
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It began when the United States declared war on 18 June 1812 and, although peace terms were agreed upon in the December 1814 Treaty of Ghent, did not officially end until the peace treaty was ratified by Congress on 17 February 1815.

The Maid of the Mist is a sightseeing boat tour of Niagara Falls, starting and ending on the American side, crossing briefly into Canada during a portion of the trip.

Fort Smith is a town in the South Slave Region of the Northwest Territories (NWT), Canada. It is located in the southeastern portion of the Northwest Territories, on the Slave River and adjacent to the Alberta border along the 60th parallel north.

The Slave River is a Canadian river that flows from the confluence of the Rivière des Rochers and Peace River in northeastern Alberta and empties into Great Slave Lake in the Northwest Territories. The river's name is thought to derive from the name for the Slavey group of the Dene First Nations, Deh Gah Got'ine, in the Athabaskan language. The Chipewyan had displaced other native people from this region.

The Radium King was built in 1937 to haul ore on the Mackenzie River, and her tributaries. This included uranium used in the US atom bombs of World War II. Later in her active career she hauled barges on Great Slave Lake.

The Pride of Baltimore was a reproduction of a typical early 19th-century "Baltimore clipper" topsail schooner. This was a style of vessel made famous by its success as a privateer commerce raider, a small warship in the War of 1812 (1812–1815) against British merchant shipping and the world-wide British Royal Navy. After the end of the war, Baltimore Clippers did not have sufficient cargo capacity for normal merchant trade, so some were used in the illegal opium trade into China and vessels of the same type were used in the transatlantic slave trade from Africa.
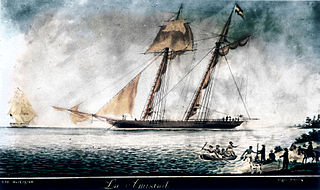
La Amistad was a 19th-century two-masted schooner, owned by a Spaniard colonizing Cuba. It became renowned in July 1839 for a slave revolt by Mende captives, who had been captured and sold to European slave traders, and illegally transported by a Portuguese ship from West Africa to Cuba in violation of existing European treaties against the Atlantic slave trade. Two Spanish plantation owners, Don José Ruiz and Don Pedro Montes, bought 53 captives, including four children, in Havana, Cuba, and were transporting them on the ship to their plantations near Puerto Príncipe. The revolt began after the schooner's cook jokingly told the slaves that they were to be "killed, salted, and cooked." Sengbe Pieh, a Mende man, also known as Joseph Cinqué, unshackled himself and the others on the third day and started the revolt. They took control of the ship, killing the captain and the cook. In the melee, three Africans were also killed.

The steamship Alaskan operated from 1884 to 1889 on the Columbia River and Puget Sound. Alaskan and her near-sistership Olympian were known as "Henry Villard's White Elephants." There were a number of vessels named Alaska and Alaskan, this large side-wheel steamboat should not be confused with them.

The PS Eliza Anderson operated from 1858 to 1898 mainly on Puget Sound, the Strait of Georgia, and the Fraser River but also for short periods in Alaska. She was generally known as the Old Anderson and was considered slow and underpowered even for the time. Even so, it was said of her that "no steamboat ever went slower and made money faster." She played a role in the Underground Railroad and had a desperate last voyage to Alaska as part of the Klondike Gold Rush.

Launched in 1850, Lot Whitcomb, later known as Annie Abernathy, was the first steam-powered craft built on the Willamette River in the U.S. state of Oregon. She was one of the first steam-driven vessels to run on the inland waters of Oregon, and contributed to the rapid economic development of the region.

The sidewheeler Idaho was a steamboat that ran on the Columbia River and Puget Sound from 1860 to 1898. There is some confusion as to the origins of the name; many historians have proposed it is the inspiration for the name of the State of Idaho. Considerable doubt has been cast on this due to the fact that it is unclear if the boat was named before or after the idea of 'Idaho' as a territory name was proposed. John Ruckel also allegedly stated he had named the boat after a Native American term meaning 'Gem of the Mountains' he got from a mining friend from what is now Colorado territory. This steamer should not be confused with the many other vessels of the same name, including the sternwheeler Idaho built in 1903 for service on Lake Coeur d'Alene and the steamship Idaho of the Pacific Coast Steamship Line which sank near Port Townsend, Washington.

