Marianus Scotus was an Irish monk and chronicler. He authored the Chronica Clara, a history of the world.

Pholidobolus is a genus of lizards in the family Gymnophthalmidae. They occur in north-western South America.

Eleanor of Arborea or Eleanor De Serra Bas was one of the most powerful and important, and one of the last, judges of the Judicate of Arborea in Sardinia, and Sardinia's most famous heroine. She is also known for updating of the Carta de Logu, promulgated by her father Marianus IV and revisited by her brother Hugh III.

The Judicate of Arborea or the Kingdom of Arborea was one of the four independent judicates into which the island of Sardinia was divided in the Middle Ages. It occupied the central-west portion of the island, wedged between Logudoro to the north and east, Cagliari to the south and east, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. To the northeast of Logudoro was Gallura, with which Arborea had far less interaction. Arborea outlasted her neighbours, surviving well into the 15th century. At its greatest territorial extent it occupied the entire island except the cities of Alghero and Cagliari. The earliest known judicial seat was Tharros, though Oristano served as capital for most of its existence.
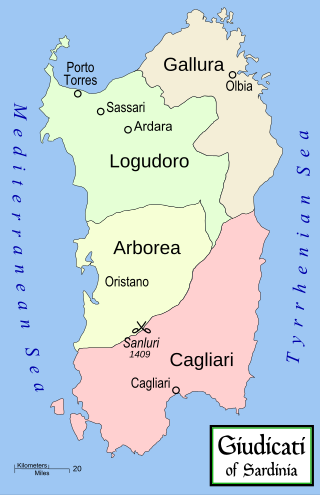
The Kings or Judges of the Arborea were the local rulers of the west of Sardinia during the Middle Ages. Theirs was the longest-lasting judgedom, surviving as an independent state until the fifteenth century.

The Codex Marianus is an Old Church Slavonic fourfold Gospel Book written in Glagolitic script, dated to the beginning of the 11th century, which is, one of the oldest manuscript witnesses to the Old Church Slavonic language, one of the two fourfold gospels being part of the Old Church Slavonic canon.

Marianus IV, called the Great, was the Judge (king) of Arborea, kingdom in the island of Sardinia, from 1347 to his death. He was, as his nickname indicates, the greatest sovereign of Arborea. He was a legislator and a warrior whose reign saw the commencement of massive codification of the laws of his realm and incessant warfare with the Crown of Aragon. He was also a religious man, who had connections to Catherine of Siena. He was, in short, an "wise legislator, able politician, and valiant warrior."

Marianus II was the Judge of Logudoro from 1218 until his death. He was an ally of the Republic of Genoa and enemy of Pisa.
Marianus Scotus of Regensburg, born Muiredach mac Robartaig, was an Irish abbot and scribe.
Marianus is a male name, formerly an ancient Roman family name, derived from Marius. Marianus may refer to:

The House of Binciola or Binčulić was one of the patrician families of Dubrovnik and the Republic of Ragusa, active between the 12th and 17th centuries.
Pholidobolus affinis, Peters's pholiodobolus, is a species of lizard in the family Gymnophthalmidae. It is endemic to Ecuador.
Pholidobolus dicrus, Uzzell's pholiodobolus, is a species of lizard in the family Gymnophthalmidae. It is endemic to Ecuador.
Pholidobolus macbrydei, MacBryde's pholiodobolus, is a species of lizard in the family Gymnophthalmidae. It is endemic to Ecuador.
Pholidobolus montium, the mountain pholiodobolus, is a species of lizard in the family Gymnophthalmidae. It is found in Ecuador and Colombia.
Pholidobolus paramuno is a species of lizard in the family Gymnophthalmidae. It is endemic to Colombia.
Pholidobolus prefrontalis, Montanucci's pholiodobolus, is a species of lizard in the family Gymnophthalmidae. It is endemic to Ecuador.

Pholidobolus vertebralis, the brown pholiodobolus, is a species of lizard in the family Gymnophthalmidae. It is found in Panama, Ecuador, Colombia, and Peru.

Pholidobolus dolichoderes is a species of lizard in the family Gymnophthalmidae. It is endemic to Ecuador.

Pholidobolus samek is a species of lizard in the family Gymnophthalmidae. It is endemic to Ecuador.









