Related Research Articles

A spermatozoon is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote.

Intracytoplasmic sperm injection is an in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in which a single sperm cell is injected directly into the cytoplasm of an egg. This technique is used in order to prepare the gametes for the obtention of embryos that may be transferred to a maternal uterus. With this method, the acrosome reaction is skipped.
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species. It is the normal state of a human child or other young offspring, because they have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of reproductive capacity.
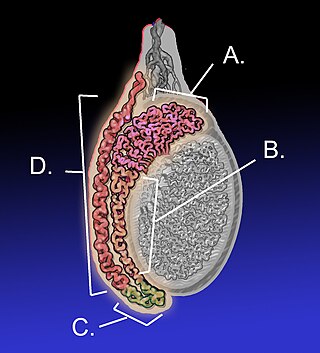
The epididymis is an elongated tubular structure attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, 6 to 7 centimetres in length. It connects the testicle to the vas deferens in the male reproductive system. The epididymis serves as an interconnection between the multiple efferent ducts at the rear of a testicle (proximally), and the vas deferens (distally). Its primary function is the storage, maturation and transport of sperm cells.

Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubules. These cells are called spermatogonial stem cells. The mitotic division of these produces two types of cells. Type A cells replenish the stem cells, and type B cells differentiate into primary spermatocytes. The primary spermatocyte divides meiotically into two secondary spermatocytes; each secondary spermatocyte divides into two equal haploid spermatids by Meiosis II. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm) by the process of spermiogenesis. These develop into mature spermatozoa, also known as sperm cells. Thus, the primary spermatocyte gives rise to two cells, the secondary spermatocytes, and the two secondary spermatocytes by their subdivision produce four spermatozoa and four haploid cells.

Seminiferous tubules are located within the testes, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa.
DNA fragmentation is the separation or breaking of DNA strands into pieces. It can be done intentionally by laboratory personnel or by cells, or can occur spontaneously. Spontaneous or accidental DNA fragmentation is fragmentation that gradually accumulates in a cell. It can be measured by e.g. the Comet assay or by the TUNEL assay.

Azoospermia is the medical condition of a man whose semen contains no sperm. It is associated with male infertility, but many forms are amenable to medical treatment. In humans, azoospermia affects about 1% of the male population and may be seen in up to 20% of male infertility situations in Canada.
Terms oligospermia, oligozoospermia, and low sperm count refer to semen with a low concentration of sperm and is a common finding in male infertility. Often semen with a decreased sperm concentration may also show significant abnormalities in sperm morphology and motility. There has been interest in replacing the descriptive terms used in semen analysis with more quantitative information.
Hypospermia is a condition in which a man has an unusually low ejaculate volume, less than 1.5 mL. It is the opposite of hyperspermia, which is a semen volume of more than 5.5 mL. It should not be confused with oligospermia, which means low sperm count. Normal ejaculate when a man is not drained from prior sex and is suitably aroused is around 1.5–6 mL, although this varies greatly with mood, physical condition, and sexual activity. Of this, around 1% by volume is sperm cells. The U.S.-based National Institutes of Health defines hypospermia as a semen volume lower than 2 mL on at least two semen analyses.
Male infertility refers to a sexually mature male's inability to impregnate a fertile female. In humans it accounts for 40–50% of infertility. It affects approximately 7% of all men. Male infertility is commonly due to deficiencies in the semen, and semen quality is used as a surrogate measure of male fecundity. More recently, advance sperm analyses that examine intracellular sperm components are being developed.

A semen analysis, also called seminogram or spermiogram, evaluates certain characteristics of a male's semen and the sperm contained therein. It is done to help evaluate male fertility, whether for those seeking pregnancy or verifying the success of vasectomy. Depending on the measurement method, just a few characteristics may be evaluated or many characteristics may be evaluated. Collection techniques and precise measurement method may influence results.
Semen quality is a measure of male fertility, a measure of the ability of sperm in semen to accomplish fertilization. Semen quality involves both sperm quantity and quality. Semen quality is a major factor for fertility.

Sperm motility describes the ability of sperm to move properly through the female reproductive tract or through water to reach the egg. Sperm motility can also be thought of as the quality, which is a factor in successful conception; sperm that do not "swim" properly will not reach the egg in order to fertilize it. Sperm motility in mammals also facilitates the passage of the sperm through the cumulus oophorus and the zona pellucida, which surround the mammalian oocyte.

