Related Research Articles

In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro. The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova from her ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.

Intracytoplasmic sperm injection is an in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in which a single sperm cell is injected directly into the cytoplasm of an egg. This technique is used in order to prepare the gametes for the obtention of embryos that may be transferred to a maternal uterus. With this method, the acrosome reaction is skipped.
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species. It is the normal state of a human child or other young offspring, because they have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of reproductive capacity.
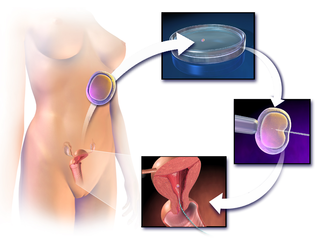
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) includes medical procedures used primarily to address infertility. This subject involves procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), cryopreservation of gametes or embryos, and/or the use of fertility medication. When used to address infertility, ART may also be referred to as fertility treatment. ART mainly belongs to the field of reproductive endocrinology and infertility. Some forms of ART may be used with regard to fertile couples for genetic purpose. ART may also be used in surrogacy arrangements, although not all surrogacy arrangements involve ART. The existence of sterility will not always require ART to be the first option to consider, as there are occasions when its cause is a mild disorder that can be solved with more conventional treatments or with behaviors based on promoting health and reproductive habits.
Zygote intra fallopian transfer (ZIFT) is an infertility treatment used when a blockage in the fallopian tubes prevents the normal binding of sperm to the egg. Egg cells are removed from a woman's ovaries, and in vitro fertilised. The resulting zygote is placed into the fallopian tube by the use of laparoscopy. The procedure is a spin-off of the gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) procedure. The pregnancy and implantation rates in ZIFT cycles are 52.3 and 23.2% which were higher than what was observed in IVF cycles which were 17.5 and 9.7%.
Terms oligospermia, oligozoospermia, and low sperm count refer to semen with a low concentration of sperm and is a common finding in male infertility. Often semen with a decreased sperm concentration may also show significant abnormalities in sperm morphology and motility. There has been interest in replacing the descriptive terms used in semen analysis with more quantitative information.

A hydrosalpinx is a condition that occurs when a Fallopian tube is blocked and fills with serous or clear fluid near the ovary. The blocked tube may become substantially distended giving the tube a characteristic sausage-like or retort-like shape. The condition is often bilateral and the affected tubes may reach several centimeters in diameter. The blocked tubes cause infertility. A Fallopian tube filled with blood is a hematosalpinx, and with pus a pyosalpinx.

Fertility clinics are medical clinics that assist couples, and sometimes individuals, who want to become parents but for medical reasons have been unable to achieve this goal via the natural course. Clinics apply a number of diagnosis tests and sometimes very advanced medical treatments to achieve conceptions and pregnancies.

A semen analysis, also called seminogram or spermiogram, evaluates certain characteristics of a male's semen and the sperm contained therein. It is done to help evaluate male fertility, whether for those seeking pregnancy or verifying the success of vasectomy. Depending on the measurement method, just a few characteristics may be evaluated or many characteristics may be evaluated. Collection techniques and precise measurement method may influence results.

