
Epaminondas is a strategy board game invented by Robert Abbott in 1975. The game is named after the Theban general Epaminondas, known for the use of phalanx strategy in combat. The concept of the phalanx is integral to the game.

TwixT is a two-player strategy board game, an early entrant in the 1960s 3M bookshelf game series. It became one of the most popular and enduring games in the series. It is a connection game where players alternate turns placing pegs and links on a pegboard in an attempt to link their opposite sides. While TwixT itself is simple, the game also requires strategy, so young children can play it, but it also appeals to adults. The game has been discontinued except in Germany and Japan.
Martian Chess is an abstract strategy game for two or four players invented by Andrew Looney in 1999. It is played with Icehouse pyramids on a chessboard. To play with a number of players other than two or four, a non-Euclidean surface can be tiled to produce a board of the required size, allowing up to six players.

Feudal is a chess-like board wargame for 2–6 players on two or four opposing sides. It was originally published by 3M Company in 1967 as part of its bookshelf game series, and was republished by Avalon Hill after they purchased 3M's game division. The object of the game is to either occupy one's opponent's castle or to capture all of one's opponent's royalty. There are six sets of plastic pieces in three shades each of blue and brown. Each set consists of thirteen mobile figures with differing methods of movement and attack, and a stationary castle piece. The play area consists of four plastic peg boards depicting empty, rough, and mountainous terrain.

Janggi, sometimes called Korean chess, is a strategy board game popular on the Korean Peninsula. The game was derived from xiangqi, and is very similar to it, including the starting position of some of the pieces, and the 9×10 gameboard, but without the xiangqi "river" dividing the board horizontally in the middle.

Sittuyin, also known as Burmese chess, is a strategy board game created in Myanmar. It is a direct offspring of the Indian game of chaturanga, which arrived in Myanmar in the 8th century thus it is part of the same family of games such as chess, and shogi. Sit is the modern Burmese word for "army" or "war"; the word sittuyin can be translated as "representation of the four characteristics of army"—chariot, elephant, cavalry and infantry.

Jetan, also known as Martian chess, is a chess variant first published in 1922. It was created by Edgar Rice Burroughs as a game played on Barsoom, his fictional version of Mars. The game was introduced in The Chessmen of Mars, the fifth book in the Barsoom series. Its rules are described in Chapter 2 and in the Appendix of the book, with an actual game partly described in Chapter 17.
Duell, also published under other names, is a two-player board game played with dice on a board of 9×8 squares. Players take turns moving one of their dice in order to capture their opponent's pieces, with the ultimate aim of capturing the opponent's key piece to win the game. It is considered a chess variant.

Breakthru is an abstract strategy board game for two players, designed by Alex Randolph and commercially released by 3M in 1965, as part of the 3M bookshelf game series. It later became part of the Avalon Hill bookcase games. It is no longer in production. The game has been compared to Fox and Hounds, although it shows more characteristics of the Tafl games of the Middle Ages, such as Hnefatafl.

Neutron is a two-player abstract strategy game invented by Robert A. Kraus. The game was first published in the Playroom section of Games & Puzzles in 1978. It is a game where each player moves two different pieces in a single turn without the use of dice.

Bear games is a category of board games of which many have historical roots in the Roman Empire. They were played in parts of the Empire as far away as Turkey and France and are still played today, especially in Italy. All of the games are two-player abstract strategy board games. Normally, the game is played with three hunters and one bear on a patterned board. It bears similarity to the hunt games such as the fox games, rimau-rimau, and bagha-chall, however, there are no captures involved. The three hunters are trying to hem in the bear, and block its movements.
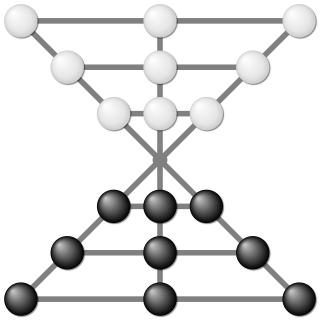
Lau kata kati is a two-player abstract strategy game from India, specifically from Lower Bengal, and also from United Provinces, Karwi Subdivision where it is called Kowwu Dunki, and it was described by H.J.R. Murray in A History of Board-Games Other Than Chess (1952). The game is related to draughts and even more so to Alquerque. Pieces are captured by leaping over them. The board is a pattern of two triangles joined together at a common vertex with further lines subdividing them. It is the same game as Butterfly (game) from Mozambique, which suggests a historical connection between the two games. Lau kata kati belongs to a specific category of games called Indian War-games, and the other games in this category are Dash-guti, Egara-guti, Pretwa, Gol-skuish. All Indian War-games have one important thing in common, and that is that all the pieces are laid out on the patterned board, with only one vacant point in the center. This forces the first move to be played on the central point, and captured by the other player's piece.
Dash-guti is a two-player abstract strategy board game from India, specifically from Central Provinces, United Provinces, Karwi Subdivision where it is called Kowwu Dunki which is the same name given to another similar game called Lau kata kati, and it was described by H.J.R. Murray in A History of Board-Games Other Than Chess (1952). The game is related to Draughts and even more so to Alquerque. Pieces are captured by leaping over them. Dash-guti consists of a Lau kata kati board, but with the addition of two line segments connected to the vertex but exterior to both triangles. Dash-guti belongs to a specific category of games called Indian War-games, and the other games in this category are Lau kata kati, Egara-guti, Pretwa, Gol-skuish. All Indian War-games have one important thing in common, and that is that all the pieces are laid out on the grid patterned board, with only one vacant point in the centre. This forces the first move to be played on the central point, and captured by the other player's piece.
Egara-guti is a two-player abstract strategy game from India, specifically from Central Provinces, and it was described by H.J.R. Murray in A History of Board-Games Other Than Chess (1952). The game is related to Draughts and even more so to Alquerque. Pieces are captured by leaping over them. Egara-Guti consists of a Lau kata kati board, but with the addition of two lines connecting the two triangles and running through them. Egara-guti belongs to a specific category of games called Indian War-games; some other games in this category are Lau kata kati, Dash-guti, Pretwa, Gol-skuish. All Indian War-games have one important thing in common, and that is that all the pieces are laid out on the grid patterned board in the beginning, with only one vacant point in the center. This forces the first move to be played on the central point, and captured by the other player's piece.

Zillions of Games is a commercial general game playing system developed by Jeff Mallett and Mark Lefler in 1998. The game rules are specified with S-expressions, Zillions rule language. It was designed to handle mostly abstract strategy board games or puzzles. After parsing the rules of the game, the system's artificial intelligence can automatically play one or more players. It treats puzzles as solitaire games and its AI can be used to solve them.

Dragonfly is a chess variant invented by Christian Freeling in 1983. There are no queens, and a captured bishop, knight, or rook becomes the property of the capturer, who may play it as their own on a turn to any open square. The board is 7×7 squares, or alternatively a 61-cell hexagon with two additional pawns per side.

Tri-chess is the name of a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board comprising 150 triangular cells. The standard chess pieces are present, minus the queens, and plus the chancellor and cardinal compound fairy pieces per side.

Congo is a chess variant invented by Demian Freeling in 1982 when he was nearly 8 years old. His father encouraged him to design a variant using a 7×7 gameboard. Demian was already familiar with chess and xiangqi, and the result blends some features from both. Congo became the second-most popular chess variant at the Fanaat games club in Enschede, the Netherlands.
This glossary of board games explains commonly used terms in board games, in alphabetical order. For a list of board games, see List of board games; for terms specific to chess, see Glossary of chess; for terms specific to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems.
















