Related Research Articles
Radiology is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose and treat diseases within the bodies of animals and humans.

Fort Sam Houston is a U.S. Army post in San Antonio, Texas. Known colloquially as "Fort Sam," it is named for the U.S. Senator from Texas, U.S. Representative from Tennessee, Tennessee and Texas Governor, and first President of the Republic of Texas, Sam Houston.
Harold Elford Johns was a Canadian medical physicist, noted for his extensive contributions to the use of ionizing radiation to treat cancer.

Brooke Army Medical Center (BAMC) is the United States Army's premier medical institution. Located on Fort Sam Houston, BAMC, a 425-bed Academic Medical Center, is the Department of Defense's largest facility and only Level 1 Trauma Center. BAMC is also home to the Center for the Intrepid, an outpatient rehabilitation facility. The center is composed of ten separate organizations, including community medical clinics, centered around the Army's largest in-patient hospital. BAMC is staffed by more than 8,000 Soldiers, Airmen, Sailors, Civilians, and Contractors providing care to wounded Service Members and the San Antonio Community at-large.

William Beaumont Army Medical Center is a Department of Defense medical facility located in El Paso, Texas. It provides comprehensive care to all beneficiaries including active duty military, their family members, and retirees. The hospital is located in the Central/Northeastern part of El Paso, and provides emergency department services for Northeast El Paso. The current 1.1-million-square-foot, 6-building medical complex opened July 10, 2021 on East Fort Bliss. WBAMC is affiliated with the Paul L. Foster School of Medicine which is also located in El Paso, Texas. WBAMC is also a participating hospital for medical residents from the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU) and nursing students from the University of Texas at El Paso School of Nursing and the El Paso Community College Nursing School. The current commander of WBAMC is Colonel Brett Venable.

O. Arthur Stiennon, Jr. was a clinical radiologist, inventor, radiation treatment pioneer, software and real estate developer in Madison, Wisconsin. He attended the University of Wisconsin–Madison, graduating Phi Beta Kappa in 1941. He received his M.D. at the University of Wisconsin in 1943 under the wartime accelerated program. He served an internship at the Royal Victoria Hospital in Montreal, P.Q., Canada. After serving in the United States Army from 1944-1947, he served a residency in Diagnostic and Therapeutic Radiology at the University of Michigan Hospitals in Ann Arbor, Michigan.

Major General (Ret.) Kevin Christopher Kiley was the 41st Surgeon General of the United States Army and commander of the U.S. Army Medical Command, Fort Sam Houston, Texas. He was commander of Walter Reed Army Medical Center and North Atlantic Regional Medical Command twice, from 2002 to 2004, and as acting commander, March 1–2, 2007. He submitted his request to retire from the U.S. Army on March 11, 2007, in the wake of the Walter Reed Army Medical Center neglect scandal, and was removed from his nominative billet as a lieutenant general. Pending retirement, he was assigned to a temporary billet at the General Officer Management Office at the Pentagon in the grade major general. His retirement in the grade of major general was subsequently approved.
Kakarla Subba Rao was an Indian radiologist who served as the first director of Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad. For his contributions to the field of medicine, Rao was conferred Padma Shri in 2000, the fourth highest civilian award by the Government of India. He was also the founder and president of the Telugu Association of North America.

The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Department of Radiology is the second largest academic department in Radiological Sciences in the United States. Its Graduate Program in Radiological Sciences offers graduate training in various tracks, including Medical Physics, Radiation biology, Medical Health Physics, and Neuroimaging. In addition the educational enterprise includes an accredited radiology residency program and a number of fellowships.

