This article needs to be updated.(February 2024) |
The Polish railway cyberattack is a series of suspected sabotage attempts in August 2023 aimed at the Polish State Railways.
This article needs to be updated.(February 2024) |
The Polish railway cyberattack is a series of suspected sabotage attempts in August 2023 aimed at the Polish State Railways.
The "radio stop" command system has a vulnerability - when a certain three tonal signal is transmitted through the railway radio network, trains stop automatically. [1]
At 9:23 pm on two sections of line near Szczecin a stop signal was broadcast by an unknown person. [1] It affected more than 20 trains and freight traffic was stopped as a precaution. [1] Services were restored within hours. [2]
Around 6pm near Gdynia a second incident took place - a freight train was also affected later that evening. [1]
Trains near Białystok were affected by fake stop signals. [1] Five passenger trains and one freight train were stopped. [3] Two men were arrested in connection with the disruption near Białystok. [3] One suspect is a police officer. [3] Prosecutors opened an investigation. [3]
Police in Białystok announced they had begun a dismissal procedure against the officer arrested on Sunday. [3] Sixteen people have been arrested as suspects in spying for Russia. [3]
The disruptions are being investigated both by police and intelligence organisations, including the Internal Security Agency. [3]
Some of the disruptive signals included the Russian anthem and part of a speech by Vladimir Putin. [2]

The Main Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, formerly the Main Intelligence Directorate, and still commonly known by its previous abbreviation GRU, is the foreign military intelligence agency of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. The GRU controls the military intelligence service and maintains its own special forces units.

The Polish State Railways is a Polish state-owned holding company comprising the rail transport holdings of the country's formerly dominant namesake railway operator. The company was reformed in 2001 when the former Polish State Railways state-owned enterprise was divided into several units based on the need for separation between infrastructure management and transport operations. Polish State Railways is the dominant company in the PKP Group collective that resulted from the split, and maintains 100% share control, being fully responsible for the assets of all of the other PKP Group component companies.

Law Enforcement Exploring, commonly referred to as Police Explorers or Police Scouts, is an American vocational education program that allows youth to explore a career in law enforcement by working with local law enforcement agencies. Founded on July 12, 1973, it is one of the Exploring programs from Learning for Life, a non-Scouting affiliate of the Boy Scouts of America. The program is generally available to qualified young adults who graduated 8th grade and are ages 14 through 21. Since its founding, adults mentors from the program have faced nearly than 200 allegations of abuse or misconduct.

The majority of Indonesia's railways are on Java, used for both passenger and freight transport. There are three noncontinuous railway networks in Sumatra while two new networks are being developed in Kalimantan and Sulawesi. Indonesia has finalized its plan for a national railway network recently. According to the plan, 3,200 km of train tracks will crisscross the islands of Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan, and Sulawesi. It has been touted as the most extensive railway project in Indonesia since its independence from the Dutch in 1945. Indonesia targets to extend the national railway network to 10,524 kilometres by 2030. As of September 2022, the network spans 7,032 km.

The Internal Security Agency is Poland's domestic counterintelligence and security agency. The ABW is responsible for analyzing, reporting and preventing threats to Poland's internal security, including terrorism, foreign espionage, arms smuggling, drug trafficking, organized crime, corruption and economic coercion. Its powers include arresting individuals, conducting searches and investigations, and combating terrorism with a specialized armed anti-terrorist force.

PKP Polskie Linie Kolejowe S.A. is the Polish railway infrastructure manager, responsible for maintenance of rail tracks, conducting trains across the country, scheduling train timetables, and management of railway land.
The history of rail transport in Poland dates back to the first half of the 19th century when railways were built under Prussian, Russian, and Austrian rule. Of course, "divided Poland" in the 19th century was the territory of the former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth rather than today's Republic of Poland. After Polish independence was declared on 11 November 1918, the independent Polish state administered its own railways until control was surrendered to German and Soviet occupiers during World War II.

Broad Gauge Metallurgy Line is the longest broad gauge railway line in Poland.

Rail transport in Ukraine is a major transport mode in Ukraine. Most railway infrastructure in Ukraine is owned by the government of Ukraine through Ukrzaliznytsia, a joint-stock company which has a de facto country-wide monopoly on passenger and freight transport by rail.

