Related Research Articles

Yukon–Koyukuk Census Area is a census area in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2010 census, the population was 5,588. It has the largest area of any county or county-equivalent in the United States. It is part of the unorganized borough of Alaska and therefore has no borough seat. Its largest communities are the cities of Galena, in the west, and Fort Yukon, in the northeast.

Cordova is a city in Chugach Census Area, Alaska, United States. It lies near the mouth of the Copper River, at the head of Orca Inlet on the east side of Prince William Sound. The population was 2,239 at the 2010 census, down from 2,454 in 2000. Cordova was named Puerto Cordova by Spanish explorer Salvador Fidalgo in 1790. No roads connect Cordova to other Alaskan communities, so a plane or ferry is required to travel there. In the Exxon Valdez oil spill of March 1989, an oil tanker ran aground northwest of Cordova, heavily damaging ecology and fishing. It was cleaned up shortly after, but there are lingering effects, such as a lowered population of some birds.

Nenana (Lower Tanana: Toghotili; is a home rule city in the Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area of the Unorganized Borough in the Interior of the U.S. state of Alaska. Nenana developed as a Lower Tanana community at the confluence where the tributary Nenana River enters the Tanana. The population was 378 at the 2010 census, down from 402 in 2000.

Tanana is a city in the Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area in the U.S. state of Alaska. At the 2010 census the population was 246, down from 308 in 2000. It was formerly known as Clachotin, adopted by Canadian French.

The Tanana River is a 584-mile (940 km) tributary of the Yukon River in the U.S. state of Alaska. According to linguist and anthropologist William Bright, the name is from the Koyukon (Athabaskan) tene no, tenene, literally "trail river".
The Eyak are a Native American indigenous group historically located on the Copper River Delta and near the town of Cordova, Alaska. Today, Eyak people live in Cordova, Yakutat, and across Alaska and the U.S. Many of them do not qualify to be tribal members in the Native Village of Eyak, a federally recognized Alaska Native tribe established through the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act in 1971, due to the enrollment qualifications that extend tribal membership only to be those who reside in the town of Cordova, Alaska for the majority of the year.

The Department of Alaska was the designation for the government of Alaska from its purchase by the United States of America in 1867 until its organization as the District of Alaska in 1884. During the department era, Alaska was variously under the jurisdiction of the U.S. Army, the U.S. Dept. of the Treasury and the U.S. Navy. The area later became the District of Alaska, then the Territory of Alaska, then the State of Alaska.

The Copper River or Ahtna River, Ahtna Athabascan ‘Atna’tuu, "river of the Ahtnas", Tlingit Eeḵhéeni, "river of copper", is a 290-mile (470 km) river in south-central Alaska in the United States. It drains a large region of the Wrangell Mountains and Chugach Mountains into the Gulf of Alaska. It is known for its extensive delta ecosystem, as well as for its prolific runs of wild salmon, which are among the most highly prized stocks in the world. The river is the tenth largest in the United States, as ranked by average discharge volume at its mouth.

The Copper River and Northwestern Railway (CR&NW) consisted of two rail lines, the Copper River line and the Northwestern line. Michael James Heney had secured the right-of-way up the Copper River in 1904. He started building the railway from Cordova, Alaska in 1906. The town of Cordova, Alaska, was actually named by Heney on March 13, 1906, based on the original name given by Salvador Fidalgo. Both these railroads were abandoned and little remains of them. Only a 0-4-0 locomotive, "Ole", located near Goose City on a siding of the Alaska Anthracite Railroad Company is the only equipment left. Many of the holdings of the CR&NW railroad including Ole were acquired for this railroad by Mr. Clark Davis and his partners in 1908 after a major storm destroyed the Katalla area facilities in 1907. The town of Cordova would like to move Ole to a memorial site in Cordova to celebrate its role in these railroads. Ole was declared eligible for the National Register of Historic Places in 1988.

