Eglin Air Force Base is a United States Air Force (USAF) base in the western Florida Panhandle, located about three miles (5 km) southwest of Valparaiso in Okaloosa County.

Hurlburt Field is a United States Air Force installation located in Okaloosa County, Florida, immediately west of the town of Mary Esther. It is part of the greater Eglin Air Force Base reservation and is home to Headquarters Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC), the 1st Special Operations Wing (1 SOW), the USAF Special Operations School (USAFSOS) and the Air Combat Command's (ACC) 505th Command and Control Wing. It was named for First Lieutenant Donald Wilson Hurlburt, who died in a crash at Eglin. The installation is nearly 6,700 acres (27 km2) and employs nearly 8,000 military personnel.

Kincheloe Air Force Base was a United States Air Force (USAF) base during the Cold War. Built in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan in 1943 during World War II, the base was in service until 1977.
Camp James E. Rudder is host to the third and final phase of a nine-week training course, dubbed the "swamp phase", of the U.S. Army Ranger School. The camp is located on the Eglin Air Force Base reservation, co-located with Eglin AFB Auxiliary Field #6 / Biancur Field, approximately fourteen miles northwest of the main Eglin AFB airfield.

Gunter Annex is a United States Air Force installation located in the North-northeast suburbs of Montgomery, Alabama. The base is named after former Montgomery mayor William Adams Gunter. Until 1992 it was known as Gunter Air Force Base or Gunter Air Force Station. It has been a military training base since its opening in 1940.

War Eagle Field is a former airfield located in the Mojave Desert, about 5-mile (8.0 km) west of Lancaster, California. It is currently used as a detention facility.

Duke Field, also known as Eglin AFB Auxiliary Field #3, is a military airport located three miles (5 km) south of the central business district of Crestview, in Okaloosa County, Florida, United States.

Sharpe Field is a closed private use airport located six nautical miles northwest of the central business district of Tuskegee, a city in Macon County, Alabama, United States. This airport is privately owned by the Bradbury Family Partnership.

Dateland Air Force Auxiliary Field is an abandoned military airfield located in Dateland, Arizona, 40 miles (64 km) east of Yuma, Arizona. Its last known military use was in 1957.

Dalhart Army Air Base is a former World War II military airfield complex near the city of Dalhart, Texas. It operated three training sites for the United States Army Air Forces from 1943 until 1945.

Naval Outlying Landing Field Choctaw is the United States Navy's designation for an auxiliary airfield that was originally constructed during World War II as Eglin Field Auxiliary Field # 10. It is located 16.6 miles northeast of Pensacola, Florida.

Wagner Field,, is a component of Eglin Air Force Base, Florida. It is located northeast of the main base, 13.9 miles northeast of Valparaiso, Florida.

Eagle Pass Army Airfield is a former World War II military airfield complex. It is located 10.6 miles (17.1 km) north of Eagle Pass, Texas. It operated as a training base for the United States Army Air Forces from 1943 until 1945.

Pierce Field,, is a satellite airfield located northeast of the Main Base, 5.5 miles north-northeast of Valparaiso, Florida.

Peel Field,, is a closed United States Air Force field. It is located 5.7 miles west of Valparaiso, Florida.
The Santa Rosa Island Range Complex is a component of the Eglin AFB testing range, located 17.5 miles west-southwest of the main base, on Santa Rosa Island, sitting between the communities of Navarre and Okaloosa Island.
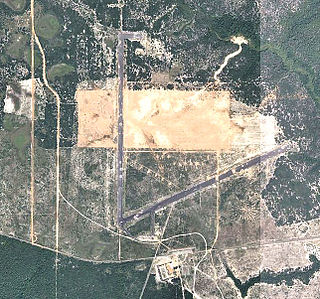
Baldsiefen Field,, is a closed United States Air Force field. It is located 10.2 miles east of Valparaiso, Florida.

Biancur Field,, , is a satellite airfield located northwest of the Main Base, 5.9 miles north-northeast of Valparaiso, Florida. It is also known as site "Test Site B6".

Epler Field,, is a satellite airfield located west-northwest of the Main Base, 18.2 miles west of Valparaiso, Florida. It is designated Site B-12.

Victorville Army Airfield auxiliary fields were four airfields used during World War II to support the Victorville Army Airfield pilot training near Victorville, California, and Adelanto, California. After the war the Victorville Army Airfield was renamed George Air Force Base on January 13, 1948. The airfields were built in 1941 by the United States Army Air Corps just before the war. Victorville Army Airfield covered 2,200-acre in the Mojave Desert. The US Army held a groundbreaking ceremony on 12 July 1941. The base, called Victorville Army Flying School, was ready to use before the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. The Army built four runways in a triangle configuration, with one runway down the middle of the triangle. Seven hangars were built to support operation. On April 23, 1943, the base was renamed Victorville Army Airfield.