
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. It separates the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range. It stretches around 2,500 km (1,600 mi) through Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. The range's highest peak is Toubkal, which is in central Morocco, with an elevation of 4,167 metres (13,671 ft). The Atlas mountains are primarily inhabited by Berber populations.

The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
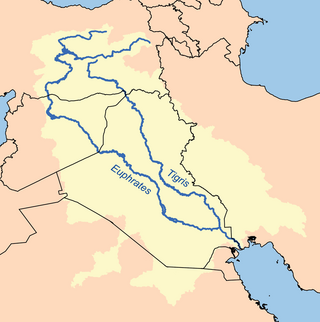
The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in Western Asia which discharges into the Persian Gulf. Its principal rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates along with smaller tributaries.

The Maghreb, also known as the Arab Maghreb and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb also includes the disputed territory of Western Sahara and the Spanish cities Ceuta and Melilla. As of 2018, the region had a population of over 100 million people.

Salmo is a genus of ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae. The single Salmo species naturally found in the Atlantic North America is the Atlantic salmon, whereas the salmon and trout of the Pacific basin belong to another genus, Oncorhynchus. The natural distribution of Salmo also extends to North Africa and to West Asia around the Black Sea basin.
Barbus lepineyi is a doubtfully distinct ray-finned fish species in the family Cyprinidae.
Cobitis maroccana is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Cobitidae.

The Mediterranean Acacia–Argania dry woodlands and succulent thickets is a Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregion in North Africa centered mainly on Morocco but also including northwestern Western Sahara and the eastern Canary Islands.

The Mediterranean woodlands and forests is an ecoregion in the coastal plains, hills, and mountains bordering the Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean in North Africa. It has a Mediterranean climate, and is in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome.

The Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe is a Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregion of North Africa. It occupies interior plateaus and mountain ranges of the Maghreb region, lying generally between the coastal Mediterranean woodlands and forests to the north and the Sahara to the south.

Southwestern Sri Lanka rivers and streams is a freshwater ecoregion in Sri Lanka. The ecoregion is listed in Global 200, a list of ecoregions compiled by the World Wide Fund for Nature for conservation priorities. The extensive network of rivers and streams of Sri Lanka drains a total of 103 distinct natural river basins. Several waterfall habitats have been formed as a result of rivers and streams flowing through high and mid elevation areas. The ecoregion spreads over 15,500 km2 in the wet zone of the southwestern part of Sri Lanka. More than a quarter of the freshwater fishes that have been discovered in Southwestern Sri Lanka rivers and streams are endemic. Nine endemic genera of freshwater fishes of Western Ghats and Sri Lanka hotspot Malpulutta are found only in Sri Lanka. Studies suggest that the number of species still to be discovered is quite high. Until recently wetlands in Sri Lanka were used for drainage, construction sites and land fills.
Luciobarbus is a genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Cyprinidae. Its members are found in fresh and brackish waters of southern Europe, northern Africa, the wider Near East, the Aral and Caspian Seas, and rivers associated with these. Several species in the genus are threatened. Most species are fairly small to medium-sized cyprinids, but the genus also includes several members that can surpass 1 m (3.3 ft) in length and the largest, the mangar can reach 2.3 m (7.5 ft).

The Nimba Range forms part of the southern extent of the Guinea Highlands. The highest peak is Mount Richard-Molard on the border of Côte d'Ivoire and Guinea, at 1,752 m (5,748 ft). "Mount Nimba" may refer either to Mount Richard-Molard or to the entire range. Other peaks include Grand Rochers at 1,694 m (5,558 ft), Mont Sempéré at 1,682 m (5,518 ft), Mont Piérré Richaud at 1,670 m (5,480 ft), Mont Tô at 1,675 m (5,495 ft), and Mont LeClerc 1,577 m (5,174 ft), all of them are located in Guinea. Mount Nimba Strict Nature Reserve of Guinea and Côte d'Ivoire covers significant portions of the Nimba Range.










