
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, classified according to the monomers used and the structure of the biopolymer formed: polynucleotides, polypeptides, and polysaccharides. The Polynucleotides, RNA and DNA, are long polymers of nucleotides. Polypeptides include proteins and shorter polymers of amino acids; some major examples include collagen, actin, and fibrin. Polysaccharides are linear or branched chains of sugar carbohydrates; examples include starch, cellulose, and alginate. Other examples of biopolymers include natural rubbers, suberin and lignin, cutin and cutan, melanin, and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs).

Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances.

Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a poor barrier to air and water vapor and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, with the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year. Polystyrene is naturally transparent, but can be colored with colorants. Uses include protective packaging, containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery, in the making of models, and as an alternative material for phonograph records.

A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.

Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)x·(C4H6)y·(C3H3N)z ) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately 105 °C (221 °F). ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.

Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals, glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.

Wood–plastic composites (WPCs) are composite materials made of wood fiber/wood flour and thermoplastic(s) such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or polylactic acid (PLA).

Microcellular plastics, otherwise known as microcellular foam, is a form of manufactured plastic fabricated to contain billions of tiny bubbles less than 50 microns wide. It is formed by dissolving gas under high pressure into various polymers, relying on the phenomenon of thermodynamic instability to cause the uniform arrangement of the gas bubbles, otherwise known as nucleation. Its main purpose was to reduce material usage while maintaining valuable mechanical properties. the density of the finished product is determined by the gas used. Depending on the gas, the foam's density can be between 5% and 99% of the pre-processed plastic. Design parameters, focused on the foam's final form and the molding process afterward, include the type of die or mold to be used, as well as the dimensions of the bubbles, or cells, that classify the material as a foam. Since the cells' size is close to the wavelength of light, to the casual observer the foam retains the appearance of a solid, light-colored plastic.
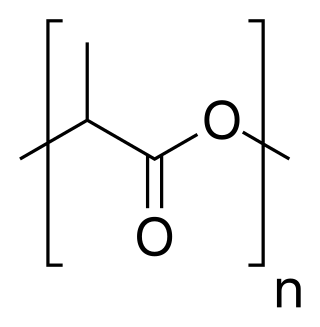
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a thermoplastic polyester with backbone formula (C
3H
4O
2)
n or [–C(CH
3)HC(=O)O–]
n, formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid C(CH
3)(OH)HCOOH with loss of water. It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide [–C(CH
3)HC(=O)O–]
2, the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit.

Bioplastics are plastic materials produced from renewable biomass sources, such as vegetable fats and oils, corn starch and rice starch, straw, woodchips, sawdust, recycled food waste, etc. Some bioplastics are obtained by processing directly from natural biopolymers including polysaccharides and proteins, while others are chemically synthesized from sugar derivatives and lipids from either plants or animals, or biologically generated by fermentation of sugars or lipids. In contrast, common plastics, such as fossil-fuel plastics are derived from petroleum or natural gas.
Polyethylene or polythene film biodegrades naturally, albeit over a long period of time. Methods are available to make it more degradable under certain conditions of sunlight, moisture, oxygen, and composting and enhancement of biodegradation by reducing the hydrophobic polymer and increasing hydrophilic properties.

Biodegradable plastics are plastics that can be decomposed by the action of living organisms, usually microbes, into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. Biodegradable plastics are commonly produced with renewable raw materials, micro-organisms, petrochemicals, or combinations of all three.

A plastic bottle is a bottle constructed from high-density or low density plastic. Plastic bottles are typically used to store liquids such as water, soft drinks, motor oil, cooking oil, medicine, shampoo, milk, ink, etc. They come in a range of sizes, from very small bottles to large carboys. Consumer blow molded containers often have integral handles or are shaped to facilitate grasping.

Filler materials are particles added to resin or binders that can improve specific properties, make the product cheaper, or a mixture of both. The two largest segments for filler material use is elastomers and plastics. Worldwide, more than 53 million tons of fillers are used every year in application areas such as paper, plastics, rubber, paints, coatings, adhesives, and sealants. As such, fillers, produced by more than 700 companies, rank among the world's major raw materials and are contained in a variety of goods for daily consumer needs. The top filler materials used are ground calcium carbonate (GCC), precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC), kaolin, talc, and carbon black.
Aseptic processing is a processing technique wherein commercially thermally sterilized liquid products are packaged into previously sterilized containers under sterile conditions to produce shelf-stable products that do not need refrigeration. Aseptic processing has almost completely replaced in-container sterilization of liquid foods, including milk, fruit juices and concentrates, cream, yogurt, salad dressing, liquid egg, and ice cream mix. There has been an increasing popularity for foods that contain small discrete particles, such as cottage cheese, baby foods, tomato products, fruit and vegetables, soups, and rice desserts.
PBAT is a biodegradable random copolymer, specifically a copolyester of adipic acid, 1,4-butanediol and terephthalic acid. PBAT is produced by many different manufacturers and may be known by the brand names ecoflex, Wango,Ecoworld, Eastar Bio, and Origo-Bi. It is also called poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and sometimes polybutyrate-adipate-terephthalate or even just "polybutyrate". It is generally marketed as a fully biodegradable alternative to low-density polyethylene, having many similar properties including flexibility and resilience, allowing it to be used for many similar uses such as plastic bags and wraps. The structure is a random-block polymer consisting of butanediol–adipic acid and butanediol-terephthalic acid blocks.

Biodegradable bags are bags that are capable of being decomposed by bacteria or other living organisms.

Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be molded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to their widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives.

Setralit is a technical natural fiber based on plant fibers whose property profile has been modified selectively in order to meet different industrial requirements. It was first manufactured in 1989 by Jean-Léon Spehner, an Alsatian engineer, and further developed by the German company ECCO Gleittechnik GmbH. The name “Setralit“ is derived from the French company Setral S.à.r.l. which is a subsidiary company of ECCO, where Spehner was employed at that time. Setralit was officially described first in 1990.

Biodegradable athletic footwear is athletic footwear that uses biodegradable materials with the ability to compost at the end-of-life phase. Such materials include natural biodegradable polymers, synthetic biodegradable polymers, and biodegradable blends. The use of biodegradable materials is a long-term solution to landfill pollution that can significantly help protect the natural environment by replacing the synthetic, non-biodegradable polymers found in athletic footwear.
















