
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials that results in a significant, observable magnetic permeability, and in many cases, a significant magnetic coercivity, allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials are familiar metals that are noticeably attracted to a magnet, a consequence of their substantial magnetic permeability. Magnetic permeability describes the induced magnetization of a material due to the presence of an external magnetic field. This temporarily induced magnetization, for example, inside a steel plate, accounts for its attraction to the permanent magnet. Whether or not that steel plate acquires a permanent magnetization itself depends not only on the strength of the applied field but on the so-called coercivity of the ferromagnetic material, which can vary greatly.

An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a coil.

Mu-metal is a nickel–iron soft ferromagnetic alloy with very high permeability, which is used for shielding sensitive electronic equipment against static or low-frequency magnetic fields.

A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, etc. and attracts or repels other magnets.
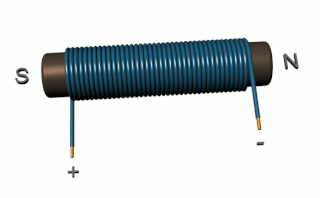
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the hole in the center of the coil. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.
Magnetostriction is a property of magnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of materials' magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ. The effect was first identified in 1842 by James Joule when observing a sample of iron.
Remanence or remanent magnetization or residual magnetism is the magnetization left behind in a ferromagnetic material after an external magnetic field is removed. Colloquially, when a magnet is "magnetized", it has remanence. The remanence of magnetic materials provides the magnetic memory in magnetic storage devices, and is used as a source of information on the past Earth's magnetic field in paleomagnetism. The word remanence is from remanent + -ence, meaning "that which remains".
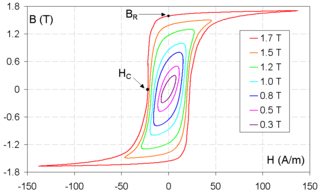
Coercivity, also called the magnetic coercivity, coercive field or coercive force, is a measure of the ability of a ferromagnetic material to withstand an external magnetic field without becoming demagnetized. Coercivity is usually measured in oersted or ampere/meter units and is denoted HC.

A neodymium magnet (also known as NdFeB, NIB or Neo magnet) is the most widely used type of rare-earth magnet. It is a permanent magnet made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron to form the Nd2Fe14B tetragonal crystalline structure. Developed independently in 1984 by General Motors and Sumitomo Special Metals, neodymium magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnet available commercially.

Alnico is a family of iron alloys which in addition to iron are composed primarily of aluminium (Al), nickel (Ni), and cobalt (Co), hence the acronym al-ni-co. They also include copper, and sometimes titanium. Alnico alloys are ferromagnetic, and are used to make permanent magnets. Before the development of rare-earth magnets in the 1970s, they were the strongest type of permanent magnet. Other trade names for alloys in this family are: Alni, Alcomax, Hycomax, Columax, and Ticonal.

In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Permeability is typically represented by the (italicized) Greek letter μ. The term was coined by William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin in 1872, and used alongside permittivity by Oliver Heaviside in 1885. The reciprocal of permeability is magnetic reluctivity.

Permalloy is a nickel–iron magnetic alloy, with about 80% nickel and 20% iron content. Invented in 1914 by physicist Gustav Elmen at Bell Telephone Laboratories, it is notable for its very high magnetic permeability, which makes it useful as a magnetic core material in electrical and electronic equipment, and also in magnetic shielding to block magnetic fields. Commercial permalloy alloys typically have relative permeability of around 100,000, compared to several thousand for ordinary steel.
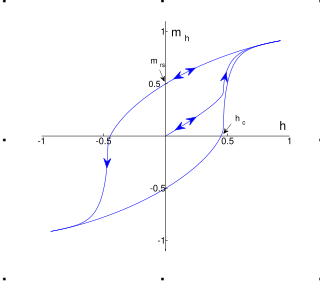
Magnetic hysteresis occurs when an external magnetic field is applied to a ferromagnet such as iron and the atomic dipoles align themselves with it. Even when the field is removed, part of the alignment will be retained: the material has become magnetized. Once magnetized, the magnet will stay magnetized indefinitely. To demagnetize it requires heat or a magnetic field in the opposite direction. This is the effect that provides the element of memory in a hard disk drive.
A magnetic core is a piece of magnetic material with a high magnetic permeability used to confine and guide magnetic fields in electrical, electromechanical and magnetic devices such as electromagnets, transformers, electric motors, generators, inductors, magnetic recording heads, and magnetic assemblies. It is made of ferromagnetic metal such as iron, or ferrimagnetic compounds such as ferrites. The high permeability, relative to the surrounding air, causes the magnetic field lines to be concentrated in the core material. The magnetic field is often created by a current-carrying coil of wire around the core.
A samarium–cobalt (SmCo) magnet, a type of rare-earth magnet, is a strong permanent magnet made of two basic elements: samarium and cobalt.
Vicalloy is a family of cobalt-iron-vanadium wrought ferromagnetic alloys which have high coercivity and are used to make permanent magnets and other magnetic components. Vicalloy is precipitation hardened and can be formed by a number of cold working techniques. It is commonly used in electromechanical device applications, such as Wiegand wires because it shows a large Wiegand effect.

Seen in some magnetic materials, saturation is the state reached when an increase in applied external magnetic field H cannot increase the magnetization of the material further, so the total magnetic flux density B more or less levels off. Saturation is a characteristic of ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic materials, such as iron, nickel, cobalt and their alloys. Different ferromagnetic materials have different saturation levels.

Rare-earth magnets are strong permanent magnets made from alloys of rare-earth elements. Developed in the 1970s and 1980s, rare-earth magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnets made, producing significantly stronger magnetic fields than other types such as ferrite or alnico magnets. The magnetic field typically produced by rare-earth magnets can exceed 1.2 teslas, whereas ferrite or ceramic magnets typically exhibit fields of 0.5 to 1 tesla.

The Barkhausen effect is a name given to the noise in the magnetic output of a ferromagnet when the magnetizing force applied to it is changed. Discovered by German physicist Heinrich Barkhausen in 1919, it is caused by rapid changes of size of magnetic domains.

A ferrite is a ceramic material made by mixing and firing large proportions of iron(III) oxide blended with small proportions of one or more additional metallic elements, such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. They are ferrimagnetic, meaning they can be magnetized or attracted to a magnet. Unlike other ferromagnetic materials, most ferrites are not electrically conductive, making them useful in applications like magnetic cores for transformers to suppress eddy currents. Ferrites can be divided into two families based on their resistance to being demagnetized.













