This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2023) |
Penile pain refers to pain in the penis of human or otherwise.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2023) |
Penile pain refers to pain in the penis of human or otherwise.
Priapus, a minor Greek god of fertility, [1] is marked by his oversized, permanent erection, which gave rise to the medical term priapism.
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also called impotence, is the type of sexual dysfunction in which the penis fails to become or stay erect during sexual activity. It is the most common sexual problem in men. Through its connection to self-image and to problems in sexual relationships, erectile dysfunction can cause psychological harm.

Priapism is a condition in which a penis remains erect for hours in the absence of stimulation or after stimulation has ended. There are three types: ischemic (low-flow), nonischemic (high-flow), and recurrent ischemic (intermittent). Most cases are ischemic. Ischemic priapism is generally painful while nonischemic priapism is not. In ischemic priapism, most of the penis is hard; however, the glans penis is not. In nonischemic priapism, the entire penis is only somewhat hard. Very rarely, clitoral priapism occurs in women.
Andrology is a name for the medical specialty that deals with male health, particularly relating to the problems of the male reproductive system and urological problems that are unique to men. It is the counterpart to gynaecology, which deals with medical issues which are specific to female health, especially reproductive and urologic health.
Persistent genital arousal disorder (PGAD), previously called persistent sexual arousal syndrome, is spontaneous, persistent, unwanted and uncontrollable genital arousal in the absence of sexual stimulation or sexual desire, and is typically not relieved by orgasm. Instead, multiple orgasms over hours or days may be required for relief.
Sexual dysfunction is difficulty experienced by an individual or partners during any stage of normal sexual activity, including physical pleasure, desire, preference, arousal, or orgasm. The World Health Organization defines sexual dysfunction as a "person's inability to participate in a sexual relationship as they would wish". This definition is broad and is subject to many interpretations. A diagnosis of sexual dysfunction under the DSM-5 requires a person to feel extreme distress and interpersonal strain for a minimum of six months. Sexual dysfunction can have a profound impact on an individual's perceived quality of sexual life. The term sexual disorder may not only refer to physical sexual dysfunction, but to paraphilias as well; this is sometimes termed disorder of sexual preference.

Penile fracture is rupture of one or both of the tunica albuginea, the fibrous coverings that envelop the penis's corpora cavernosa. It is caused by rapid blunt force to an erect penis, usually during vaginal intercourse, or aggressive masturbation. It sometimes also involves partial or complete rupture of the urethra or injury to the dorsal nerves, veins and arteries.
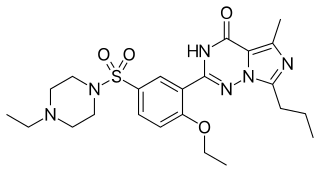
Vardenafil, sold under the brand name Levitra among others, is a medication that is used for treating erectile dysfunction. It is a PDE5 inhibitor. It is taken by mouth.
Tumescence is the quality or state of being tumescent or swollen. Tumescence usually refers to the normal engorgement with blood of the erectile tissues, marking sexual excitation, and possible readiness for sexual activity. The tumescent sexual organ in males is the penis and in females is the clitoris and other parts of the genitalia like the vestibular bulbs. Arteries in the penis dilate to increase blood volume.
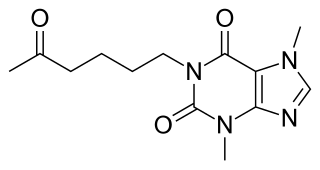
Pentoxifylline, also known as oxpentifylline, is a xanthine derivative used as a drug to treat muscle pain in people with peripheral artery disease. It is generic and sold under many brand names worldwide.

Phoneutria nigriventer is a species of medically significant spider in the family Ctenidae, found in the Southern Cone of South America. Along with other members of the genus, they are often referred to as Brazilian wandering spiders.

Prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), also known as alprostadil, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin which is used as a medication. In infants with congenital heart defects, it is delivered by slow injection into a vein to open the ductus arteriosus until surgery can be carried out. By injection into the penis or placement in the urethra, it is used to treat erectile dysfunction.
Nocturnal penile tumescence is a spontaneous erection of the penis during sleep or when waking up. Along with nocturnal clitoral tumescence, it is also known as sleep-related erection. Men without physiological erectile dysfunction or severe depression experience nocturnal penile tumescence, usually three to five times during a period of sleep, typically during rapid eye movement sleep. Nocturnal penile tumescence is believed to contribute to penile health.

An erection is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is often associated with sexual arousal or sexual attraction, although erections can also be spontaneous. The shape, angle, and direction of an erection vary considerably between humans.
An intracavernousinjection is an injection into the base of the penis. This injection site is often used to administer medications to check for or treat erectile dysfunction in adult men. The more common medications administered in this manner include Caverject, Trimix, Bimix, and Quadmix. These medications are all types of vasodilators and cause tumescence within 10-15 minutes. Common side effects include priapism, bruising, fibrosis, Peyronie's disease, and pain.

Clitoral erection is a physiological phenomenon where the clitoris becomes enlarged and firm.
A penile injury is a medical emergency that afflicts the penis. Common injuries include fracture, avulsion injury, strangulation, entrapment, and amputation.
Penile ulltrasonography is medical ultrasonography of the penis. Ultrasound is an excellent method for the study of the penis, such as indicated in trauma, priapism, erectile dysfunction or suspected Peyronie's disease.
A penis extender is an external medical device with tentative evidence as of 2019 for Peyronie's disease. It acts as a mechanical, traction device that stretches the human penis in the flaccid state to make it longer.
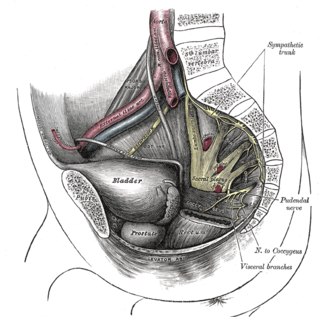
Hard flaccid syndrome (HFS), also known as hard flaccid (HF), is a chronic painful condition characterized by a semi-rigid penis at the flaccid state, a soft glans at the erect state, pelvic pain, low libido, erectile dysfunction, erectile pain, pain on ejaculation, penile sensory changes (numbness or coldness), lower urinary tract symptoms, contraction of the pelvic floor muscles, and psychological distress. Other complaints include rectal and perineal discomfort, cold hands and feet, and a hollow or detached feeling inside the penile shaft. The majority of HFS patients are in their 20s–30s and symptoms significantly affect one's quality of life.