
A watch is a portable timepiece intended to be carried or worn by a person. It is designed to keep a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is designed to be worn around the wrist, attached by a watch strap or other type of bracelet, including metal bands, leather straps, or any other kind of bracelet. A pocket watch is designed for a person to carry in a pocket, often attached to a chain.

The grasshopper escapement is a low-friction escapement for pendulum clocks invented by British clockmaker John Harrison around 1722. An escapement, part of every mechanical clock, is the mechanism that gives the clock's pendulum periodic pushes to keep it swinging, and each swing releases the clock's gears to move forward by a fixed amount, thus moving the hands forward at a steady rate. The grasshopper escapement was used in a few regulator clocks built during Harrison's time, and a few others over the years, but has never seen wide use. The term "grasshopper" in this connection, apparently from the kicking action of the pallets, first appears in the Horological Journal in the late 19th century.
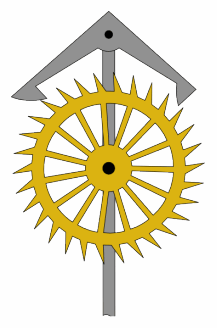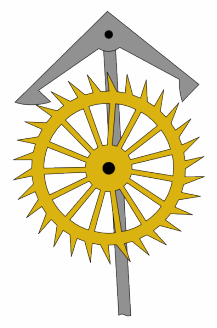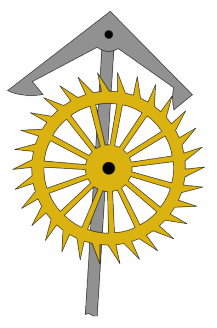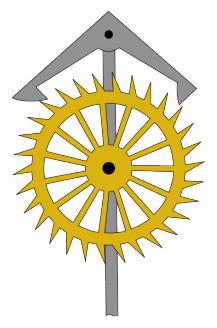
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy to the clock's timekeeping element to replace the energy lost to friction during its cycle and keep the timekeeper oscillating. The escapement is driven by force from a coiled spring or a suspended weight, transmitted through the timepiece's gear train. Each swing of the pendulum or balance wheel releases a tooth of the escapement's escape wheel, allowing the clock's gear train to advance or "escape" by a fixed amount. This regular periodic advancement moves the clock's hands forward at a steady rate. At the same time, the tooth gives the timekeeping element a push, before another tooth catches on the escapement's pallet, returning the escapement to its "locked" state. The sudden stopping of the escapement's tooth is what generates the characteristic "ticking" sound heard in operating mechanical clocks and watches.

A pocket watch is a watch that is made to be carried in a pocket, as opposed to a wristwatch, which is strapped to the wrist.

In horology, a movement, also known as a caliber or calibre, is the mechanism of a watch or timepiece, as opposed to the case, which encloses and protects the movement, and the face, which displays the time. The term originated with mechanical timepieces, whose clockwork movements are made of many moving parts. The movement of a digital watch is more commonly known as a module.

A mainspring is a spiral torsion spring of metal ribbon—commonly spring steel—used as a power source in mechanical watches, some clocks, and other clockwork mechanisms. Winding the timepiece, by turning a knob or key, stores energy in the mainspring by twisting the spiral tighter. The force of the mainspring then turns the clock's wheels as it unwinds, until the next winding is needed. The adjectives wind-up and spring-powered refer to mechanisms powered by mainsprings, which also include kitchen timers, metronomes, music boxes, wind-up toys and clockwork radios.

In horology, the anchor escapement is a type of escapement used in pendulum clocks. The escapement is a mechanism in a mechanical clock that maintains the swing of the pendulum by giving it a small push each swing, and allows the clock's wheels to advance a fixed amount with each swing, moving the clock's hands forward. The anchor escapement was so named because one of its principal parts is shaped vaguely like a ship's anchor.

The vergeescapement is the earliest known type of mechanical escapement, the mechanism in a mechanical clock that controls its rate by allowing the gear train to advance at regular intervals or 'ticks'. Verge escapements were used from the late 13th century until the mid 19th century in clocks and pocketwatches. The name verge comes from the Latin virga, meaning stick or rod.

