Imaging studies
Ultrasound examination is able to depict the tunica albuginea tear in the majority of cases (as a hypoechoic discontinuity in the normally echogenic tunica). In a study on 25 patients, Zare Mehrjardi et al. concluded that ultrasound is unable to find the tear just when it is located at the penile base. In their study magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) accurately diagnosed all of the tears (as a discontinuity in the normally low signal tunica on both T1- and T2-weighted sequences). They concluded that ultrasound should be considered as the initial imaging method, and MRI can be helpful in cases that ultrasound does not depict any tear but clinical suspicions for fracture are still high. In the same study, authors investigated accuracy of ultrasound and MRI for determining the tear location (mapping of fracture) in order to perform a tailored surgical repair. MRI was more accurate than ultrasound for this purpose, but ultrasound mapping was well correlated with surgical results in cases where the tear was clearly visualized on ultrasound exam. [10] The advantage of ultrasound in the diagnosis of penile fracture is unrivaled when its noninvasive, cost-effective, and nonionising nature are considered. [11]
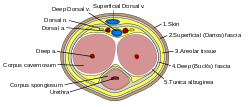
Penile trauma can result from a blunt or penetrating injury, the latter being rarely investigated by imaging methods, almost always requiring immediate surgical exploration. In the erect penis, trauma results from stretching and narrowing of the tunica albuginea, which can undergo segmental rupture of one or both of the corpora cavernosa, constituting a penile fracture. [2]
In the ultrasound examination, a lesion of the tunica albuginea presents as an interruption in (loss of continuity of) the echoic line representing it (Figure 4). Small, moderate, or broad hematomas demonstrate the extent of that discontinuity. Intracavernous hematomas, sometimes without the presence of a tunica albuginea fracture, can be observed when there is a lesion of the smooth muscle of the trabeculae surrounding the sinusoid spaces or the subtunical venular plexus. [2]
Figure 4 A: Ultrasound of the penis, right lateral view. Longitudinal section showing rupture of the tunica albuginea with an adjacent 1.92
cm hematoma (between calipers), due to trauma.
[2] B: Axial T2-weighted turbo spin-echo magnetic resonance imaging scan showing left-sided discontinuity of the tunica albuginea (arrow), secondary to fracture.
[2]
In 10–15% of penile traumas, there can be an accompanying urethral lesion. When blood is observed in the urethral meatus, contrast-enhanced evaluation of the urethra is necessary. In cases in which the ultrasound findings are inconclusive, the use of magnetic resonance imaging can facilitate the diagnosis and is recommended by various authors. [2]