The Polish railways network consists of around 18,510 kilometres (11,500 mi) of track as of 2019, of which 11,998 km (7,455 mi) is electrified. The national electrification system runs at 3 kV DC.
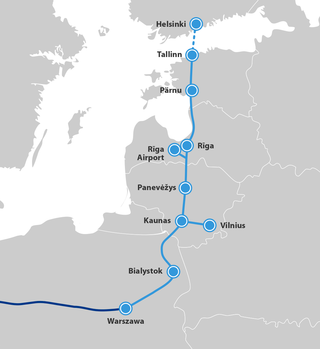
Rail Baltica is an under-construction rail infrastructure project that is intended to integrate the Baltic states in the European rail network. Its purpose is to provide passenger and freight service between participating countries and improve rail connections between Central and Northern Europe, specifically the area southeast of the Baltic Sea. It is also intended as a catalyst for building the economic corridor in Northeastern Europe. The project envisages a continuous rail link from Tallinn (Estonia) to Warsaw (Poland), consisting of links via Riga (Latvia), Kaunas, and Vilnius (Lithuania). Its total length in the Baltic States is 870 kilometres (540 mi), with 213 kilometres (132 mi) in Estonia, 265 kilometres (165 mi) in Latvia, and 392 kilometres (244 mi) in Lithuania. Rail Baltica is one of the priority projects of the European Union (EU). It is part of the North Sea–Baltic Corridor of the Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T).

Georgian Railway LLC is the national railway company of Georgia.

Saint Petersburg–Warsaw Railway is a 1,333 km (828 mi) long railway, built in the 19th century by the Russian Empire to connect Russia with Central Europe. At the time the entire railway was within the Russian Empire: Warsaw was under a Russian partition of Poland. Due to territorial changes, the line now lies within five countries and crosses the eastern border of the European Union three times. Therefore, no passenger trains follow the entire route. Passenger trains between Saint Petersburg and Warsaw used to travel through Brest instead and a new line called Rail Baltica is under development to improve the direct connection between Poland and Lithuania.

Białystok railway station is the most important railway station in the city of Białystok, Poland. It is sometimes referred to as Białystok Central, to distinguish it from six other, much smaller, stations located in the city.

The Grodzisk Mazowiecki–Zawiercie railway better known as the Central Rail Line, designated by Polish national railway infrastructure manager PKP Polskie Linie Kolejowe as rail line number 4, is a 224 km (139 mi) long railway line in Poland between Zawiercie outside the Katowice urban area and Grodzisk Mazowiecki in the suburbs of Warsaw.

The Frankfurt (Oder) station is the main passenger station in Frankfurt (Oder). It is one of the most important railway stations in the German state of Brandenburg. It is served by regional and long-distance services and since 1945 it has been a border station for transport to and from Poland. The station has been substantially rebuilt several times. A building on the grounds of the first Frankfurt station, north of the current station, is heritage-listed, as are the Kiliansberg apartments, which were built as a railway settlement at the station forecourt, and a monument to railwaymen who fell in the First World War in the same area.

The Szczekociny rail crash occurred on 3 March 2012 when two passenger trains collided head-on near the town of Szczekociny, Silesian Voivodeship, Poland. Sixteen people died in the incident and 58 were injured. An investigative report showed that the cause of the crash was due to human error by train dispatchers and the train drivers.

The Belarusian–Polish border is the state border between the Republic of Poland and the Republic of Belarus. It has a total length of 398.6 km (247.7 mi), 418 km (260 mi) or 416 km (258 mi). It starts from the triple junction of the borders with Lithuania in the north and stretches to the triple junction borders with Ukraine to the south. It is also part of the EU border with Belarus. The border runs along the administrative borders of two Voivodships Podlaskie and Lubelskie in the Polish side and Grodno and Brest Vobłasć in the Belarusian side. In the Polish side, the 246.93 km (153.44 mi) section is under the protection of the Podlaski Border Guard Regional Unit, while the 171.31 km (106.45 mi) section is in the operation area of the Bug Border Guard Regional Unit. Border rivers are Czarna Hańcza, Wołkuszanka, Świsłocz, Narew, and Bug.
The rail war began in different regions of Russia in the spring of 2022 after a similar rail war in Belarus.