
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient education, physical intervention, rehabilitation, disease prevention, and health promotion. Physical therapists are known as physiotherapists in many countries.

Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a psychiatric treatment where a generalized seizure is electrically induced to manage refractory mental disorders. Typically, 70 to 120 volts are applied externally to the patient's head, resulting in approximately 800 milliamperes of direct current passing between the electrodes, for a duration of 100 milliseconds to 6 seconds, either from temple to temple or from front to back of one side of the head. However, only about 1% of the electrical current crosses the bony skull into the brain because skull impedance is about 100 times higher than skin impedance.

A lobotomy or leucotomy is a form of neurosurgical treatment for psychiatric disorder or neurological disorder that involves severing connections in the brain's prefrontal cortex. The surgery causes most of the connections to and from the prefrontal cortex, the anterior part of the frontal lobes of the brain, to be severed.
Reiki is a Japanese form of energy healing, a type of alternative medicine. Reiki practitioners use a technique called palm healing or hands-on healing through which a "universal energy" is said to be transferred through the palms of the practitioner to the patient in order to encourage emotional or physical healing.

Music therapy, an allied health profession, "is the clinical and evidence-based use of music interventions to accomplish individualized goals within a therapeutic relationship by a credentialed professional who has completed an approved music therapy program." It is also a vocation, involving a deep commitment to music and the desire to use it as a medium to help others. Although music therapy has only been established as a profession relatively recently, the connection between music and therapy is not new

Pharmacy is the science and practice of discovering, producing, preparing, dispensing, reviewing and monitoring medications, aiming to ensure the safe, effective, and affordable use of medicines. It is a miscellaneous science as it links health sciences with pharmaceutical sciences and natural sciences. The professional practice is becoming more clinically oriented as most of the drugs are now manufactured by pharmaceutical industries. Based on the setting, pharmacy practice is either classified as community or institutional pharmacy. Providing direct patient care in the community of institutional pharmacies is considered clinical pharmacy.

Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure higher than atmospheric pressure, and therapeutic recompression for decompression illness, intended to reduce the injurious effects of systemic gas bubbles by physically reducing their size and providing improved conditions for elimination of bubbles and excess dissolved gas.

Oxygen therapy, also known as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as medical treatment. Acute indications for therapy include hypoxemia, carbon monoxide toxicity and cluster headache. It may also be prophylactically given to maintain blood oxygen levels during the induction of anesthesia. Oxygen therapy is often useful in chronic hypoxemia caused by conditions such as severe COPD or cystic fibrosis. Oxygen can be delivered via nasal cannula or face mask, or via high pressure conditions such as in endotracheal intubation or hyperbaric chamber. It can also be given through bypassing the airway, such as in ECMO therapy.

A therapy dog is a dog that is trained to provide affection, comfort and support to people, often in settings such as hospitals, retirement homes, nursing homes, schools, libraries, hospices, or disaster areas. In contrast to assistance dogs, which are trained to assist specific patients with their day-to-day physical needs, therapy dogs are trained to interact with all kinds of people, not just their handlers.

Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental health includes subjective well-being, perceived self-efficacy, autonomy, competence, intergenerational dependence, and self-actualization of one's intellectual and emotional potential, among others.From the perspectives of positive psychology or holism, mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and to create a balance between life activities and efforts to achieve psychological resilience. Cultural differences, subjective assessments, and competing professional theories all affect how one defines "mental health". Some early signs related to mental health difficulties are sleep irritation, lack of energy, lack of appetite and thinking of harming yourself or others.

In medicine, proton therapy, or proton radiotherapy, is a type of particle therapy that uses a beam of protons to irradiate diseased tissue, most often to treat cancer. The chief advantage of proton therapy over other types of external beam radiotherapy is that the dose of protons is deposited over a narrow range of depth; hence in minimal entry, exit, or scattered radiation dose to healthy nearby tissues.

Max Gerson was a German-born American physician who developed the Gerson Therapy, a dietary-based alternative cancer treatment that he claimed could cure cancer and most chronic, degenerative diseases.
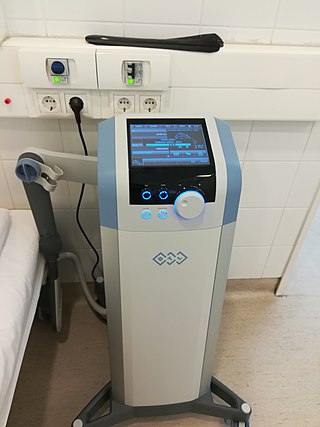
Electrotherapy is the use of electrical energy as a medical treatment. In medicine, the term electrotherapy can apply to a variety of treatments, including the use of electrical devices such as deep brain stimulators for neurological disease. The term has also been applied specifically to the use of electric current to speed wound healing. Additionally, the term "electrotherapy" or "electromagnetic therapy" has also been applied to a range of alternative medical devices and treatments.
Bibliotherapy is a creative arts therapy that involves storytelling or the reading of specific texts. It uses an individual's relationship to the content of books and poetry and other written words as therapy. Bibliotherapy partially overlaps with, and is often combined with, writing therapy.
The Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS) is an organization based in the US which supports research on matters of hyperbaric medicine and physiology, and provides a certificate of added qualification for physicians with an unrestricted license to practice medicine and for limited licensed practitioners, at the completion of the Program for Advanced Training in Hyperbaric Medicine. They support an extensive library and are a primary source of information for diving and hyperbaric medicine physiology worldwide.

Kinetic Concepts, Inc., (KCI) is a global corporation that produces medical technology related to wounds and wound healing. KCI produced the first product developed specifically for negative pressure wound therapy. In 2013, the company employed 5,000 people and marketed its products in more than 25 countries. Its headquarters is in San Antonio, Texas.

Green Lane Hospital is a psychiatric hospital in the Wick district of Devizes in Wiltshire, England. It is managed by the Avon and Wiltshire Mental Health Partnership NHS Trust.
The profession of occupational therapy was established in India in 1950. Despite its 70 years of existence in India, the profession has gained momentum in the healthcare sector of India only in the past decade.
Vaidya Balendu Prakash is an Indian Ayurveda practitioner. He is a former physician to the President of India and the founder of Paadav, a specialty Ayurvedic hospital in Dehradun. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian award of the Padma Shri in 1999.
Karen Jennings is an American former basketball player who played with the Nebraska Cornhuskers women's basketball between 1990 and 1993 and set the record for the most career points for Nebraska with 2,405 points. She was the recipient of the 1993 Wade Trophy and was inducted into the University of Nebraska Athletics Hall of Fame in 2013. Outside of college basketball, Jennings worked in sports medicine for the Methodist Hospital between 1998 and 2002. Since 2002 she has been a real estate agent in Omaha, Nebraska.













