Related Research Articles

The hypothalamus is a small part of the brain that contains a number of nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. It forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.
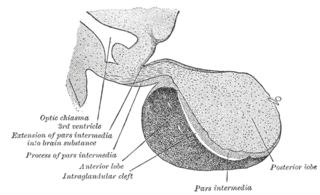
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe makes up the pituitary gland (hypophysis) which, in humans, is located at the base of the brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus.

Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion.

The paraventricular nucleus is a nucleus in the hypothalamus. Anatomically, it is adjacent to the third ventricle and many of its neurons project to the posterior pituitary. These projecting neurons secrete oxytocin and a smaller amount of vasopressin, otherwise the nucleus also secretes corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). CRH and TRH are secreted into the hypophyseal portal system and act on different targets neurons in the anterior pituitary. PVN is thought to mediate many diverse functions through these different hormones, including osmoregulation, appetite, and the response of the body to stress.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and released from GnRH neurons within the hypothalamus. The peptide belongs to gonadotropin-releasing hormone family. It constitutes the initial step in the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis.
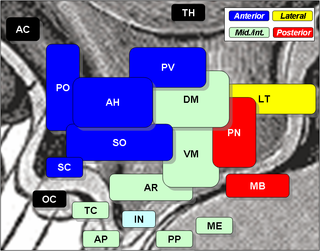
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region. The function of the arcuate nucleus relies on its diversity of neurons, but its central role is involved in homeostasis. The arcuate nucleus provides many physiological roles involved in feeding, metabolism, fertility, and cardiovascular regulation.

Ghrelin is a hormone primarily produced by enteroendocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, and is often called a "hunger hormone" because it increases the drive to eat. Blood levels of ghrelin are highest before meals when hungry, returning to lower levels after mealtimes. Ghrelin may help prepare for food intake by increasing gastric motility and stimulating the secretion of gastric acid.

Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a 36 amino-acid neuropeptide that is involved in various physiological and homeostatic processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. It is secreted alongside other neurotransmitters such as GABA and glutamate.
Releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones are hormones whose main purpose is to control the release of other hormones, either by stimulating or inhibiting their release. They are also called liberins and statins (respectively), or releasing factors and inhibiting factors. The principal examples are hypothalamic-pituitary hormones that can be classified from several viewpoints: they are hypothalamic hormones, they are hypophysiotropic hormones, and they are tropic hormones.

Agouti-related protein (AgRP), also called agouti-related peptide, is a neuropeptide produced in the brain by the AgRP/NPY neuron. It is synthesized in neuropeptide Y (NPY)-containing cell bodies located in the ventromedial part of the arcuate nucleus in the hypothalamus. AgRP is co-expressed with NPY and acts to increase appetite and decrease metabolism and energy expenditure. It is one of the most potent and long-lasting of appetite stimulators. In humans, the agouti-related peptide is encoded by the AGRP gene.
Neuroendocrinology is the branch of biology which studies the interaction between the nervous system and the endocrine system; i.e. how the brain regulates the hormonal activity in the body. The nervous and endocrine systems often act together in a process called neuroendocrine integration, to regulate the physiological processes of the human body. Neuroendocrinology arose from the recognition that the brain, especially the hypothalamus, controls secretion of pituitary gland hormones, and has subsequently expanded to investigate numerous interconnections of the endocrine and nervous systems.

The hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis refers to the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and gonadal glands as if these individual endocrine glands were a single entity. Because these glands often act in concert, physiologists and endocrinologists find it convenient and descriptive to speak of them as a single system.
Growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH), also known as somatocrinin or by several other names in its endogenous forms and as somatorelin (INN) in its pharmaceutical form, is a releasing hormone of growth hormone (GH). It is a 44-amino acid peptide hormone produced in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus.

Kisspeptins are proteins encoded by the KISS1 gene in humans. Kisspeptins are ligands of the G-protein coupled receptor, GPR54. Kiss1 was originally identified as a human metastasis suppressor gene that has the ability to suppress melanoma and breast cancer metastasis. Kisspeptin-GPR54 signaling has an important role in initiating secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) at puberty, the extent of which is an area of ongoing research. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone is released from the hypothalamus to act on the anterior pituitary triggering the release of luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). These gonadotropic hormones lead to sexual maturation and gametogenesis. Disrupting GPR54 signaling can cause hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism in rodents and humans. The Kiss1 gene is located on chromosome 1. It is transcribed in the brain, adrenal gland, and pancreas.

Neurokinin B (NKB) belongs in the family of tachykinin peptides. Neurokinin B is implicated in a variety of human functions and pathways such as the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Additionally, NKB is associated with pregnancy in females and maturation in young adults. Reproductive function is highly dependent on levels of both neurokinin B and also the G-protein coupled receptor ligand kisspeptin. The first NKB studies done attempted to resolve why high levels of the peptide may be implicated in pre-eclampsia during pregnancy. NKB, kisspeptin, and dynorphin together are found in the arcuate nucleus (ARC) known as the KNDy subpopulation. This subpopulation is targeted by many steroid hormones and works to form a network that feeds back to GnRH pulse generator.