Orca Inlet is an arm of Prince William Sound in southern Alaska. The town of Cordova was founded on its coast in 1906. All marine traffic reaches the town through Orca Inlet.
The Alaska Native Regional Corporations were established in 1971 when the United States Congress passed the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA) which settled land and financial claims made by the Alaska Natives and provided for the establishment of 13 regional corporations to administer those claims.
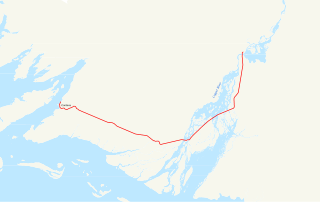
The Copper River Highway extends 49.5 miles (79.7 km) from Cordova along the old railbed of the Copper River and Northwestern Railway. Construction began in 1945, and was originally intended to link Cordova with the state highway system at Chitina. The Million Dollar Bridge, which had carried trains until the CR&NW shut down, was converted for highway use. It is one of two discontinuous segments of Alaska Route 10.

Cape Nome is a headland on the Seward Peninsula in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is situated on the northern shore of Norton Sound, 15 miles (24 km) to the east of Nome also on Norton Sound. It is delimited by the Norton Sound to the south, Hastings Creek on the west, a lagoon on the east and an estuary formed by the Flambeau River and the Eldorado River. From the sea shore, Cape Nome extends inland by about 4 miles (6.4 km), connected by road with Nome.
John Bremner (1833–1887) was a prospector and early explorer of Alaska.
Baker Creek is a right bank tributary of the Tanana River in the U.S. state of Alaska. Baker Creek tributaries include Thanksgiving, Gold Run, Eureka, and Pioneer creeks; Seattle Junior Creek is a tributary of Pioneer Creek. The Baker Creek diggings of the early 20th century were situated approximately 30 miles (48 km) south of Rampart.
Valdez-Yukon Railroad was an early 20th century railway in the U.S. state of Alaska, built subsequent to the Klondike Gold Rush. The Valdez-Yukon Railroad Company was organized in 1905 for the purpose of building a railroad from Valdez to Eagle City, and to tap the rich copper and gold districts of the Copper, Chitina, and Tanana rivers. The line was discontinued after reaching Keystone Canyon.
Arthur Harper (1835–1897) was an Irish-born Yukon River prospector, trader, and explorer, recognized as the first man to enter the Yukon country seeking gold. He mined in California in the 1850s, and British Columbia through the 1860s, before taking off for the Yukon in 1871. He reached Fort Yukon in 1873, and ran a store with Jack McQuesten at the Fortymile River. Harper formed a trading partnership with McQuesten and Captain Al Mayo; their company founded Fort Reliance in 1874 and other posts in the Yukon. Harper was known as the best prospector of the trio, and while he did not achieve major success in his pursuit of gold, he sometimes pointed others to finds. He traded and prospected in Alaska until just before his death.
Moira Sound is a branching inlet on the east side of the southern end of Prince of Wales Island in U.S. state of Alaska. It is situated within the Tongass National Forest.

Nuchek (Núciq) is an abandoned village in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on Hinchinbrook Island at Port Etches bay, Prince William Sound. It is situated approximately 50 miles (80 km) to the west of the mouth of Copper River and 432 miles (695 km) west of Sitka.
References
- ↑ Allen 1887, p. 36.
- ↑ Baker 1906, p. 674.
- ↑ "The Eyak People". Cordova Museum. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
Bibliography
- Allen, Henry Tureman (1887). Report of an Expedition to the Copper, Tananá, and Kóyukuk Rivers, in the Territory of Alaska in the Year 1885: For the Purpose of Obtaining All Information which Will be Valuable and Important, Especially to the Military Branch of the Government : Made Under the Direction of Nelson A. Miles ... (Public domain ed.). U.S. Government Printing Office.
- Baker, Marcus (1906). Geographic Dictionary of Alaska (Public domain ed.). U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 674.
Attribution
-
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : H. T. Allen's Report of an Expedition to the Copper, Tananá, and Kóyukuk Rivers, in the Territory of Alaska in the Year 1885: For the Purpose of Obtaining All Information which Will be Valuable and Important, Especially to the Military Branch of the Government : Made Under the Direction of Nelson A. Miles (1887)
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : H. T. Allen's Report of an Expedition to the Copper, Tananá, and Kóyukuk Rivers, in the Territory of Alaska in the Year 1885: For the Purpose of Obtaining All Information which Will be Valuable and Important, Especially to the Military Branch of the Government : Made Under the Direction of Nelson A. Miles (1887) -
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : M. Baker's Geographic Dictionary of Alaska (1906)
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : M. Baker's Geographic Dictionary of Alaska (1906)