
Tagalog is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the population of the Philippines, and as a second language by the majority. Its standardized form, officially named Filipino, is the national language of the Philippines, and is one of two official languages, alongside English.

There are some 120 to 187 languages spoken in the Philippines, depending on the method of classification. Almost all are Malayo-Polynesian languages native to the archipelago. A number of Spanish-influenced creole varieties generally called Chavacano are also spoken in certain communities. The 1987 constitution designates Filipino, a standardized version of Tagalog, as the national language and an official language along with English. Filipino is regulated by Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino and serves as a lingua franca used by Filipinos of various ethnolinguistic backgrounds.
Philippine English is any variety of English native to the Philippines, including those used by the media and the vast majority of educated Filipinos and English learners in the Philippines from adjacent Asian countries. English is taught in schools as one of the two official languages of the country, the other being Filipino (Tagalog). Due to the influx of Filipino English teachers overseas, Philippine English is also becoming the prevalent variety of English being learned in the Far East as taught by Filipino teachers in various Asian countries such as Korea, Japan and Thailand, among others. Due to the highly multilingual nature of the Philippines, code-switching such as Taglish and Bislish is prevalent across domains from casual settings to formal situations.

Chinese Filipinos are Filipinos of Chinese descent, mostly of Hoklo (Hokkien) ancestry, where the majority are born and raised in the Philippines. Chinese Filipinos are one of the largest overseas Chinese communities in Southeast Asia. Chinese immigration to the Philippines occurred mostly during the Spanish colonization of the islands between the 16th and 19th centuries, attracted by the lucrative trade of the Manila galleons and since the late 20th century. In 2013, according to the Senate of the Philippines, there were approximately 1.35 million Ethnic Chinese within the Philippine population, while Filipinos with any Chinese descent comprised 22.8 million of the population. However, the actual current figures are not known since the Philippine census does not usually take into account questions about ethnicity.
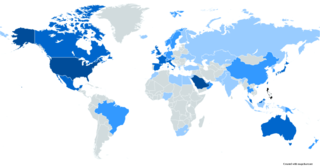
An overseas Filipino is a person of full or partial Filipino origin—i.e. people who trace back their ancestry to the Philippines but living or residing outside the country. This term generally applies to both people of Filipino ancestry and citizens abroad. As of 2019, there were over 12 million Filipinos overseas.
The New English School, founded in 1969 by Tareq Rajab, is a co-educational British curriculum, English medium, private school in Jabriya, Kuwait, which caters for children between the ages of 3½ and 19.
There are a large number of expatriates in Kuwait, with most residing in Kuwait City. Expatriates are primarily attracted by the employment opportunities in Kuwait. Expatriates account for 69% of Kuwait's total population.

Cebu International School (CIS), was founded as the Cebu American School in 1924, and renamed in 1973. It is a co-educational day school, non-profit, non-sectarian institution, governed by a ten-member Board of Trustees. The current legal status of the school is defined in Republic Act No. 9190 (2003). English is the language of instruction at CIS.
Filipinos in Kuwait are either migrants from or descendants of the Philippines living in Kuwait. As of 2020, there are roughly 241,000 of these Filipinos in Kuwait. Most people in the Filipino community are migrant workers, and approximately 60% of Filipinos in Kuwait are employed as domestic workers.
Filipinos in Saudi Arabia are either migrants or descendants of the Philippines living in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Arabia is currently the largest hirer of Overseas Filipino Workers (OFWs), and has the largest Filipino population in the Middle East. Filipinos make up the fourth-largest group of foreigners in Saudi Arabia, and are the second-largest source of remittances to the Philippines.
Filipinos in Indonesia were estimated to number 4,800 individuals as of 2001, according to the statistics of the Philippine government. Most are based in Jakarta, though there is also a community in Surabaya. This represented growth of nearly five times over the government's 1998 estimate of 1,046 individuals.

The Commission on Filipinos Overseas (CFO) is an agency of the government of the Philippines under the Office of the President of the Philippines. CFO was established on 16 June 1980 through the proclamation of Batas Pambansa Blg. 79. The agency is responsible for promoting and upholding the interest of Filipino emigrants and Filipino permanent residents in other countries. It is also responsible for preserving and strengthening ties with Filipino communities outside the Philippines. It is headed by the Chairman of the Commission on Filipinos Overseas.
Filipinos in Oman are either migrants or descendants of the Philippines living in Oman. As of 2011, there are between 40,000 and 46,000 of these Filipinos in Oman. A large destination for Overseas Filipino workers (OFWs), Oman was the only Middle Eastern nation included on the Philippine Overseas Employment Administration's list of nations safe for OFWs. The country still holds the title up to this day.
Philippine School in Greece (PSG), formerly the Katipunan Philippine Cultural Academy-Philippine School (KAPHILCA-PSG) is a Philippine international school in Vyronas, Attica, Greece; it was previously in Ambelokipi, Athens. The Commission on Filipinos Overseas (CFO) supervises the school, which operates under the Cultural Section of the Philippine embassy in Athens. It is Europe's sole Philippine international school.

International Philippine School in Jeddah is a Philippine international school in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. It serves levels pre-elementary through senior high school. As of 2005 it had over 1,000 students, making it the world's largest Philippine international school.
The New Kuwait Philippines International School is a private school located at Jleeb Al-Shuyoukh, Kuwait. It is one of the two Philippine schools in Kuwait.
A diplomatic crisis began between the countries of Kuwait and the Philippines in early 2018 over concerns of the latter over the situation of Filipino migrant workers in the gulf country.

Overseas Filipinos, including Filipino migrant workers outside the Philippines, have been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. As of June 1, 2021, there have been 19,765 confirmed COVID-19 cases of Filipino citizens residing outside the Philippines with 12,037 recoveries and 1,194 deaths. The official count from the Department of Foreign Affairs (DFA) on the cases of overseas Filipinos is not included in the national tally of the Philippine government. Repatriates on the other hand are included in the national tally of the Department of Health (DOH) but are listed separately from regional counts.