The Mackenzie River in Canada's Northwest Territories is a historic waterway, used for centuries by Indigenous peoples, specifically the Dene, as a travel and hunting corridor. Also known as the Deh Cho, it is part of a larger watershed that includes the Slave, Athabasca, and Peace rivers extending from northern Alberta. In the 1780s, Peter Pond, a trader with the North West Company became the first known European to visit this watershed and begin viable trade with the Athapascan-speaking Dene of these rivers. The Mackenzie River itself, the great waterway extending to the Arctic Ocean, was first put on European maps by Alexander Mackenzie in 1789, the Scottish trader who explored the river. The watershed thus became a vital part of the North American fur trade, and before the advent of the airplane or road networks, the river was the only communication link between northern trading posts and the south. Water travel increased in the late 19th century as traders, dominated primarily by the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), looked to increase water services in the Mackenzie River District.

The Ingham Incident, or the Montezuma Affair, was a naval battle fought in 1835, the first between Mexico and the United States. The Mexican warship Montezuma patrolled the coast of Texas to prevent the smuggling of contraband into the territory. During the cruise, the Mexicans captured the American merchant ship Martha and later the Texan ship Columbia which led to a response by the United States Revenue-Marine revenue cutter USRC Ingham. A bloodless engagement was fought on June 14, and ended when the Montezuma was purposely run aground to prevent capture.

Portland is a sternwheel steamboat built in 1947 for the Port of Portland, Oregon, in the United States.

The Nimbin was a steel screw steamer built in 1927 at Copenhagen, that was the first motor vessel placed into the New South Wales coastal trade. It was owned and operated by the North Coast Steam Navigation Company and was the first Australian registered merchant ship to be lost during World War II when it struck a mine laid by the German auxiliary cruiser Pinguin. The Nimbin was on its way from Coffs Harbour to its home port, Sydney, with a cargo of bundled three-ply timber and a cargo of pigs. One third of the ship was blown away and it sank in three minutes. Seven men were killed. The remaining thirteen clung to bundles of plywood. Some hours later an air force plane from RAAF Base Rathmines saw the survivors and directed the coastal ship SS Bonalbo to the scene to retrieve them.

The Radium Express is a Russel Brothers tugboat operated by the Northern Transportation Company. The vessel was built in Owen Sound, Ontario, disassembled, and then shipped by rail to Waterways, Alberta, which was then the terminus of the North American railway grid.

The Radium Yellowknife is a Canadian tugboat. Like other vessels built for service on the MacKenzie River, its tributaries, and Great Bear Lake and Great Slave Lake, she was first built in a shipyard in Vancouver, British Columbia, then disassembled and shipped by rail to Waterways, Alberta. There she was reassembled and launched into Clearwater River on August 18, 1948 - late in the season, as the rivers used to freeze in late September or early October. Her reassembly was delayed initially by floods in the Fraser valley in May hindering transport, and then by a derailment of several of the railway cars carrying her components. After launch, she sailed to the portage on the Slave River at Fort Smith, Northwest Territories and was dragged overland across the portage to the lower river, where she could then access the Great Slave Lake, the MacKenzie River, and the Beaufort Sea.

The Radium Cruiser was a Russel Brothers tugboat operated on the Mackenzie River system for the "Radium Line". She was constructed in Owen Sound, Ontario, in 1939, then disassembled and shipped by rail to Waterways, Alberta. Waterways is a river port, and was then the northern terminus of the North American railway grid. Waterways is on the Clearwater River, not far upstream from where the river empties into Lake Athabasca. The waters of Lake Athabasca flow into Great Slave Lake down the Slave River, and then down the Mackenzie River to the Arctic Ocean.

The Radium Gilbert was a tugboat built for transporting supplies to, and ore from, the radium and uranium mines in Canada's Northwest Territories. Like the other tugs in the Radium Line she was steel-hulled.

Polly Strong was an enslaved woman in the Northwest Territory, in present-day Indiana. She was born after the Northwest Ordinance prohibited slavery. Slavery was prohibited by the Constitution of Indiana in 1816. Two years later, Strong's mother Jenny and attorney Moses Tabbs asked for a writ of habeas corpus for Polly and her brother James in 1818. Judge Thomas H. Blake produced indentures, Polly for 12 more years and James for four more years of servitude. The case was dismissed in 1819.





















