Related Research Articles
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the binding of Ca2+ is required for the activation of calmodulin. Once bound to Ca2+, calmodulin acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway by modifying its interactions with various target proteins such as kinases or phosphatases.

Calcineurin (CaN) is a calcium and calmodulin dependent serine/threonine protein phosphatase. It activates the T cells of the immune system and can be blocked by drugs. Calcineurin activates nuclear factor of activated T cell cytoplasmic (NFATc), a transcription factor, by dephosphorylating it. The activated NFATc is then translocated into the nucleus, where it upregulates the expression of interleukin 2 (IL-2), which, in turn, stimulates the growth and differentiation of the T cell response. Calcineurin is the target of a class of drugs called calcineurin inhibitors, which include ciclosporin, voclosporin, pimecrolimus and tacrolimus.
Calmodulin-binding proteins are, as their name implies, proteins which bind calmodulin. Calmodulin can bind to a variety of proteins through a two-step binding mechanism, namely "conformational and mutually induced fit", where typically two domains of calmodulin wrap around an emerging helical calmodulin binding domain from the target protein.

Caldesmon is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALD1 gene.

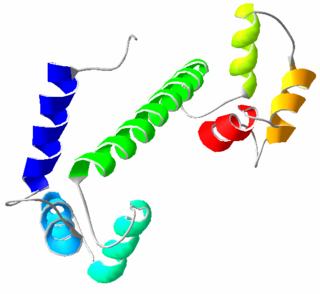
Calmodulin 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALM1 gene.

Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II beta chain is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK2B gene.

Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF1 gene.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK4 gene.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II gamma chain is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK2G gene.
In enzymology, an elongation factor 2 kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a myosin-heavy-chain kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
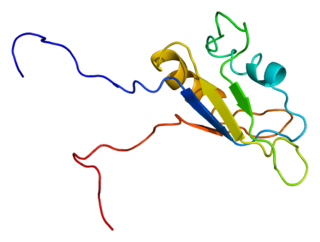
RNA-binding protein EWS is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EWSR1 gene on human chromosome 22, specifically 22q12.2. It is one of 3 proteins in the FET protein family. The q22.2 region of chromosome 22 encodes the N-terminal transactivation domain of the EWS protein and that region may become joined to one of several other chromosomes which encode various transcription factors, see and the FET protein family. The expression of a chimeric protein with the EWS transactivation domain fused to the DNA binding region of a transcription factor generates a powerful oncogenic protein causing Ewing sarcoma and other members of the Ewing family of tumors. These translocations can occur due to chromoplexy, a burst of complex chromosomal rearrangements seen in cancer cells. The normal EWS gene encodes an RNA binding protein closely related to FUS (gene) and TAF15, all of which have been associated to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.

Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 (IQGAP1) also known as p195 is a ubiquitously expressed protein that in humans is encoded by the IQGAP1 gene. IQGAP1 is a scaffold protein involved in regulating various cellular processes ranging from organization of the actin cytoskeleton, transcription, and cellular adhesion to regulating the cell cycle.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK1 gene.

Nuclear receptor coactivator 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCOA6 gene.

Phosphorylase b kinase gamma catalytic chain, skeletal muscle isoform is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PHKG1 gene.

Calmodulin-like protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALML3 gene.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMKK1 gene.

Calmodulin-like protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALML5 gene.
References
- 1 2 3 Reddy VS, Ali GS, Reddy AS (May 2003). "Characterization of a pathogen-induced calmodulin-binding protein: mapping of four Ca2+-dependent calmodulin-binding domains". Plant Mol. Biol. 52 (1): 143–59. doi:10.1023/A:1023993713849. PMID 12825696. S2CID 17859588.
- 1 2 3 Reddy AS, Day IS, Narasimhulu SB, Safadi F, Reddy VS, Golovkin M, Harnly MJ (February 2002). "Isolation and characterization of a novel calmodulin-binding protein from potato". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (6): 4206–14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M104595200 . PMID 11684678.