Oocyte cryopreservation is a procedure to preserve a woman's eggs (oocytes). This technique has been used to enable women to postpone pregnancy to a later date – whether for medical or social reasons. Several studies have shown that most infertility problems are due to germ cell deterioration related to aging. The intention of the procedure is that the woman may choose to have the eggs thawed, fertilized, and transferred to the uterus as embryos to facilitate a pregnancy in the future. The procedure's success rate varies depending on the age of the woman, with odds being higher in younger, adult women.
Semen quality is a measure of male fertility, a measure of the ability of sperm in semen to accomplish fertilization. Semen quality involves both sperm quantity and quality. Semen quality is a major factor for fertility.
Sertoli cell-only syndrome is a disorder characterized by male sterility without sexual abnormality. It describes a condition of the testes in which only Sertoli cells line is present in seminiferous tubules.
Pregnancy rate is the success rate for getting pregnant. It is the percentage of all attempts that leads to pregnancy, with attempts generally referring to menstrual cycles where insemination or any artificial equivalent is used, which may be simple artificial insemination (AI) or AI with additional in vitro fertilization (IVF).
The Genetics & IVF Institute (GIVF) is an international provider of infertility and genetics services and products, and also engages in biomedical research in these fields. The Institute was founded in 1984 by Dr. Joseph D. Schulman and associates. GIVF headquarters are in Fairfax, VA, US, and its facilities include locations in Pennsylvania, Minnesota, California, and Texas in the United States, as well as in China, Mexico, and several other countries.
Vasectomy reversal is a term used for surgical procedures that reconnect the male reproductive tract after interruption by a vasectomy. Two procedures are possible at the time of vasectomy reversal: vasovasostomy and vasoepididymostomy. Although vasectomy is considered a permanent form of contraception, advances in microsurgery have improved the success of vasectomy reversal procedures. The procedures remain technically demanding and may not restore the pre-vasectomy condition.
FNA mapping is an application of fine-needle aspiration (FNA) to the testis for the diagnosis of male infertility. FNA cytology has been used to examine pathological human tissue from various organs for over 100 years. As an alternative to open testicular biopsy for the last 40 years, FNA mapping has helped to characterize states of human male infertility due to defective spermatogenesis. Although recognized as a reliable, and informative technique, testis FNA has not been widely used in U.S. to evaluate male infertility. Recently, however, testicular FNA has gained popularity as both a diagnostic and therapeutic tool for the management of clinical male infertility for several reasons:
- The testis is an ideal organ for evaluation by FNA because of its uniform cellularity and easy accessibility.
- The trend toward minimally invasive procedures and cost-containment views FNA favorably compared to surgical testis biopsy.
- The realization that the specific histologic abnormality observed on testis biopsy has no definite correlation to either the etiology of infertility or to the ability to find sperm for assisted reproduction.
- Assisted reproduction has undergone dramatic advances such that testis sperm are routinely used for biological pregnancies, thus fueling the development of novel FNA techniques to both locate and procure sperm.
Jacques Cohen is a Dutch embryologist based in New York, U.S. He is currently Director at Reprogenetics LLC, Laboratory Director at ART Institute of Washington at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, and Scientific Director of R & D at IVF-online.
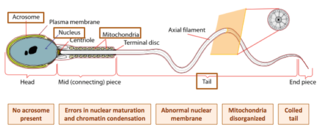
Globozoospermia is a rare and severe form of monomorphic teratozoospermia. This means that the spermatozoa show the same abnormality, and over 85% of spermatozoa in sperm have this abnormality. Globozoospermia is responsible for less than 0.1% of male infertility. It is characterised by round-headed spermatozoa without acrosomes, an abnormal nuclear membrane and midpiece defects. Affected males therefore suffer from either reduced fertility or infertility. Studies suggest that globozoospermia can be either total or partial, however it is unclear whether these two forms are variations on the same syndrome, or actually different syndromes.
The intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection (IMSI) is a laboratory technique used for In vitro fertilisation treatments. High-quality sperms are injected into the egg for fertilization, it is an advanced version of ICSI. A high powered microscope is used to pick out and the best sperm cells which are then used in a traditional ICSI protocol. In ICSI a magnification of x400 is used, while in IMSI an amplification of x6000 to x10,000 is used, increasing the magnification by a factor of 15. This allows the sperm to be examined in greater detail, including the nucleus which contains the sperm's genetic material. The use of this method has resulted in higher pregnancy and delivery rates and lower abortion rates. IMSI is a method that can be chosen by for anyone who has failed IVF cycles in the past, and for couples who have a component of male infertility.
Dmitri Dozortsev is a Russian-American physician scientist, inventor and researcher. Dozortsev's contributions in research and publications are mostly in the areas of human reproductive medicine and biology. In particular, he is best known for his studies of in vitro fertilisation and embryo transfer. Dozortsev currently serves as President of the American College of Embryology and as Director of Omni-Med laboratories.
References
- ↑ "Etiology of male infertility and Oligo-, Astheno-, Teratospermia (OAT)".
- ↑ Page 155 in: Hermann Behre; Eberhard Nieschlag (2000). Andrology : Male Reproductive Health and Dysfunction. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 3-540-67224-9.
- 1 2 "Medical treatment of male infertility".
- ↑ "Endotext.com - Endocrinology of Male Reproduction, Clinical Management of Male Infertility". Archived from the original on 2008-11-21. Retrieved 2008-12-07.
- ↑ Egashira A, Murakami M, Haigo K, Horiuchi T, Kuramoto T (September 2009). "A successful pregnancy and live birth after intracytoplasmic sperm injection with globozoospermic sperm and electrical oocyte activation". Fertil. Steril. 92 (6): 2037.e5–2037.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.08.013 . PMID 19800059.
- 1 2 3 French DB, Sabanegh ES, Goldfarb J, Desai N (March 2010). "Does severe teratozoospermia affect blastocyst formation, live birth rate, and other clinical outcome parameters in ICSI cycles?". Fertil Steril. 93 (4): 1097–1103. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.10.051 . PMID 19200957.