| Pineal gland cyst | |
|---|---|
 | |
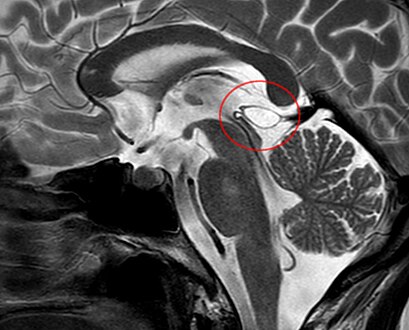
| Calcified cyst of pineal gland in CT. Sagittal MPR. |
A pineal gland cyst is a usually benign (non-malignant) cyst in the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland in the brain. Historically, these fluid-filled bodies appeared on 1-4% of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain scans, but were more frequently diagnosed at death, seen in 4-11% of autopsies. [1] A 2007 study by Pu et al. found a frequency of 23% in brain scans (with a mean diameter of 4.3 mm). [1]
Contents
The National Organization for Rare Disorders states that pineal cysts larger than 5.0 mm are "rare findings" and are possibly symptomatic. If narrowing of the cerebral aqueduct occurs, many neurological symptoms may exist, including headaches, vertigo, nausea, muscle fasciculations, eye sensitivity, and ataxia. Continued monitoring of the cyst might be recommended to monitor its growth, and surgery may be necessary. [2]