Related Research Articles

The People's Union of Estonia was a political party in Estonia. Its last leader was Margo Miljand.

The Estonian Reform Party is a liberal political party in Estonia. The party has been led by Kaja Kallas since 2018. It is colloquially known as the "Squirrel Party".
Res Publica Party was a political party in Estonia that self-identified as conservative. Established as a party on 8 December 2001, the political organisation Res Publica was founded already as early as 1989 and existed as a community of young conservatives, mostly associated with the Pro Patria Union party during the 1990s. Res Publica was a member of the EPP on the European level. It merged with Pro Patria Union in 2006 to form the Pro Patria and Res Publica Union.

The prime minister of Estonia is the head of government of the Republic of Estonia. The prime minister is nominated by the president after appropriate consultations with the parliamentary factions and confirmed by the parliament (Riigikogu). In case of disagreement, the parliament can reject the president's nomination and choose their own candidate. In practice, since the prime minister must maintain the confidence of parliament in order to remain in office, they are usually the leader of the senior partner in the governing coalition. The current prime minister is Kaja Kallas of the Reform Party. She took the office on 26 January 2021 following the resignation of Jüri Ratas.

The Social Democratic Party is a centre-left political party in Estonia. It is currently led by Lauri Läänemets. The party was formerly known as the Moderate People's Party. The SDE has been a member of the Party of European Socialists since 16 May 2003 and was a member of the Socialist International from November 1990 to 2017. It is orientated towards the principles of social-democracy, and it supports Estonia's membership in the European Union. From April 2023, the party has been a junior coalition partner in the third Kallas government.
The Pro Patria Union was a national-conservative political party in Estonia. The party was founded on 2 December 1995 from a merger of the Estonian National Independence Party and the Pro Patria National Coalition.

Parliamentary elections were held in Estonia on 2 March 2003. The newly elected 101 members of the 10th Riigikogu assembled at Toompea Castle in Tallinn within ten days of the election. Two opposing parties won the most seats, with both the Centre Party and Res Publica Party winning 28 seats in the Riigikogu. Res Publica was able to gain enough support in negotiations after the elections to form a coalition government.

Parliamentary elections were held in Estonia on 7 March 1999. The newly elected 101 members of the 9th Riigikogu assembled at Toompea Castle in Tallinn within ten days of the election. The elections proved disastrous for the ruling Estonian Coalition Party, which won only seven seats together with two of its smaller allies. Following the elections, a coalition government was formed by Mart Laar of the Pro Patria Union, including the Reform Party and the Moderates. It remained in office until Laar resigned in December 2001, after the Reform Party had left the same governing coalition in Tallinn municipality, making opposition leader Edgar Savisaar new Mayor of Tallinn. The Reform Party and the Estonian Centre Party then formed a coalition government that lasted until the 2003 elections.
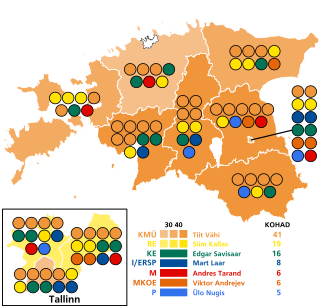
Parliamentary elections were held in Estonia on 5 March 1995. The newly elected 101 members of the 8th Riigikogu assembled at Toompea Castle in Tallinn within ten days of the election. The governing parties were heavily defeated, except for the Reform Party, the successor of Estonian Liberal Democratic Party. The biggest winner was election alliance consisting of Coalition Party and its rural allies, which won in a landslide victory. The alliance won 41 seats, which is the best result in Estonian parliamentary election so far.

Parliamentary elections were held in Estonia on 4 March 2007. The newly elected 101 members of the 11th Riigikogu assembled at Toompea Castle in Tallinn within ten days of the election. It was the world's first nationwide vote where part of the voting was carried out in the form of remote electronic voting via the internet.

Isamaa is a Christian-democratic and national-conservative political party in Estonia.
The Republican Party was a political party in Estonia, founded in 1999. The chairman of the party was Kristjan-Olari Leping, a lecturer of economic theory at the pärnu college of the University of Tartu. The party was of neo-conservative, new rightist and national conservative orientation; it identifies itself as close to Pro Patria Union and Reform Party of Estonia, but more radical. The organization was also strongly eurosceptic.
Pro Patria National Coalition Party was an Estonian political party founded in 1992. In 1995 it merged, with the Estonian National Independence Party, into Pro Patria Union.
The Estonian People's Party was a centre-right political party in Estonia.

The Conservative People's Party of Estonia is a nationalist and right-wing populist political party in Estonia, currently led by Martin Helme. It was founded in March 2012, with the merger of People's Union of Estonia and Estonian Patriotic Movement. Its first leader, Margo Miljand, served as the chairman until 2013 when he was succeeded by Mart Helme. Its popularity remained low until late 2014, when the party began to draw supporters from the right; further, in the 2015 Estonian parliamentary election, it passed the electoral threshold and won seats in parliament for the first time. Since then its support has grown, turning it into one of the largest parties in Estonia. In the 2019 Estonian parliamentary election, EKRE placed third, winning 19 seats in total. Mart was succeeded as party chairman by his son, Martin Helme, in July 2020.
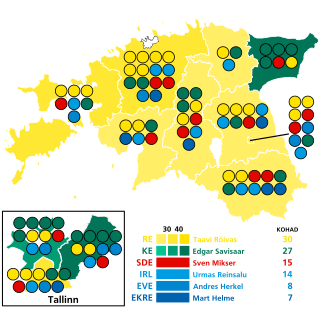
Parliamentary elections were held in Estonia on 1 March 2015. Advance voting was held between 19 and 25 February with a turnout of 33 percent. The Reform Party remained the largest in the Riigikogu, winning 30 of the 101 seats. Its leader, Taavi Rõivas, remained Prime Minister. The newly elected 101 members of the 13th Riigikogu assembled at Toompea Castle in Tallinn within ten days of the election. Two political newcomers, the Free Party and the Conservative People's Party (EKRE) crossed the threshold to enter the Riigikogu.

Illar Hallaste was an Estonian cleric, politician, lawyer, and businessman, most notable for being a voter for the Estonian restoration of Independence.

Triple Alliance is a commonly used political term in Estonia to refer to the various coalition governments between the centre-left Social Democratic Party, centre-right Reform Party and conservative Isamaa or their predecessors. This coalition has formed four times in history - from 1999 to 2002, from 2007 to 2009, from 2015 to 2016 and from 2022 to 2023. None of the coalitions governments have lasted a full parliamentary term. All of the Triple Alliance cabinets have been the second ones of the respective Prime Minister.
References
- Notes
- Sources
- Toomla, Rein, Eesti Erakonnad, Tallinn, 1999