The KiSS1-derived peptide receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor which binds the peptide hormone kisspeptin (metastin). Kisspeptin is encoded by the metastasis suppressor gene KISS1, which is expressed in a variety of endocrine and gonadal tissues. Activation of the kisspeptin receptor is linked to the phospholipase C and inositol trisphosphate second messenger cascades inside the cell.
Hypothalamic–pituitary hormones are hormones that are produced by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Although the organs in which they are produced are relatively small, the effects of these hormones cascade throughout the body. They can be classified as a hypothalamic–pituitary axis of which the adrenal, gonadal, thyroid, somatotropic, and prolactin axes are branches.
The anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV) is a small cluster of cells located in the preoptic area of hypothalamus of the brain that is abundant in nuclear hormone receptors in a sexually dimorphic manner, strongly implicated, in rat models, as being neonatally imprinted and subsequently controlling sex-typical physiology and behaviors. This nucleus or cluster of cells is typically of bigger size in females than males, contrary to the sexually dimorphic nucleus (SDN) that is bigger in males.
Kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin (KNDy) neurons are neurons in the hypothalamus of the brain that are central to the hormonal control of reproduction.
Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH) is a RFamide-related peptide coded by the NPVF gene in mammals.
References
- ↑ Ueno M, Akiguchi I, Hosokawa M, Kotani H, Kanenishi K, Sakamoto H (2000). "Blood-brain barrier permeability in the periventricular areas of the normal mouse brain". Acta Neuropathologica. 99 (4): 385–92. doi:10.1007/s004010051140. PMID 10787037. S2CID 125429.
- ↑ Seckl JR (1997). "11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase in the Brain: A Novel Regulator of Glucocorticoid Action?". Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology. 18 (1): 49–99. doi:10.1006/frne.1996.0143. PMID 9000459. S2CID 46477930.
- ↑ Chiba, A. (2005-07-01). "Neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive (NPY-ir) structures in the brain of the gar Lepisosteus oculatus (Lepisosteiformes, Osteichthyes) with special regard to their anatomical relations to gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)-ir structures in the hypothalamus and the terminal nerve". General and Comparative Endocrinology. 142 (3): 336–346. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.02.010. PMID 15935160.
- ↑ Rudolph, L. M.; Bentley, G. E.; Calandra, R. S.; Paredes, A. H.; Tesone, M.; Wu, T. J.; Micevych, P. E. (2016-07-01). "Peripheral and Central Mechanisms Involved in the Hormonal Control of Male and Female Reproduction". Journal of Neuroendocrinology. 28 (7): 10.1111/jne.12405. doi:10.1111/jne.12405. ISSN 1365-2826. PMC 5146987 . PMID 27329133.
- ↑ Orikasa, Chitose; Kondo, Yasuhiko; Hayashi, Shinji; McEwen, Bruce S.; Sakuma, Yasuo (2002-03-05). "Sexually dimorphic expression of estrogen receptor β in the anteroventral periventricular nucleus of the rat preoptic area: Implication in luteinizing hormone surge". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 99 (5): 3306–3311. Bibcode:2002PNAS...99.3306O. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052707299 . ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 122514 . PMID 11854469.
- ↑ Kiss, József; Csaba, Zsolt; Csáki, Ágnes; Halász, Béla (2006-10-16). "Glutamatergic innervation of growth hormone-releasing hormone-containing neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus and somatostatin-containing neurons in the anterior periventricular nucleus of the rat". Brain Research Bulletin. 70 (4–6): 278–288. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2006.05.006. PMID 17027763. S2CID 3184096.
- ↑ Murray; Simonian (2001). "Correlation of hypothalamic somatostatin mRNA expression and peptide content with secretion: sexual dimorphism and differential regulation by gonadal factors". Neuroendocrinology. 11 (1): 27–33. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2826.1999.00286.x. PMID 9918226. S2CID 12731896.
- ↑ Carro, E.; Señarís, R. M.; Seoane, L. M.; Frohman, L. A.; Arimura, A.; Casanueva, F. F.; Diéguez, C. (1999-01-01). "Role of growth hormone (GH)-releasing hormone and somatostatin on leptin-induced GH secretion". Neuroendocrinology. 69 (1): 3–10. doi:10.1159/000054397. ISSN 0028-3835. PMID 9892845. S2CID 8220028.
- ↑ Håkansson, Marie-Louise; Brown, Hilary; Ghilardi, Nico; Skoda, Radek C.; Meister, Björn (1998-01-01). "Leptin Receptor Immunoreactivity in Chemically Defined Target Neurons of the Hypothalamus". Journal of Neuroscience. 18 (1): 559–572. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-01-00559.1998. ISSN 0270-6474. PMC 6793379 . PMID 9412531.
- ↑ Kasagi, Yoko; Tokita, Reiko; Nakata, Tomoko; Imaki, Toshihiro; Minami, Shiro (2004-04-01). "Human growth hormone induces SOCS3 and CIS mRNA increase in the hypothalamic neurons of hypophysectomized rats". Endocrine Journal. 51 (2): 145–154. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.51.145 . ISSN 0918-8959. PMID 15118263.