
The banded cat-eyed snake is a species of medium-sized, mildly venomous, colubrid snake endemic to the New World.

Leptodeira is a genus of colubrid snakes commonly referred to as cat-eyed snakes. The genus consists of 12 species that are native to primarily Mexico and Central America, but range as far north as the southern tip of Texas in United States and as far south as Argentina in South America.

Theileria is a genus of parasites that belongs to the phylum Apicomplexa and is closely related to Plasmodium. Two Theileria species, T. annulata and T. parva, are important cattle parasites. T. annulata causes tropical theileriosis and T. parva causes East Coast fever. Theileria are transmitted by ticks. The genomes of T. orientalis Shintoku, Theileria equi WA, Theileria annulata Ankara and Theileria parva Muguga have been sequenced and published.
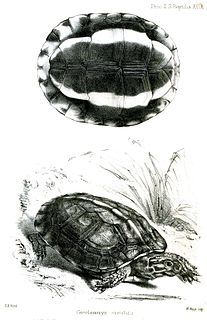
The brown wood turtle or brown land turtle is a species of turtle in the family Geoemydidae. The species is endemic to Central America and northern South America.

Trithemis annulata, known commonly as the violet dropwing, violet-marked darter, purple-blushed darter or plum-coloured dropwing, is a species of dragonfly in the family Libellulidae. It is found in most of Africa, in the Middle East, in the Arabian Peninsula and southern Europe. These insects are called dropwings because of their habit of immediately lowering their wings after landing on a perch. Males of this species are violet-red with red veins in the wings while females are yellow and brown. Both sexes have red eyes.

Naja annulata, commonly known as the banded water cobra or the ringed water cobra, is a species of water cobra native to western and central Africa. The species is one of the two species of water cobras in the world, the other one being the Congo water cobra.

The bandy-bandy, also commonly known as the hoop snake, is a species of venomous snake in the family Elapidae. The species is endemic to Australia. It is considered weakly venomous.

Nyctemera annulata, commonly known as the magpie moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is endemic to New Zealand and found in all parts of the country.

Naja christyi, commonly known as the Congo water cobra or Christy's water cobra, is a species of venomous snakes belonging to the family Elapidae. The species is native to Sub-Saharan Africa. This species was formerly in the genus Boulengerina, but more recent research by Wallach et al. has shown that Boulengerina is actually a subgenus and Boulengerina christyi is a synonym of Naja christyi. This species has no known subspecies.

Bartholomea annulata is a species of sea anemone in the family Aiptasiidae, commonly known as the ringed anemone or corkscrew anemone. It is one of the most common anemones found on reefs in the Caribbean Sea.
This article lists the various snakes of Australia which live in a wide variety of habitats around the continent. The amethystine python or scrub python is considered Australia's largest native snake.
Tragocephalini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the Lamiinae subfamily. It was described by Thomson in 1857.
Phymasterna is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
Chariesthes obscura is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Charles Joseph Gahan in 1890, originally under the genus Phymasterna. It has a wide distribution in Africa.
Phymasterna affinis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1980. It is known from Madagascar.
Phymasterna gracilis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1957. It is known from Madagascar.
Phymasterna lacteoguttata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Laporte de Castelnau in 1840. It is known from Madagascar. It contains the varietas Phymasterna lacteoguttata var. confluens.
Phymasterna maculifrons is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Charles Joseph Gahan in 1890. It is known from Madagascar.
Phymasterna rufocastanea is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Léon Fairmaire in 1889. It is known from Madagascar.
Phymasterna cyaneoguttata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Léon Fairmaire in 1886. It is known from Madagascar.












