
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis, organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules. The production of many man-made chemicals such as drugs, plastics, food additives, fabrics depend on organic reactions.

Dibenzofuran is a heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical structure shown at right. It is an aromatic compound that has two benzene rings fused to a central furan ring. All the numbered carbon atoms have a hydrogen atom bonded to each of them. It is a volatile white solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It is obtained from coal tar, where it exists as a 1% component.

Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the structural nucleus of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants.
The Ferrier rearrangement is an organic reaction that involves a nucleophilic substitution reaction combined with an allylic shift in a glycal. It was discovered by the carbohydrate chemist Robert J. Ferrier.
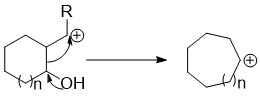
Ring expansion and ring contraction reactions expand or contract rings, usually in organic chemistry. The term usually refers to reactions involve making and breaking C-C bonds, Diverse mechanisms lead to these kinds of reactions.
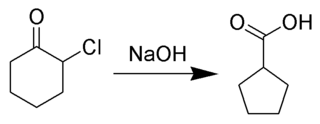
The Favorskii rearrangement is principally a rearrangement of cyclopropanones and α-halo ketones that leads to carboxylic acid derivatives. In the case of cyclic α-halo ketones, the Favorskii rearrangement constitutes a ring contraction. This rearrangement takes place in the presence of a base, sometimes hydroxide, to yield a carboxylic acid, but usually either an alkoxide base or an amine to yield an ester or an amide, respectively. α,α'-Dihaloketones eliminate HX under the reaction conditions to give α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Note that trihalomethyl ketone substrates will result in haloform and carboxylate formation via the haloform reaction instead.

The pinacol–pinacolone rearrangement is a method for converting a 1,2-diol to a carbonyl compound in organic chemistry. The 1,2-rearrangement takes place under acidic conditions. The name of the rearrangement reaction comes from the rearrangement of pinacol to pinacolone.

The Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement is the chemical reaction of a 1-aminomethyl-cycloalkanol with nitrous acid to form an enlarged cycloketone.
The Demjanov rearrangement is the chemical reaction of primary amines with nitrous acid to give rearranged alcohols. It involves substitution by a hydroxyl group with a possible ring expansion. It is named after the Russian chemist Nikolai Jakovlevich Demjanov , who first reported it in 1903.

The Bartoli indole synthesis is the chemical reaction of ortho-substituted nitroarenes and nitrosoarenes with vinyl Grignard reagents to form substituted indoles.
The benzilic acid rearrangement is formally the 1,2-rearrangement of 1,2-diketones to form α-hydroxy–carboxylic acids using a base. This reaction receives its name from the reaction of benzil with potassium hydroxide to form benzilic acid. First performed by Justus von Liebig in 1838, it is the first reported example of a rearrangement reaction. It has become a classic reaction in organic synthesis and has been reviewed many times before. It can be viewed as an intramolecular redox reaction, as one carbon center is oxidized while the other is reduced.
The Ramberg–Bäcklund reaction is an organic reaction converting an α-halo sulfone into an alkene in presence of a base with extrusion of sulfur dioxide. The reaction is named after the two Swedish chemists Ludwig Ramberg and Birger Bäcklund. The carbanion formed by deprotonation gives an unstable episulfone that decomposes with elimination of sulfur dioxide. This elimination step is considered to be a concerted cheletropic extrusion.

The Wolff rearrangement is a reaction in organic chemistry in which an α-diazocarbonyl compound is converted into a ketene by loss of dinitrogen with accompanying 1,2-rearrangement. The Wolff rearrangement yields a ketene as an intermediate product, which can undergo nucleophilic attack with weakly acidic nucleophiles such as water, alcohols, and amines, to generate carboxylic acid derivatives or undergo [2+2] cycloaddition reactions to form four-membered rings. The mechanism of the Wolff rearrangement has been the subject of debate since its first use. No single mechanism sufficiently describes the reaction, and there are often competing concerted and carbene-mediated pathways; for simplicity, only the textbook, concerted mechanism is shown below. The reaction was discovered by Ludwig Wolff in 1902. The Wolff rearrangement has great synthetic utility due to the accessibility of α-diazocarbonyl compounds, variety of reactions from the ketene intermediate, and stereochemical retention of the migrating group. However, the Wolff rearrangement has limitations due to the highly reactive nature of α-diazocarbonyl compounds, which can undergo a variety of competing reactions.
The vinylcyclopropane rearrangement or vinylcyclopropane-cyclopentene rearrangement is a ring expansion reaction, converting a vinyl-substituted cyclopropane ring into a cyclopentene ring.

In mass spectrometry, fragmentation is the dissociation of energetically unstable molecular ions formed from passing the molecules mass spectrum. These reactions are well documented over the decades and fragmentation patterns are useful to determine the molar weight and structural information of unknown molecules. Fragmentation that occurs in tandem mass spectrometry experiments has been a recent focus of research, because this data helps facilitate the identification of molecules.
Rearrangements, especially those that can participate in cascade reactions, such as the aza-Cope rearrangements, are of high practical as well as conceptual importance in organic chemistry, due to their ability to quickly build structural complexity out of simple starting materials. The aza-Cope rearrangements are examples of heteroatom versions of the Cope rearrangement, which is a [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement that shifts single and double bonds between two allylic components. In accordance with the Woodward-Hoffman rules, thermal aza-Cope rearrangements proceed suprafacially. Aza-Cope rearrangements are generally classified by the position of the nitrogen in the molecule :
The Danheiser benzannulation is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry to generate highly substituted phenols in a single step. It is named after Rick L. Danheiser who developed the reaction.
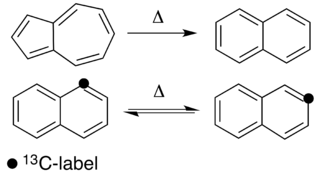
Thermal rearrangements of aromatic hydrocarbons are considered to be unimolecular reactions that directly involve the atoms of an aromatic ring structure and require no other reagent than heat. These reactions can be categorized in two major types: one that involves a complete and permanent skeletal reorganization (isomerization), and one in which the atoms are scrambled but no net change in the aromatic ring occurs (automerization). The general reaction schemes of the two types are illustrated in Figure 1.
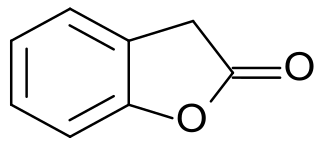
2-Cumaranone is a bicyclic heteroaromatic compound in which a six-membered benzene ring is annulated with a five-membered γ-butyrolactone ring. The 2(3H)-benzofuranone can also be considered as a lactone of (2-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid. The benzofuranone basic structure is the basis of some natural products – such as rosmadial, which is isolatable from rosemary oil, and some substances with high pharmacological activity, such as griseofulvin and rifampicin. Furthermore, 2-cumaranone is utilized as a starting material for the preparation of chemiluminescent and fluorescent dyes, for synthetic pharmaceutical agents, like the antiarrhythmic drug dronedarone, and especially for the fungicide azoxystrobin.












