Related Research Articles
In software quality assurance, performance testing is in general a testing practice performed to determine how a system performs in terms of responsiveness and stability under a particular workload. It can also serve to investigate, measure, validate or verify other quality attributes of the system, such as scalability, reliability and resource usage.

Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots tele, 'remote', and metron, 'measure'. Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry: telecommand.
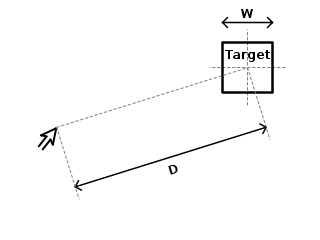
Fitts's law is a predictive model of human movement primarily used in human–computer interaction and ergonomics. The law predicts that the time required to rapidly move to a target area is a function of the ratio between the distance to the target and the width of the target. Fitts's law is used to model the act of pointing, either by physically touching an object with a hand or finger, or virtually, by pointing to an object on a computer monitor using a pointing device. It was initially developed by Paul Fitts.
The Special Sensor Microwave/Imager (SSM/I) is a seven-channel, four-frequency, linearly polarized passive microwave radiometer system. It is flown on board the United States Air Force Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) Block 5D-2 satellites. The instrument measures surface/atmospheric microwave brightness temperatures (TBs) at 19.35, 22.235, 37.0 and 85.5 GHz. The four frequencies are sampled in both horizontal and vertical polarizations, except the 22 GHz which is sampled in the vertical only.
Monitoring may refer to:

A network analyzer is an instrument that measures the network parameters of electrical networks. Today, network analyzers commonly measure s–parameters because reflection and transmission of electrical networks are easy to measure at high frequencies, but there are other network parameter sets such as y-parameters, z-parameters, and h-parameters. Network analyzers are often used to characterize two-port networks such as amplifiers and filters, but they can be used on networks with an arbitrary number of ports.
Capacity management's goal is to ensure that information technology resources are sufficient to meet upcoming business requirements cost-effectively. One common interpretation of capacity management is described in the ITIL framework. ITIL version 3 views capacity management as comprising three sub-processes: business capacity management, service capacity management, and component capacity management.

A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an index of refraction (refractometry). The index of refraction is calculated from the observed refraction angle using Snell's law. For mixtures, the index of refraction then allows the concentration to be determined using mixing rules such as the Gladstone–Dale relation and Lorentz–Lorenz equation.
Capacitance–voltage profiling is a technique for characterizing semiconductor materials and devices. The applied voltage is varied, and the capacitance is measured and plotted as a function of voltage. The technique uses a metal–semiconductor junction or a p–n junction or a MOSFET to create a depletion region, a region which is empty of conducting electrons and holes, but may contain ionized donors and electrically active defects or traps. The depletion region with its ionized charges inside behaves like a capacitor. By varying the voltage applied to the junction it is possible to vary the depletion width. The dependence of the depletion width upon the applied voltage provides information on the semiconductor's internal characteristics, such as its doping profile and electrically active defect densities., Measurements may be done at DC, or using both DC and a small-signal AC signal, or using a large-signal transient voltage.

A curve tracer is a specialised piece of electronic test equipment used to analyze the characteristics of discrete electronic components, such as diodes, transistors, thyristors, and vacuum tubes. The device contains voltage and current sources that can be used to stimulate the device under test (DUT).
Iometer is an I/O subsystem measurement and characterization tool for single and clustered systems. It is used as a benchmark and troubleshooting tool and is easily configured to replicate the behaviour of many popular applications. One commonly quoted measurement provided by the tool is IOPS.
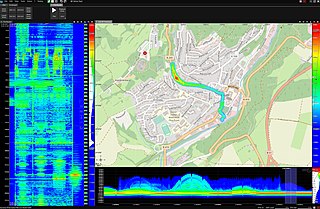
RF Drive testing is a method of measuring and assessing the coverage, capacity and Quality of Service (QoS) of a mobile radio network.
The Project 25 Inter RF Subsystem Interface is a non-proprietary interface that enables RF subsystems (RFSSs) built by different manufacturers to be connected together into wide area networks so that users on different networks can talk with each other. The wide area network connections using the ISSI provide an extended coverage area for subscriber units (SUs) that are roaming. The extended coverage area is important for public safety first responders that provide assistance in other jurisdictions during an emergency.
An energy service company (ESCO) is a company that provides a broad range of energy solutions including designs and implementation of energy savings projects, retrofitting, energy conservation, energy infrastructure outsourcing, power generation, energy supply, and risk management.
In control theory a self-tuning system is capable of optimizing its own internal running parameters in order to maximize or minimize the fulfilment of an objective function; typically the maximization of efficiency or error minimization.

A noise dosimeter or noise dosemeter is a specialized sound level meter intended specifically to measure the noise exposure of a person integrated over a period of time; usually to comply with Health and Safety regulations such as the Occupational Safety and Health (OSHA) 29 CFR 1910.95 Occupational Noise Exposure Standard or EU Directive 2003/10/EC.
A Transportation Management System (TMS) is a subset of supply chain management concerning transportation operations, which may be part of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system.

EMVA1288 is an electronic measurement standard developed by the European Machine Vision Association (EMVA). Its purpose is to define the methods to measure and characterize image sensors and cameras that are used in machine vision. It also provides rules and guidelines on how to report results and how to write device datasheets.
Design of robust and reliable networks and network services relies on an understanding of the traffic characteristics of the network. Throughout history, different models of network traffic have been developed and used for evaluating existing and proposed networks and services.
An impedance analyzer is a type of electronic test equipment used to measure complex electrical impedance as a function of test frequency.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).