CatSper1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CATSPER1 gene. CatSper1 is a member of the cation channels of sperm family of protein. The four proteins in this family together form a Ca2+-permeant ion channel specific essential for the correct function of sperm cells.
Semen cryopreservation is a procedure to preserve sperm cells. Semen can be used successfully indefinitely after cryopreservation. It can be used for sperm donation where the recipient wants the treatment in a different time or place, or as a means of preserving fertility for men undergoing vasectomy or treatments that may compromise their fertility, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy or surgery. It is also often used by trans women prior to medically transitioning in ways that affect fertility, such as feminizing hormone therapy and orchiectomies.
An aneugen is a substance that causes a daughter cell to have an abnormal number of chromosomes or aneuploidy. A substance's aneugenicity reflects its ability to induce aneuploidy. Unlike clastogens, aneugenic events do not damage the physical structure of the chromosome, but represent a deletion or insertion of an additional copy of a whole chromosome. Aneugens and clastogens can be differentiated via certain stains, using the technique of Fluorescence in situ hybridization.
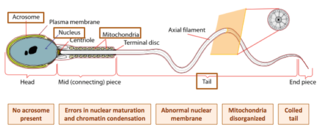
Globozoospermia is a rare and severe form of monomorphic teratozoospermia. This means that the spermatozoa show the same abnormality, and over 85% of spermatozoa in sperm have this abnormality. Globozoospermia is responsible for less than 0.1% of male infertility. It is characterised by round-headed spermatozoa without acrosomes, an abnormal nuclear membrane and midpiece defects. Affected males therefore suffer from either reduced fertility or infertility. Studies suggest that globozoospermia can be either total or partial, however it is unclear whether these two forms are variations on the same syndrome, or actually different syndromes.
The intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection (IMSI) is a laboratory technique used for In vitro fertilisation treatments. High-quality sperms are injected into the egg for fertilization, it is an advanced version of ICSI.

Sperm Chromatin Structure Assay (SCSA) is a diagnostic approach that detects sperm abnormality with a large extent of DNA fragmentation. First described by Evenson in 1980, the assay is a flow cytometric test that detects the vulnerability of sperm DNA to acid-induced denaturation DNA in situ. SCSA measures sperm DNA fragmentation attributed to intrinsic and extrinsic factors and reports the degree of fragmentation in terms of DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI). The use of SCSA expands from evaluation of male infertility and subfertility, toxicology studies and evaluation of quality of laboratory semen samples. Notably, SCSA outcompetes other convention sperm DNA fragmentation (sDF) assays such as TUNEL and COMET in terms of efficiency, objectivity, and repeatability.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Ortega, C.; Verheyen, G.; Raick, D.; Camus, M.; Devroey, P.; Tournaye, H. (2011). "Absolute asthenozoospermia and ICSI: What are the options?". Human Reproduction Update. 17 (5): 684–692. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmr018 . PMID 21816768.
- ↑ Belloc S, Benkhalifa M, Cohen-Bacrie M, Dalleac A, Chahine H, Amar E, Zini A (2014). "Which isolated sperm abnormality is most related to sperm DNA damage in men presenting for infertility evaluation". J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 31 (5): 527–32. doi:10.1007/s10815-014-0194-3. PMC 4016368 . PMID 24566945.
- ↑ Wright C, Milne S, Leeson H (2014). "Sperm DNA damage caused by oxidative stress: modifiable clinical, lifestyle and nutritional factors in male infertility". Reprod. Biomed. Online. 28 (6): 684–703. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.02.004 . PMID 24745838.
- ↑ Eslamian, Ghazaleh; Amirjannati, Naser; Noori, Nazanin; Sadeghi, Mohammad-Reza; Hekmatdoost, Azita (2020). "Effects of coadministration of DHA and vitamin E on spermatogram, seminal oxidative stress, and sperm phospholipids in asthenozoospermic men: a randomized controlled trial". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Elsevier BV. 112 (3): 707–719. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa124 . ISSN 0002-9165.
- 1 2 Martínez-Soto, Juan Carlos; Domingo, Joan Carles; Cordobilla, Begoña; Nicolás, María; Fernández, Laura; Albero, Pilar; Gadea, Joaquín; Landeras, José (October 28, 2016). "Dietary supplementation with docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) improves seminal antioxidant status and decreases sperm DNA fragmentation". Systems Biology in Reproductive Medicine. Informa UK Limited. 62 (6): 387–395. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2016.1246623 . ISSN 1939-6368.