Related Research Articles
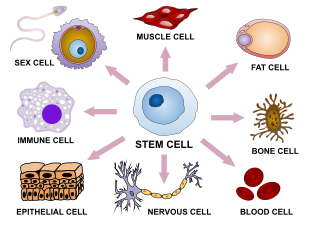
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell changes from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. However, metabolic composition does get altered quite dramatically where stem cells are characterized by abundant metabolites with highly unsaturated structures whose levels decrease upon differentiation. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.

In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism's cells that develop into germ cells. In other words, they are the cells that form gametes, which can come together to form a zygote. They differentiate in the gonads from primordial germ cells into gametogonia, which develop into gametocytes, which develop into the final gametes. This process is known as gametogenesis.
In biology, reprogramming refers to erasure and remodeling of epigenetic marks, such as DNA methylation, during mammalian development or in cell culture. Such control is also often associated with alternative covalent modifications of histones.
In developmental biology, the cells that give rise to the gametes are often set aside during embryonic cleavage. During development, these cells will differentiate into primordial germ cells, migrate to the location of the gonad, and form the germline of the animal.
Computational epigenetics uses statistical methods and mathematical modelling in epigenetic research. Due to the recent explosion of epigenome datasets, computational methods play an increasing role in all areas of epigenetic research.

For molecular biology in mammals, DNA demethylation causes replacement of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) in a DNA sequence by cytosine (C). DNA demethylation can occur by an active process at the site of a 5mC in a DNA sequence or, in replicating cells, by preventing addition of methyl groups to DNA so that the replicated DNA will largely have cytosine in the DNA sequence.

Sir Adrian Peter Bird, is a British geneticist and Buchanan Professor of Genetics at the University of Edinburgh. Bird has spent much of his academic career in Edinburgh, from receiving his PhD in 1970 to working at the MRC Mammalian Genome Unit and later serving as director of the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell Biology. His research focuses on understanding DNA methylation and CpG islands, and their role in diseases such as Rett syndrome.

Cell potency is a cell's ability to differentiate into other cell types. The more cell types a cell can differentiate into, the greater its potency. Potency is also described as the gene activation potential within a cell, which like a continuum, begins with totipotency to designate a cell with the most differentiation potential, pluripotency, multipotency, oligopotency, and finally unipotency.

Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the transmission of epigenetic markers and modifications from one generation to multiple subsequent generations without altering the primary structure of DNA. Thus, the regulation of genes via epigenetic mechanisms can be heritable; the amount of transcripts and proteins produced can be altered by inherited epigenetic changes. In order for epigenetic marks to be heritable, however, they must occur in the gametes in animals, but since plants lack a definitive germline and can propagate, epigenetic marks in any tissue can be heritable.
Edith Heard is a British-French researcher in epigenetics who has been serving as the Director General of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) since January 2019. She is also Professor at the Collège de France, holding the Chair of Epigenetics and Cellular Memory.

Wolf Reik FRS is a German-British molecular biologist and an honorary group leader at the Babraham Institute, honorary professor of Epigenetics at the University of Cambridge and associate faculty at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. He was announced as the director of Altos Labs Cambridge Institute when the company launched on 19 January 2022.

Dame Amanda Gay Fisher is a British cell biologist and Director of the Medical Research Council (MRC) London Institute of Medical Sciences at the Hammersmith Hospital campus of Imperial College London, where she is also a Professor leading the Institute of Clinical Sciences. She has made contributions to multiple areas of cell biology, including determining the function of several genes in HIV and describing the importance of a gene's location within the cell nucleus.

Robin Campbell Allshire is Professor of Chromosome Biology at University of Edinburgh and a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow. His research group at the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell Biology focuses on the epigenetic mechanisms governing the assembly of specialised domains of chromatin and their transmission through cell division.

Anne Carla Ferguson-Smith is a mammalian developmental geneticist. She is the Arthur Balfour Professor of Genetics and Pro-Vice Chancellor for Research and International Partnerships at the University of Cambridge. Formerly head of the Department of Genetics at the University of Cambridge, she is a Fellow of Darwin College, Cambridge and serves as President of the Genetics Society.

Thomas Jenuwein is a German scientist working in the fields of epigenetics, chromatin biology, gene regulation and genome function.
Azim Surani is a Kenyan-British developmental biologist who has been Marshall–Walton Professor at the Wellcome Trust/Cancer Research UK Gurdon Institute at the University of Cambridge since 1992, and Director of Germline and Epigenomics Research since 2013.

Kathrin Muegge is a German physician and molecular biologist researching chromatin organization during embryonic development and in tumor progression. She is a senior investigator and head of the epigenetics section at the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research.

The TET enzymes are a family of ten-eleven translocation (TET) methylcytosine dioxygenases. They are instrumental in DNA demethylation. 5-Methylcytosine is a methylated form of the DNA base cytosine (C) that often regulates gene transcription and has several other functions in the genome.
Axel Schumacher, is a German epigenetics researcher. He invented the first microarray technologies for epigenetic biomarker discovery, developed the ‘epigenetic theory of aging’ with his research leading to the worldwide first proof of whole genome epigenetic abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease.

Irene Miguel-Aliaga is a Spanish-British physiologist who is Professor of Genetics and Physiology at Imperial College London. Her research investigates the plasticity of adult organs, and why certain organs change shape in response to environmental changes. She was elected Fellow of the Royal Society in 2022.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "People - Imperial College London". profiles.imperial.ac.uk. Retrieved 2024-05-29.
- 1 2 "Reprogramming and Chromatin Research Group | Petra Hajkova". LMS Laboratory of Medical Sciences. Retrieved 2024-05-29.
- 1 2 3 "Mary Lyon Medal 2017". Genetics Society. Retrieved 2024-05-29.
- ↑ Stevens-Smith, Jenna (2018-05-14). "MRC LMS's Petra Hajkova elected as a member of EMBO". LMS Laboratory of Medical Sciences. Retrieved 2024-05-29.
- ↑ "Professor Petra Hajkova". acmedsci.ac.uk. Retrieved 2024-05-29.
- ↑ "Petra Hajkova FMedSci". babraham.ac.uk. Retrieved 2024-05-29.