developed a process to mass-produce citric acid using Aspergillus. Thom played an important role in the development of penicillin in World War II.
Penicillium allii is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium. Penicillium allii is a pathogen of garlic.
Medicinal fungi are those fungi which produce medically significant metabolites or can be induced to produce such metabolites using biotechnology. The range of medically active compounds that have been identified include antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, cholesterol inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, immunosuppressants and even fungicides. Although initial discoveries centred on simple moulds of the type that cause spoilage of food, later work identified useful compounds across a wide range of fungi.
Penicillium cecidicola is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces pentacecilide A, pentacecilide B, pentacecilide C.
Penicillium citrinum is an anamorph, mesophilic fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces tanzawaic acid A-D, ACC, Mevastatin, Quinocitrinine A, Quinocitrinine B, and nephrotoxic citrinin. Penicillium citrinum is often found on moldy citrus fruits and occasionally it occurs in tropical spices and cereals. This Penicillium species also causes mortality for the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus. Because of its mesophilic character, Penicillium citrinum occurs worldwide. The first statin (Mevastatin) was 1970 isolated from this species.
Penicillium corylophilum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which occurs in damp buildings in United States, Canada and western Europe but it can also be found in a variety of foods and mosquitoes. Penicillium corylophilum produces the alkaloid epoxyagroclavine and citrinin and is a pathogen to mosquitoes.
Penicillium decaturense is a species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from a fungus in North America. Penicillium decaturense produces citrinin, 15-Deoxyoxalicine B, decaturins A and decaturins A
Penicillium euglaucum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from soil in Argentina.
Penicillium islandicum is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which produces luteoskyrin, simatoxin, cyclochlorotine, rugulosin, islanditoxin and chitosanase.
Penicillium janczewskii is an anamorph and filamentous species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from the rhizosphere of Vernonia herbacea. Penicillium janczewskii produces griseofulvin
Penicillium commune is an indoor fungus belonging to the genus of Penicillium. It is known as one of the most common fungi spoilage moulds on cheese. It also grows on and spoils other foods such as meat products and fat-containing products like nuts and margarine. Cyclopiazonic acid and regulovasine A and B are the most important mycotoxins produced by P. commune. The fungus is the only known species to be able to produce both penitrem A and roquefortine. Although this species does not produce penicillin, it has shown to have anti-pathogenic activity. There are no known plant, animal or human diseases caused by P. commune.