Oris SA is a Swiss luxury manufacturer of mechanical watches. The company was founded in 1904 and is based in Hölstein in the canton of Basel-Landschaft.

In horology, a tourbillon is an addition to the mechanics of a watch escapement to increase accuracy. Conceived by the British watchmaker and inventor John Arnold, it was developed by his friend the Swiss-French watchmaker Abraham-Louis Breguet and patented by Breguet on 26 June 1801. In a tourbillon the escapement and balance wheel are mounted in a rotating cage, with the goal of eliminating errors of poise in the balance giving a uniform weight.

The pallet fork is a component of the lever escapement of a mechanical watch. The pallet fork and the lever form one component that sits between the escape wheel and the balance wheel. Its purpose is to lock the escape wheel, and release it one tooth at a time at each swing of the balance wheel, and also give the balance wheel small pushes to keep it going.

A dollar watch was a pocket watch or later, a wristwatch, that sold for about one US dollar.
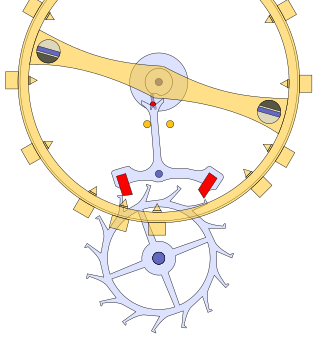
The lever escapement, invented by the English clockmaker Thomas Mudge in 1754, is a type of escapement that is used in almost all mechanical watches, as well as small mechanical non-pendulum clocks, alarm clocks, and kitchen timers.

The history of watches began in 16th-century Europe, where watches evolved from portable spring-driven clocks, which first appeared in the 15th century.

The coaxial escapement is a type of modern watch escapement mechanism invented by English watchmaker George Daniels in 1976 and patented in 1980. It is one of the few watch escapements to be invented in modern times and is used in most of the mechanical watch models currently produced by Omega SA.

A mechanical watch is a watch that uses a clockwork mechanism to measure the passage of time, as opposed to quartz watches which function using the vibration modes of a piezoelectric quartz tuning fork, or radio watches, which are quartz watches synchronized to an atomic clock via radio waves. A mechanical watch is driven by a mainspring which must be wound either periodically by hand or via a self-winding mechanism. Its force is transmitted through a series of gears to power the balance wheel, a weighted wheel which oscillates back and forth at a constant rate. A device called an escapement releases the watch's wheels to move forward a small amount with each swing of the balance wheel, moving the watch's hands forward at a constant rate. The escapement is what makes the 'ticking' sound which is heard in an operating mechanical watch. Mechanical watches evolved in Europe in the 17th century from spring powered clocks, which appeared in the 15th century.

Georges Frederic Roskopf, the inventor of the pin-pallet escapement, was born in Germany and became a naturalized Swiss citizen.
In horology, a wheel train is the gear train of a mechanical watch or clock. Although the term is used for other types of gear trains, the long history of mechanical timepieces has created a traditional terminology for their gear trains which is not used in other applications of gears.
The échappement naturel was the invention of Abraham-Louis Breguet, one of the most eminent watchmakers of all time. Following the introduction of the detent chronometer escapement with a temperature compensated balance, very close rates could be achieved in marine chronometers and to a lesser degree in pocket chronometers. This achievement was due, other things being equal, to the minimal interference with the balance during unlocking and impulse. A further key advantage of this escapement was that there was no need for oil on the escapement's working surfaces and hence no deterioration in the friction between the working surfaces as the oil aged. A drawback was that the detent escapement as it was used in pocket chronometers was prone to stopping as a result of motion. Most escapements are capable of being stopped by a sudden movement but the detent escapement gives an impulse to the balance only when it is moving in one direction. The escapement is therefore not self-starting. The lever escapement, as used in most modern mechanical watches, avoided this problem. In common with most other escapements it gave an impulse to the balance in both directions of the balance swing. This creates another problem in doing so because the introduction of a lever between the balance and the final (escape) wheel of the escapement requires lubrication on the acting surfaces.

