Hal Bruce Jennings, Jr. was an American plastic surgeon who served as Surgeon General of the United States Army from October 10, 1969, to September 30, 1973.
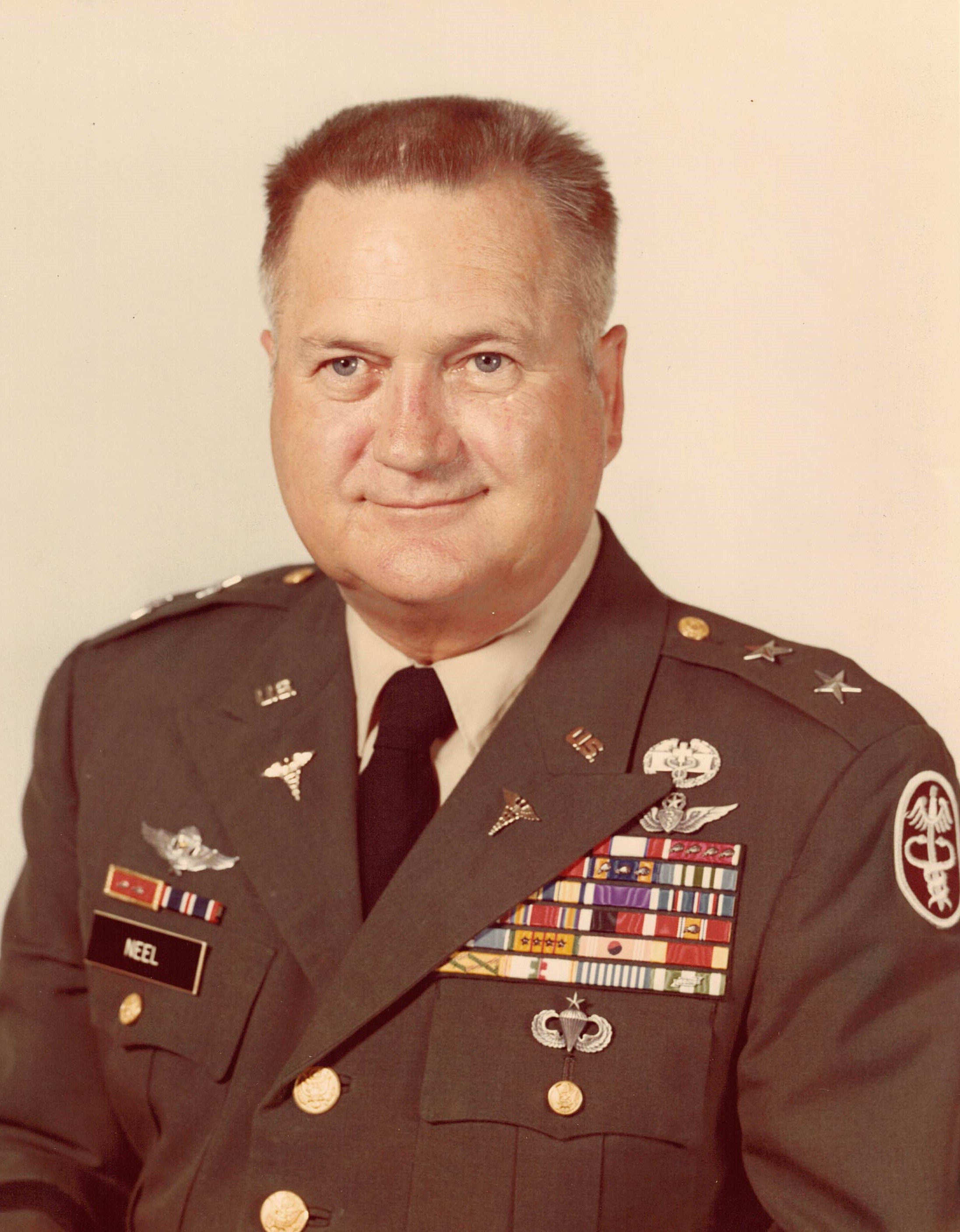
Major General Spurgeon Neel, MD, was a United States Army physician who pioneered the development of aeromedical evacuation of battlefield casualties.
Alexander R. Margulis was a Serbian American physician who was a professor of radiology at Weill Cornell Medical College, Cornell University. He was formerly the Associate Chancellor and Chairman of Radiology at University of California, San Francisco. Over 8 of his papers have each been cited over 100 times.

Edith Hinkley Quimby was an American medical researcher and physicist, best known as one of the founders of nuclear medicine. Her work involved developing diagnostic and therapeutic applications of X-rays. One of her main concerns was protecting both those handling the radioactive material and making sure that those being treated were given the lowest dose necessary.
Joaquín Gómez Mira is a scientist and physician specialized in radiation oncology. Born and raised in Spain, he completed his studies and developed his career in the United States, where he moved in 1967. He is a member of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, and a Fellow and appointed councilor of the American College of Radiology. His work, achievements and lectures in the field of radiation oncology are held in high regard.

James Ralston Kennedy "RP" Paterson, CBE, MC, MD, FRCSEd, FRCR, DMRE (Cantab) was a radiologist and oncologist in Scotland. Along with Herbert Parker, pioneered the development of the Paterson-Parker rules for the Radium Dosage System also known as the Manchester system.

Captain John Henry Ebersole, M.D., MC USN a pioneer in submarine medicine and radiation oncology, selected by Admiral Hyman G. Rickover to serve as medical officer aboard the US Navy's first two nuclear powered submarines, the USS Nautilus and the USS Seawolf. He was the radiologist for NASA that screened the Mercury Seven astronauts for Project Mercury. Ebersole was the radiologist responsible for the x-rays taken during the autopsy of John F. Kennedy on 22 November 1963 at Bethesda Naval Medical Center.
Eleanor D. Montague was an American radiologist and educator who established breast-conserving therapy in the United States and improved radiation therapy techniques. She became a member of the Texas Women's Hall of Fame in 1993.
Cesare Gianturco was an Italian-American physician and one of the earliest contributors to the specialty of interventional radiology. After many years as the radiology chief at the Carle Clinic in Illinois and a faculty member at the University of Illinois College of Medicine, Gianturco moved to Houston, where he conducted research at MD Anderson Hospital.

Ernest Hinds was a career officer in the United States Army. A veteran of the Spanish–American War, Philippine–American War, and World War I, he attained the rank of major general and was notable for his service as Chief of Artillery for the American Expeditionary Forces during the First World War and his post war command of the 2nd Division and United States Army Field Artillery School.
Granville C. Coggs was an American medical doctor, radiologist, U.S. Army Air Force/U.S. Air Force/U.S. Air Force Reserves officer, and trained bombardier pilot with the 477th Bombardment Group attached to the famed Tuskegee Airmen. He was one of the 1007 documented Tuskegee Airmen Pilots.